Uncategorized
Iran, Abraham Accords and Bibi’s trial: What Trump said in his historic Knesset speech

As the last of the Israeli hostages were released from Gaza, President Donald Trump addressed the country’s parliament — and was given a hero’s welcome.
Trump’s speech to the Knesset on Monday offered effusive praise for the state of Israel, warm — but not unguarded — praise for Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu, and an outline for a vision of a future in which Israel is a full partner of every other nation in the region. And in typical Trump fashion, it was delivered with a mixture of bravado and unpredictable asides, some of which cut at the heart of several tensions in the Middle East.
Here are the big takeaways from Trump’s speech to the Knesset.
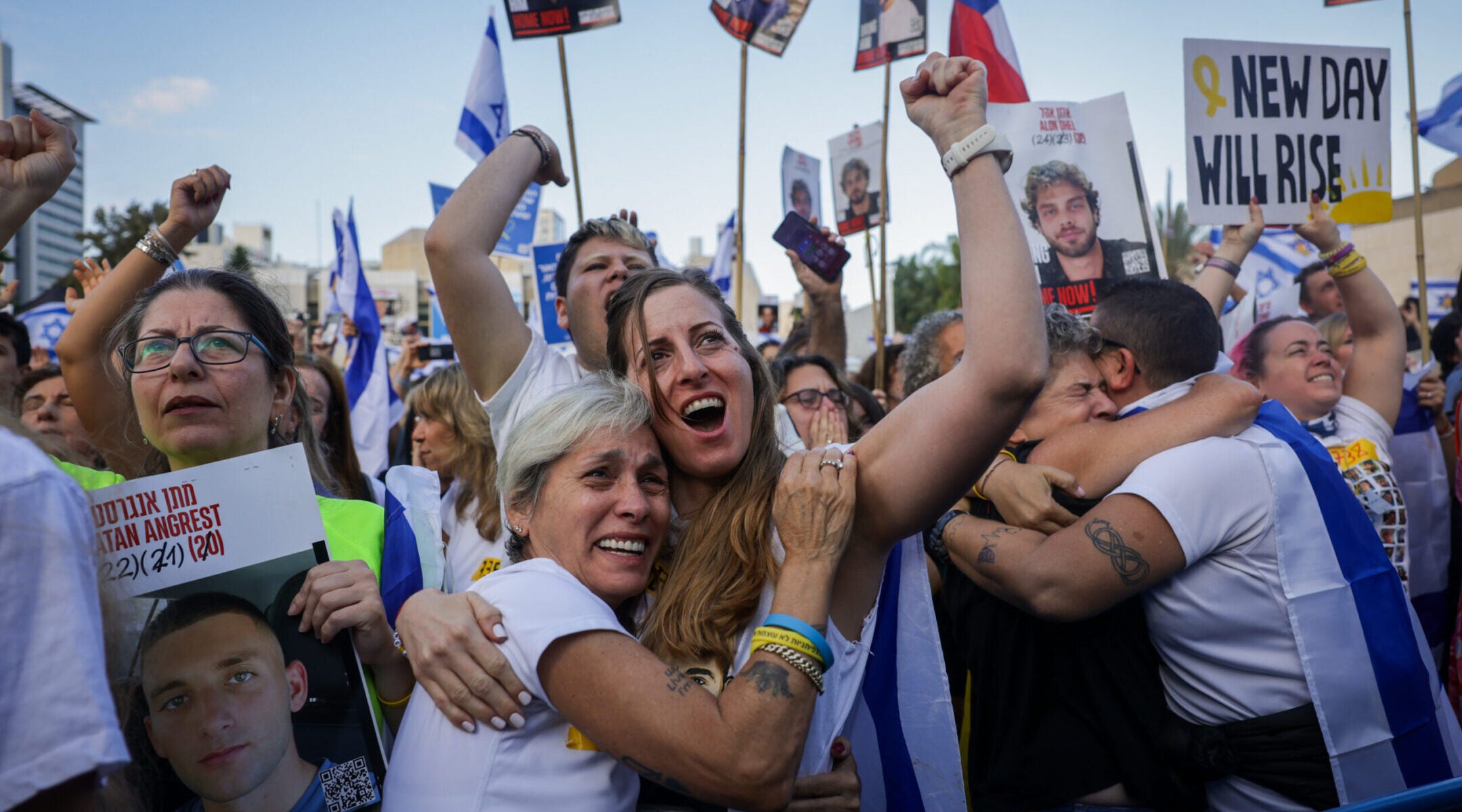
Thousands gather at Hostage Square to celebrate the return of the hostages, October 13, 2025. (Miriam Alster/Flash90)
‘You’ve won’
With the hostages released, Trump made clear that, in his view, the era of Israeli military action in Gaza is over.
“Israel, with our help, has won all that they can by force of arms,” he said. “You’ve won. I mean, you’ve won. Now it’s time to translate these victories against terrorists on the battlefield into the ultimate prize of peace and prosperity for the entire Middle East.”
Speaking of the hostages later, the president reflected on meeting with their families and the spirit he saw igniting them.
“Over the past two years, I’ve met many of the families of the Israelis taken hostage and those that were taken hostage, unbelievable. I’ve looked into their eyes. I’ve seen the worst nightmares of their suffering, but I’ve also seen something else, the beautiful love of the people,” he said. “It’s that love that’s defeated the enemies of civilization, built this incredible country and this unbelievable economy and forged one of the great democracies of the world.”
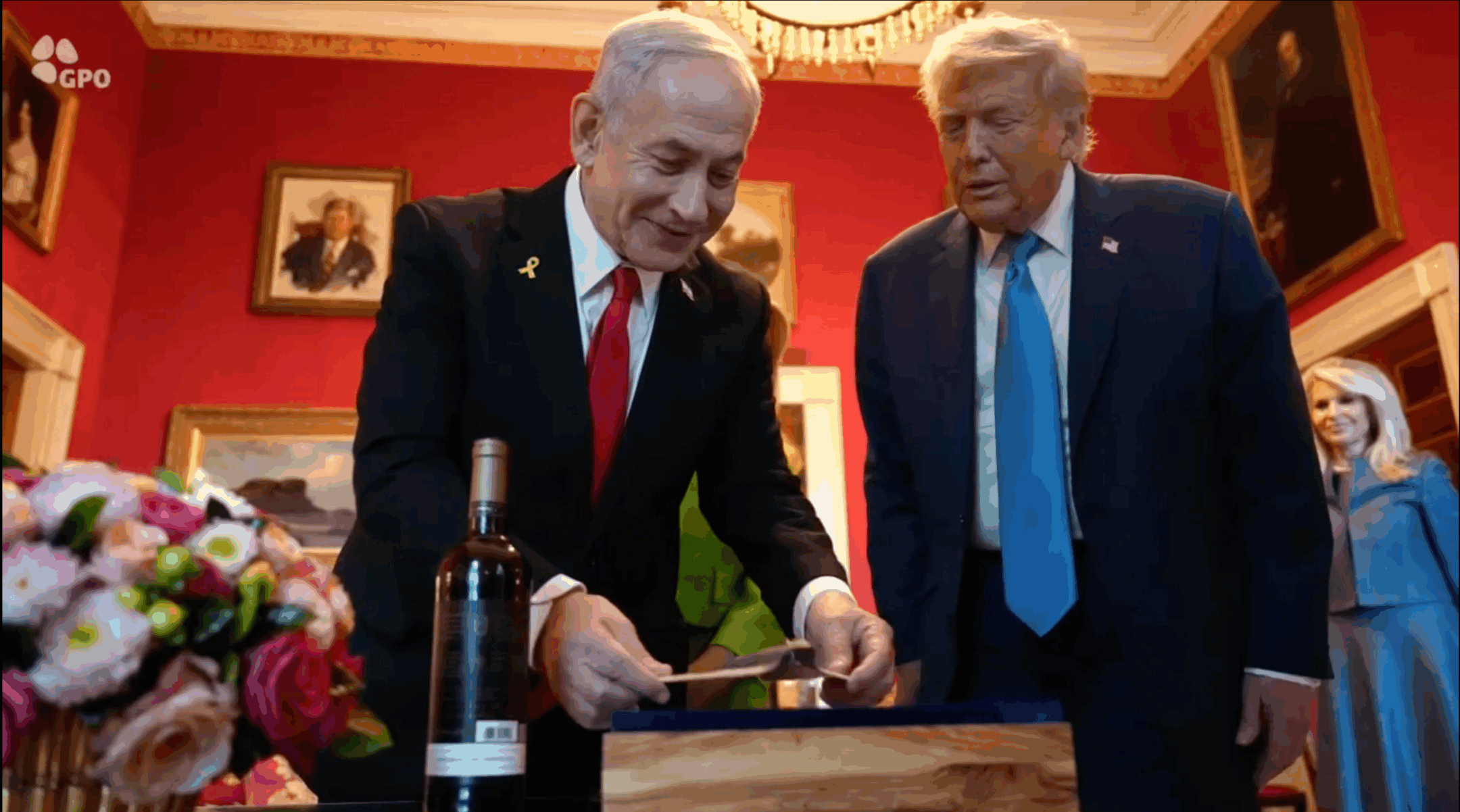

Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu presents U.S. President Donald Trump with a mezuzah in the shape of a B-2 bomber at the White House, July 7, 2025. (Screenshot from GPO footage)
‘You could be a little bit nicer, Bibi’
Amid reports that Trump had been frustrated by Netanyahu’s pace in negotiations to end the war in Gaza, the president had broadcast total alignment with Jerusalem. He had Netanyahu by his side at the White House last week when he announced that Israel had agreed to a ceasefire proposal that would be presented to Hamas, which later signed on. He invited Netanyahu into his motorcade on his way from Ben Gurion airport to the parliament building on Monday.
And he began his speech by praising Netanyahu — but not as effusively as he might have.
“I want to express my gratitude to a man of exceptional courage and patriotism whose partnership did so much to make this momentous day possible. You know what I’m talking about. There’s only one prime minister, Benjamin Netanyahu,” Trump said. “He is not easy. I want to tell you he’s not the easiest guy to deal with, but that’s what makes him great.”
Later, as he praised opposition leader Yair Lapid as a “very nice guy,” Trump reacted to the reaction he perceived in Netanyahu and offered a rebuke.
“Now you can be a little bit nicer, Bibi, because you’re not at war anymore, Bibi, you did it.”
Bibi’s trial
Even while alluding to his frustrations with Netanyahu, Trump still took a moment to stump for him in the prime minister’s still-ongoing trial for political corruption. Turning to Israeli President Isaac Herzog at one point, Trump made a highly unusual show of intervening in the case, calling on him to use his pardon powers to settle the matter.
“Hey, I have an idea. Mr. President, why don’t you give him a pardon?” Trump said, to hoots and applause. “Give him the pardon. Come on.”
As chants of “Bibi!” could be heard, Trump continued, “It’s not in the speech, as you probably know, but I happen to like this gentleman right over here. And it just seems to make so much sense. You know, whether we like it or not, this has been one of the greatest wartime presidents.”
Trump then made specific reference to some of the bribery charges against Netanyahu, one of the cases that a large movement of Israeli protesters — including many hostage families — had cited as a reason why the prime minister should cede power.
“And cigars and champagne, who the hell cares about that?”
The U.S.-Israel relationship
As the war dragged on, segments of both the left and right in American politics have begun to question U.S. support for Israel. Trump vocally reaffirmed the bond.
“Israel will always remain a vital ally of the United States of America,” he said. “Israelis share our values, field one of the world’s most powerful militaries. You really do.” He added, “I’m proud to be the best friend that Israel has ever had.”
He also referenced the U.S. citizens who were abducted in Gaza in what he noted was “the worst slaughter of Jews since the Holocaust,” painting American and Israeli grief over Oct. 7 as one and the same.
“The United States of America grieved alongside you, and we mourn for our own citizens who were so viciously taken that day,” he said. “And to all the families whose lives were forever changed by the atrocities of that day, and all of the people of Israel, please know that America joins you in those two everlasting vows: Never forget, and never again.”
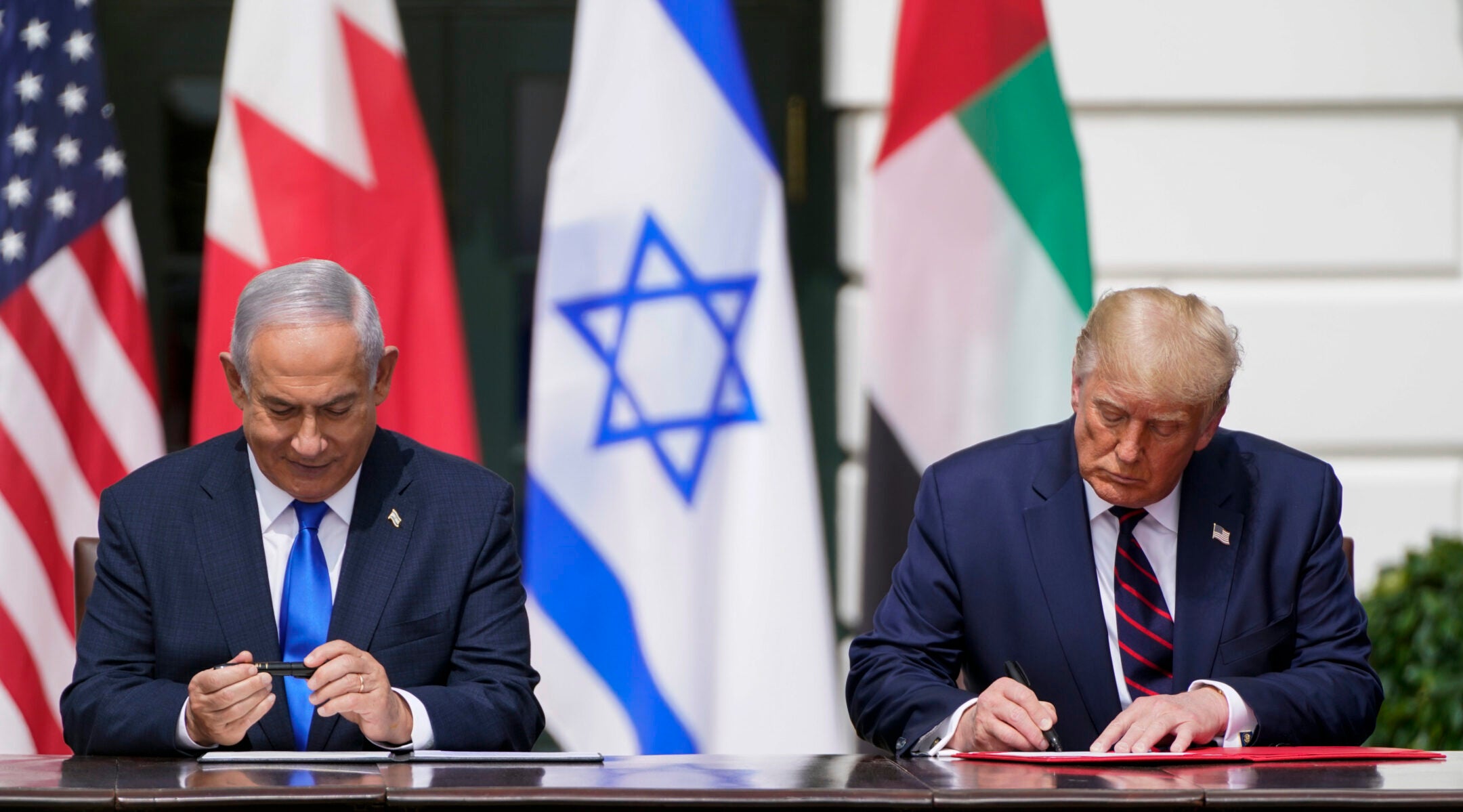

President Donald Trump and Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu sign the Abraham Accords at a White House ceremony, Sept. 15, 2020. (Jabin Botsford/The Washington Post via Getty Images)
What’s next for the ‘Avraham Accords’
At various points during his speech, Trump turned to his first administration’s signature foreign-policy accomplishment: the normalization agreements between Israel and a handful of Arab states, known as the Abraham Accords. On Monday he pronounced it the Hebrew way, “Avraham.”
“I like calling it the Avraham Accords. Avraham. It’s so cool. It’s so much nicer, you know? The Abraham versus the Avraham,” he said.
In the wake of what he said would be a concentrated rebuilding effort in Gaza, Trump also urged Israel and several Arab and Muslim nations to add to these accords. “Now we’re going to forge a future that is worthy of our heritage. We’re going to build a legacy that all the people of this region can be proud of,” he said.
“So instead of building fortresses to keep enemies at bay, the nations of this region should be building infrastructure to weave your commerce closer together, because you’ve got to compete with a big world out there in commerce. Now it’s a different kind of competition. Instead of making weapons and missiles, the wealth of this region should flow to schools and medicine, industry. And frankly, the new hot thing, artificial intelligence.”
Toward the end of his speech, Trump provided a list of countries and their capitals he said he would like to see forge stronger relations with Israel and each other. Some of them already have diplomatic ties to the country.
“New bonds of friendship, cooperation and commerce will join Tel Aviv to Dubai, Haifa to Beirut, Jerusalem to Damascus, and from Israel to Egypt, from Saudi Arabia to Qatar, from India to Pakistan, from Indonesia to Iraq, from Syria to Bahrain, Turkey to Jordan, the United Arab Emirates to Oman and Armenia to Azerbaijan,” he said.
How such an ambitious realignment would play on the larger diplomatic stage, as many countries remain furious at Israel for its handling of the Gaza war, remains to be seen. The president of Indonesia, one Muslim-majority nation long in discussions to join the accords, scuttled a planned historic visit to Israel Monday over reported concerns of pushback at home, though he attended the day’s summit between Israel and Hamas held in Egypt.
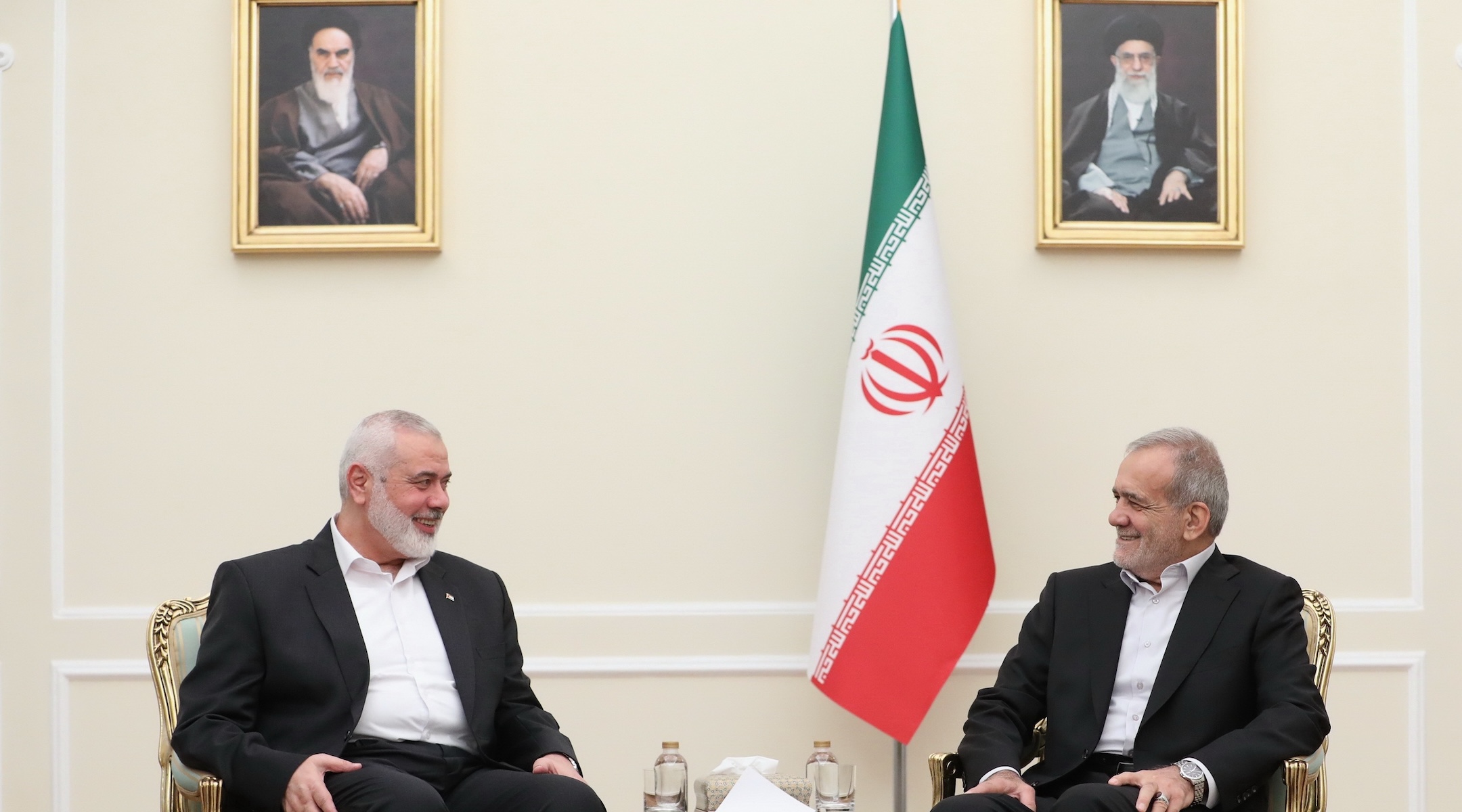

Iranian newly-elected President Masoud Pezeshkian, right, meets Head of the Palestinian Hamas group’s political bureau Ismail Haniyeh, left in Tehran, Iran on July 30, 2024. (Iranian Presidency / Handout/Anadolu via Getty Images)
‘Make a deal’ with Iran
Amid talks of normalization, Trump paid special attention to the elephant in the room by urging the Knesset to use their momentum to “make a deal” with Iran, which both the United States and Israel had bombed at various times during the Israel-Gaza war.
“And even to Iran, whose regime has inflicted so much death on the Middle East, the hand of friendship and cooperation is open,” he said. I’m telling you, they want to make a deal.”
“Neither the United States nor Israel bear the people of Iran any hostility,” Trump continued. “We merely want to live in peace. We don’t want any looming threats over our heads.”
The moment stood out, as both the United States and Israel have had fraught relationships with Iran for nearly half a century. Netanyahu spoke to Congress in an effort to unravel a nuclear deal with Iran during the Obama administration; that deal wound up going through, only to be scuttled by Trump in his first term in office. Trump himself acknowledged this with some dark humor.
“As president I terminated the disastrous Iran nuclear deal, and ultimately I terminated Iran’s nuclear program with things called B-2 bombers,” he said. Yet, Trump pressed on, now a new deal should be reached, one predicated on Israel’s strengths.
He added, “A lot of Iranians in the United States are good people, smart, hardworking people. They don’t want to see what’s happened to their country. The story of fierce Israeli resolve and triumph since Oct. 7 should be proof to the entire world that those who seek to destroy this nation are doomed to bitter failure. The State of Israel is strong and it will live and thrive forever.”
Bibi’s demand for weapons
Trump was open about one aspect of U.S. support for Israel that had received particular scrutiny and protest during the war: the transfer of weapons for Israel to use in Gaza.
“We make the best weapons in the world, and we’ve got a lot of them, and we’ve given a lot to Israel, frankly,” he said. Deeming himself “all about stopping wars,” Trump said he “hated” some of the weapons the United States makes “because the level of power is so enormous, so dangerous, so bad.”
Yet, Trump said, the United States gave Israel all the weapons it needed. He even ribbed Netanyahu’s desire for military supplies.
“I mean, Bibi would call me so many times: ‘Can you get me this weapon, that weapon, that weapon?’ Some of them I never heard of, Bibi. And I made them,” Trump said. “But you used them well. It also takes people that know how to use them, and you obviously use them very well, but so many that Israel became strong and powerful, which ultimately led to peace. That’s what led to peace.”
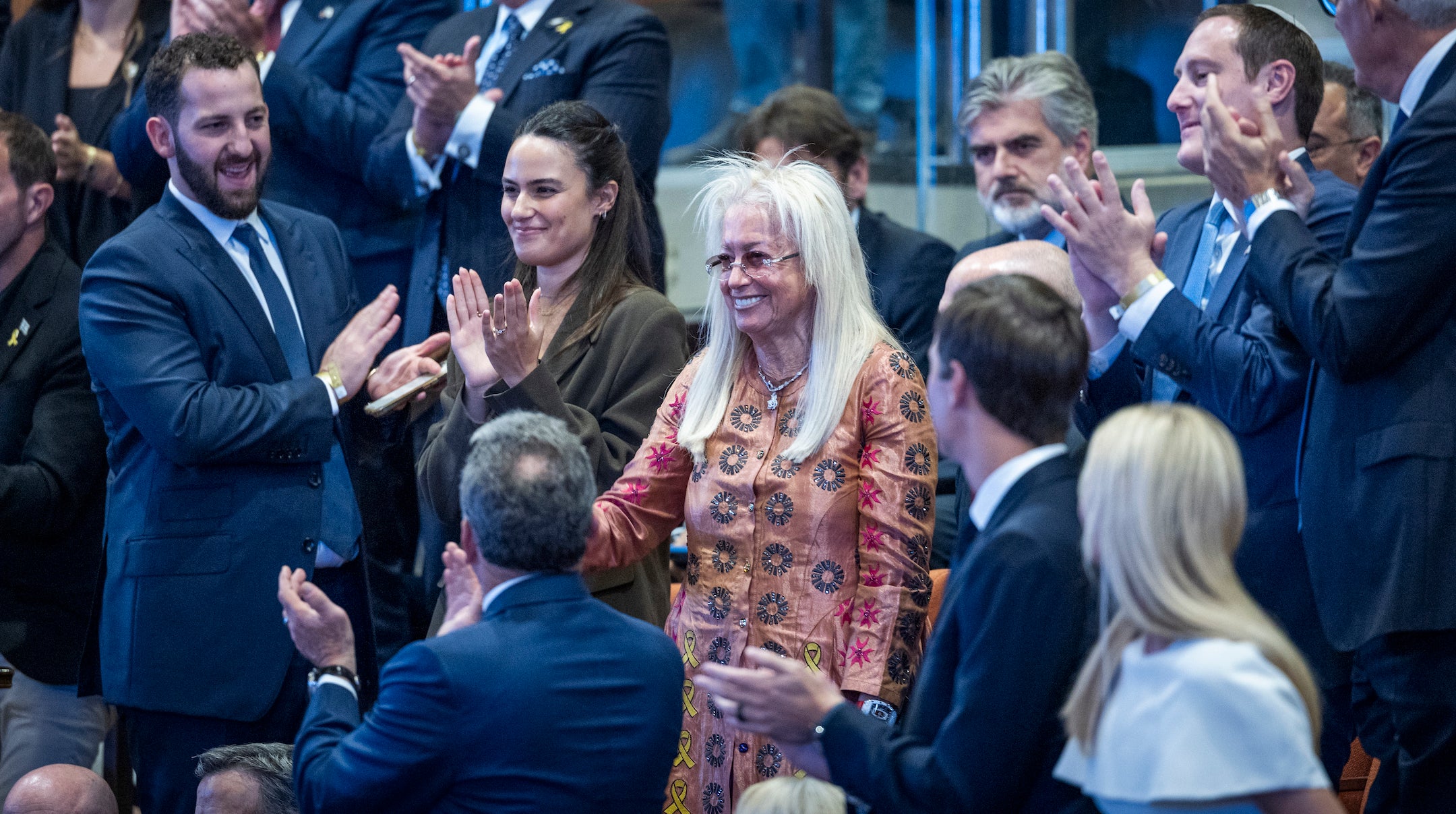

Israeli-American billionaire Miriam Adelson is recognized during a special plenum session in honor of U.S. President Donald Trump at the Knesset, the Israeli parliament in Jerusalem, on October 13, 2025. (Yonatan Sindel/Flash90)
Miriam Adelson
Trump gave a special shout-out to one of his wealthiest and most stalwart pro-Israel donors in the United States, Miriam Adelson — widow to casino magnate Sheldon. While praising her, he also suggested she “loves” Israel more than the United States — flirting with the kind of “dual loyalty” trope that mainstream Jewish organizations have tended to condemn in the past.
The Adelsons, he said with an unusual degree of candor for a president referencing a top financial backer, had been a large influence on his Israel policy.
“I kept my promise and officially recognized the capital of Israel and moved the American embassy to Jerusalem,” Trump said, to applause. “Isn’t that right, Miriam?” He then urged Adelson to “stand up” for recognition.
During his first term, Trump told the Knesset, “Miriam and Sheldon, they would come into the office… I think they had more trips to the White House than anybody else. Look at her sitting there so innocently. She’s got $60 billion in the bank… But she loves Israel. And they would come in, and her husband was a very aggressive man, but I loved them.”
Trump described his relationship with the Adelsons as one where they would needle him to drop by the White House. “He’d call up, ‘Can I come over and see you?’ I’d say, ‘Sheldon, I’m the president of the United States. It doesn’t work that way.’ He’d come in,” the president said. “But they were very responsible for so much.”
“I’m going to get in trouble for this,” Trump said. “But I actually asked her once, I said, ‘So, Miriam, I know you love Israel. What do you love more? The United States or Israel?’ She refused to answer. That means, that might mean Israel.”
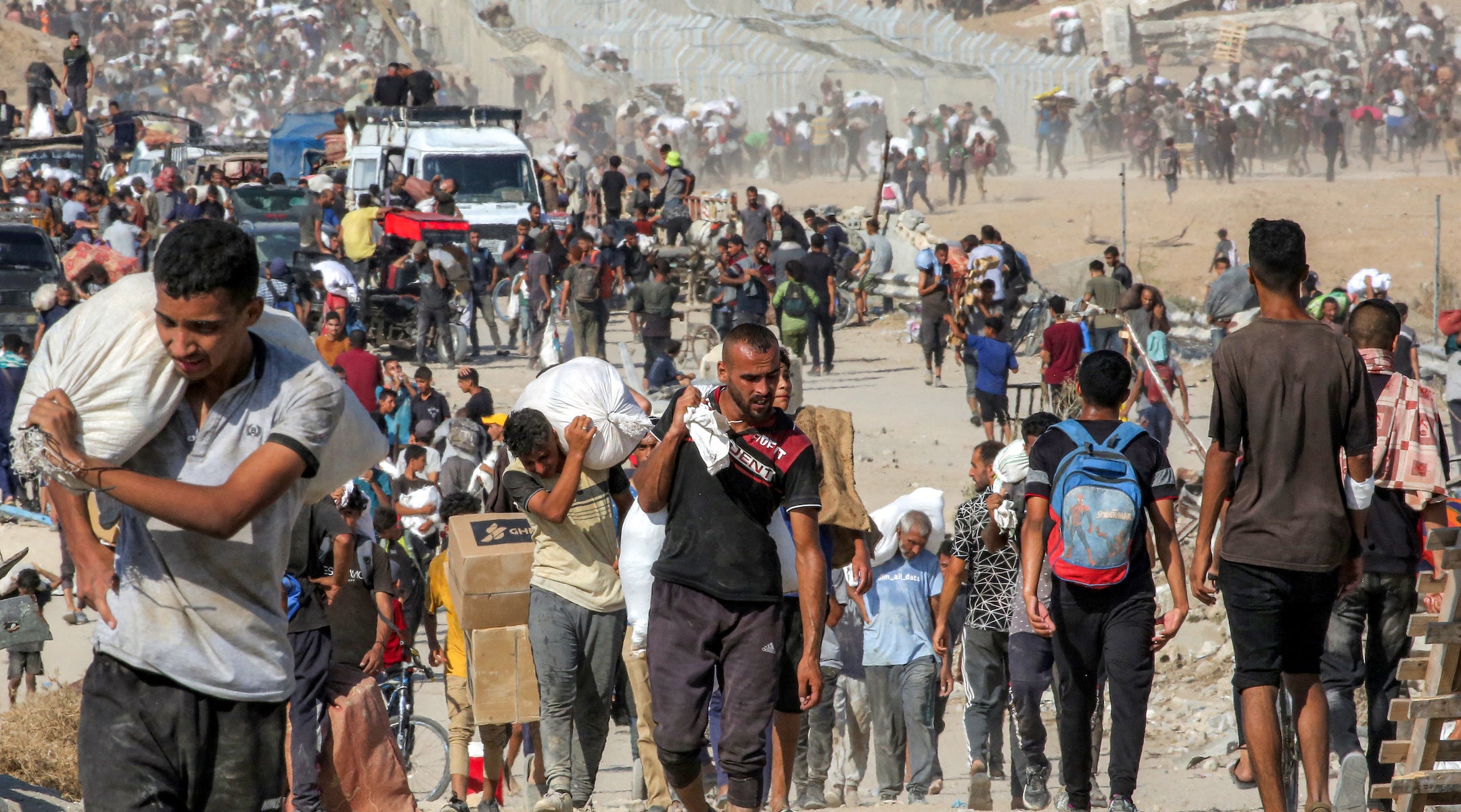

People walk with bags of humanitarian aid they received at a distribution centre run by the US and Israeli-backed Gaza Humanitarian Foundation (GHF), as they cross the so-called “Netzarim corridor” in the central Gaza Strip, on August 22, 2025. The United Nations officially declared a famine in Gaza on August 22, the first time it has done so in the Middle East, with experts warning 500,000 people face “catastrophic” hunger. UN agencies have long been warning of the deteriorating humanitarian situation in Gaza, particularly as Israel steps up its offensive against Hamas. (Eyad Baba / AFP)
The word on Gaza, and ‘the Board of Peace’
When Trump’s remarks touched on what should come next for Gaza, he painted his vision as one of international cooperation and prosperity, should the Palestinians want it.
Says several “very wealthy” Arab and Muslim nations have committed “to support a safe gilding of Gaza and beyond,” Trump added, “The total focus of Gazans must be on restoring the fundamentals of stability, safety, dignity and economic development so they can finally have the better life that their children really do deserve after all these decades of horror. I intend to be a partner in this effort.”
The “day after” plan for Gaza was one of the major sticking points of the negotiations between Israel and Hamas, the latter of which has not committed to relinquishing control of the territory despite Trump and Israel’s demands. Some members of Israel’s far-right governing coalition, meanwhile, have urged for the expulsion of all Palestinians and for Israel to control or resettle the strip.
In the past, Trump has promoted the idea of the United States, or his personal business interests, taking Gaza for itself and turning it into a resort. His tone was more measured in the Knesset, saying his plan for rebuilding Gaza involved a “board of peace” that would be “unbelievably popular.”
“Is that a beautiful name? Like a board, of peace,” he said. “The only bad thing, from my standpoint: every single nation involved has asked me to be the chair. And I’ll tell you, I’m very busy. I didn’t count on that.”
Trump framed Gaza’s future as one up to Palestinians.
“The choice for Palestinians could not be more clear,” he said. “This is their chance to turn forever from the path of terror and violence, it’s been extreme, to exile the wicked forces of hate that are in their midst. And I think that’s going to happen.”
Jared and Ivanka
How much does Trump’s Jewish son-in-law, Jared Kushner, love Israel? “He loves it so much that my daughter converted,” the president said.
Trump continued to riff on Ivanka’s conversion for a while. “I didn’t know this was going to happen,” he said. “And she is so happy, and they are so happy, at least, I think they’re happy. If they’re not, we have a big story, right?”
—
The post Iran, Abraham Accords and Bibi’s trial: What Trump said in his historic Knesset speech appeared first on Jewish Telegraphic Agency.
Uncategorized
Australian Bar Shut Down for Displaying Posters of Netanyahu, Putin, Trump in Nazi-Like Uniforms

Adolf Hitler in Nuremberg in 1938. Photo: Imperial War Museums.
A live music bar and cafe in Australia was shut down by local police on Wednesday for displaying posters that depict world leaders and others, including Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu and US President Donald Trump, wearing Nazi-like uniforms.
The Dissent Cafe and Bar in Canberra Central said in a Facebook post that ACT Policing, the community policing arm of the Australian Federal Police, shut down the venue for two and a half hours on Wednesday night. Police said they were investigating a complaint about possible hate imagery relating to five posters in the venue’s window display. A scheduled performance at the bar and cafe was also canceled because of the shutdown.
ACT Policing said in a statement on Thursday that it declared the cafe a crime scene and officers would investigate whether there was a breach of new Commonwealth law about hate symbols. Police noted that they asked the venue’s owner to remove the posters and he refused.
“Officers attended the premises and had a discussion with the owner, with officers seeking to remove the posters as part of their investigation into the matter. The owner declined this request and so a crime scene was established,” read the police statement. “Five posters were subsequently seized and will be considered under recently enacted Commonwealth legislation regarding hate symbols.”
The Dissent Cafe and Bar had displayed in its front windows posters depicting Netanyahu, Trump, Russia’s President Vladimir Putin, US Vice President JD Vance and Tesla co-founder Elon Musk in Nazi-like uniforms. The posters were created by the artist group Grow Up Art and underneath them were signs in the window that said “Sanction Israel” and “Stop Genocide.” Grow Up Art displayed the same images as part of a billboard poster campaign last summer and they are also sold on t-shirts. The artist group nicknamed the men in the posters collectively as “The Turd Reich,” a play on the Third Reich, the name for the Nazi dictatorship in Germany under Adolf Hitler’s rule.
Dissent Cafe and Bar has defended the artwork, saying it is “clearly and obviously parody art with a distinct anti fascist [sic] message.”
“In what is obviously harassment the ACT police have declared a crime scene at Dissent and tonight’s gig is unfortunately canceled,” Dissent Cafe and Bar wrote on Facebook when the closure happened on Wednesday.
The posters have since been placed back in the windows of the live music bar, but the images are now covered with the word “CENSORED” in red. ACT Policing said on Thursday they are still investigating the posters and are also “seeking legal advice on their legality.”
“ACT Policing remains committed to ensuring that alleged antisemitic, racist, and hate incidents are addressed promptly and thoroughly, and when possible criminality is identified, ACT Policing will not hesitate to take appropriate action,” police added.
Uncategorized
At Board of Peace Debut, Trump Announces Global Commitments for Gaza Reconstruction

USPresident Donald Trump speaks at the inaugural Board of Peace meeting at the US Institute of Peace in Washington, DC, US, Feb. 19, 2026. Photo: REUTERS/Kevin Lamarque
US President Donald Trump told the first meeting of his Board of Peace on Thursday that nations had contributed $7 billion to a Gaza reconstruction fund that aims to rebuild the enclave once Hamas disarms, an objective that is far from becoming a reality.
The disarmament of Hamas terrorists and accompanying withdrawal of Israeli troops, the size of the reconstruction fund, and the flow of humanitarian aid to the war-battered populace of Gaza are among the major questions likely to test the effectiveness of the board in the months ahead.
The meeting in Washington came amid a broader push by Trump to build a reputation as a peacemaker. It also took place as the United States threatens war against Iran and has embarked on a massive military buildup in the region in case Tehran refuses to give up its nuclear program.
The Board‘s founding membership does not include some key US Western allies concerned about the scope of the initiative.
In a flurry of announcements at the end of a long, winding speech to representatives from 47 nations, Trump said the United States will contribute $10 billion to the Board of Peace. He did not say where the money would come from or whether he would seek it from the US Congress.
MOSTLY MIDDLE EASTERN MEMBERSHIP
Trump said contributing nations had raised $7 billion as an initial down payment for Gaza reconstruction. Contributors included Kazakhstan, Azerbaijan, United Arab Emirates, Morocco, Bahrain, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Uzbekistan, and Kuwait, he said. The membership is mostly made up of Middle Eastern countries, plus leaders from outside the region who may be looking to gain favor with Trump.
Estimates for rebuilding Gaza, which was reduced to rubble after two years of war, range up to $70 billion.
Trump proposed the board in September when he announced his plan to end Israel’s war in Gaza. He later made clear the board‘s remit would expand beyond Gaza to tackle other conflicts worldwide, a point he reiterated on Wednesday by saying it would look into “hotspots” around the world.
Trump said FIFA will raise $75 million for soccer-related projects in Gaza and that the United Nations will chip in $2 billion for humanitarian assistance.
The Board of Peace includes Israel but not Palestinian representatives. Trump‘s suggestion that the Board could eventually address challenges beyond Gaza has stirred anxiety that it could undermine the UN’s role as the main platform for global diplomacy and conflict resolution.
“We’re going to strengthen the United Nations,” Trump said, trying to assuage his critics, even though the United States is in arrears on making payments.
Trump said Norway would host a Board of Peace event, but Norway clarified it was not joining the board.
IRAN SABER-RATTLING
Even as he talked up himself as a man of peace, Trump rattled sabers against Iran.
Trump said he should know in 10 days whether a deal is possible to end a standoff with Tehran. “We have to have a meaningful deal,” he said.
Trump said several nations are planning to send thousands of troops to participate in an International Stabilization Force that will help keep the peace in Gaza when it eventually deploys.
Indonesian President Prabowo Subianto announced his country would contribute up to 8,000 troops to the force.
The plan for the force is to begin working in areas Israel controls in the absence of Hamas disarmament. The force, led by a US general with an Indonesian deputy, will start in Israeli-controlled Rafah. The aim is to train 12,000 police and have 20,000 troops.
“The first five countries have committed troops to serve in the ISF – Indonesia, Morocco, Kazakhstan, Kosovo, and Albania. Two countries have committed to train police – Egypt and Jordan,” International Stabilization Force commander Army Major General Jasper Jeffers said on Thursday.
HAMAS DISARMAMENT A KEY ISSUE
Hamas has been reluctant to hand over weaponry as part of Trump‘s 20-point Gaza plan that brought about a fragile ceasefire last October in the two-year Gaza war.
Trump said he hoped the use of force to disarm Hamas would be unnecessary. He said Hamas had promised to disarm and it “looks like they’re going to be doing that, but we’ll have to find out.”
Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu said in Israel that Hamas will be disarmed one way or the other. “Very soon, Hamas will face a dilemma – to disarm peacefully or disarmed forcefully,” he said.
In Gaza, Hamas spokesperson Hazem Qassem said in a statement that the real test of the Board of Peace “lies in their ability to compel the occupation to halt its violations of the ceasefire, to oblige it to meet its obligations, and to initiate a genuine relief effort and launch the reconstruction process.”
The Board of Peace event had the feel of a Trump campaign rally, with music blaring from his eclectic playlist that included Elvis Presley and the Beach Boys. Participants received red Trump hats.
Hamas, which has resumed administration of nearly half the enclave, says it is ready to hand over to a US-backed committee of Palestinian technocrats led by Ali Shaath, but that Israel has not allowed the group into Gaza. Israel has yet to comment on those assertions.
Nickolay Mladenov, a Bulgarian with a senior role in the Board of Peace, said at the meeting that 2,000 Palestinians have applied to join a new transitional Palestinian police force.
“We have to get this right. There is no plan B for Gaza. Plan B is going back to war. No one here wants that,” said US Secretary of State Marco Rubio.
Uncategorized
Andreas E. Mach’s Monument to Memory: Jüdische Familienunternehmer in Hitlers München

A store damaged during Kristallnacht. Photo: German Federal Archives via Wikimedia Commons.
In an age of slogans and shortcuts, Andreas E. Mach has written a meticulous, unflinching book. Jüdische Familienunternehmer in Hitlers München (“Jewish Family Entrepreneurs in Hitler’s Munich”) is not only a history of businesses — it is a map back to a city that once existed, and a ledger of how it was unmade.
Mach’s canvas is Munich from the 19th century through the aftermath of 1945. His method is documentary and patient: city directories and business registers; police and tax files; contemporary newspapers; memoirs and family papers. From this archive he reconstructs the families who shaped Munich’s modern economy — department stores like Bamberger & Hertz, fashion and textile manufacturers, breweries and beverage firms, banks, and the great art dealerships (Bernheimer, Drey, Heinemann, Thannhauser, Rosenthal, Helbing). He shows how these Jewish-founded enterprises fueled jobs, style, philanthropy, and civic leadership — and how, step by step, they were boycotted, expropriated, “Aryanized,” and erased from the city’s commercial map.
The book opens with a foreword by Dr. h.c. Charlotte Knobloch (July 2024), president of the Jewish Community of Munich and Upper Bavaria and former president of the Central Council of Jews in Germany. Her message is clear: remembrance is responsibility amid rising antisemitism.
Mach is a political scientist and historian from a southern German entrepreneurial family, with studies in Germany, Italy, and the Netherlands (M.A.) and in the U.S. (M.P.I.A.), early work in investment banking, and, since 2005, the founding of the international family-enterprise forum ALPHAZIRKEL.
A photographic essay explains the cover image: in March 1933, Munich lawyer Dr. Michael Siegel was beaten, forced barefoot through the city, and made to wear a placard. Mach places that humiliation inside a system that very quickly moved from intimidation to dispossession. He then widens the lens: a historical overview traces the growth of Munich’s Jewish community — from 1,206 members in 1852 to more than 11,000 by 1910 — its institutions (the 1887 main synagogue on Herzog-Max-Straße with roughly 2,000 seats; Ohel Jakob; prayer houses and charities), and its contributions to a capital that became internationally respected in art and culture. He notes that by 2022 the community again counted roughly 11,000 members, and that Jewish life is once more visible in the cityscape with the 2006 synagogue and cultural center at Jakobsplatz.
Mach’s narrative is careful about complexity. He documents assimilation and civic engagement — business leadership, philanthropy, even sports (Kurt Landauer’s presidency at FC Bayern) — but he also records the persistence of antisemitism before 1918, debates over Zionism, and the arrival of poorer Eastern Jews whose visibility fed prejudice. He includes wartime service and suspicion side by side: around 100,000 Jews served in the German army in World War I; the humiliating Judenzählung of Nov. 1, 1916 sought to prove Jews shirked the front, yet subsequent figures showed similar front-line rates (and decorations) to non-Jews — but the results were not published at the time. Mach quotes and paraphrases contemporary Jewish voices who felt they were fighting “on two fronts” — for the country and for equal rights.
The revolutionary crisis of 1918–1919 is presented as prelude rather than detour. Mach recounts the proclamation of the Free State of Bavaria on Nov. 8, 1918, by Kurt Eisner; his assassination on Feb. 21, 1919; the brief council republics; and the brutal “white terror” that followed. He names the murdered and condemned — Gustav Landauer beaten to death after arrest; Eugen Leviné executed; Ernst Toller sentenced; Erich Mühsam imprisoned — and records the double standard in sentencing: perpetrators from the Reichswehr and Freikorps often received lenient treatment while revolutionaries were abused and, in some cases, murdered. The period also ushers in figures who will define the next era: Rudolf Heß, Alfred Rosenberg, Hans Frank, Dietrich Eckart, and Adolf Hitler’s first steps in 1919 under Captain Karl Mayr, including the antisemitic “Mayr letter.” Mach’s point is cumulative: explanations, enemies, and habits of looking away were practiced in these years, and Munich became the stage on which they would later be performed.
When Mach turns fully to “Hitler’s Munich,” the argument is anchored by street-level facts. He documents the April 1, 1933 boycott — photographed, staged, and effective as intimidation. He details the demolition of the main synagogue in June 1938 on Hitler’s order: the contractor (Leonhard Moll), the speed (within a month), and the compensation (200,000 Reichsmarks) to remove what Hitler called an “eyesore.” He tracks the Nov. 9–10, 1938 pogrom in Munich with specific images and captions (smashed windows at the Bernheimer gallery on Lenbachplatz; the boycott poster at Bamberger & Hertz on Kaufingerstraße), and notes that nearly all adult Jewish men were deported to Dachau in the aftermath. Individual fates punctuate the narrative — among them the arrest of banker Emil Krämer. Administrative theft is made visible: Jews were compelled to declare assets; by 1938, Jewish losses in Germany totaled roughly 12 billion RM; in Munich alone Mach cites roughly 600 million RM in real estate and nearly 150 million RM in securities and balances registered in 1938. On countless forms, one formula recurs: “The property falls to the Reich.”
Mach also reproduces the texture of “Aryanization” as it appeared to the public. He cites a Völkischer Beobachter advertisement of July 25, 1938 announcing that the porcelain, glass, and household goods firm “formerly Martin Pauson” had been transferred into “German ownership.” He shows how city paperwork could continue to list Jewish firms even as their owners were being forced from homes into Judenhäuser, or into hiding. At Munich’s liberation on April 30, 1945, only 34 Jews were found in hiding in the city. Mach references research on Jews who attempted to survive underground in Munich and Upper Bavaria, the dangers they and their helpers faced, and the gap between postwar stories of universal assistance and the record of denunciation and greed.
The book’s architecture makes its case. After the narrative chapters — “Jüdisches Leben in München – ein historischer Überblick bis 1918” (“Jewish Life in Munich – A Historical Overview Until 1918”), “Das München der Revolution – Prélude des Holocaust” (“The Munich of the Revolution – Prelude to the Holocaust”), “Hitlers München: die ‘braune’ Stadt” (“Hitler’s Munich: the ‘brown’ city”), “Arisierung und Restitution” (“Aryanization and Restitution”), and the detailed account of November 1938 — Mach opens into registers readers can use: a directory of businesses affected during the pogrom; a reprint-based listing of Jewish business owners recorded by the trade police in 1938; and studies of Nazi art plunder in Munich. He then offers sector and firm profiles: leading art dealers (A.S. Drey, Heinemann, Thannhauser, Bernheimer, Helbing, Caspari, and others); selected family companies (including bank and retail houses); Jewish lawyers; and a long section on fashion and textiles (department stores, manufacturers, tailors, wholesalers). A distinct contribution is the inclusion of Lotte Bamberger’s memoir (with German translation), which threads one family’s trajectory through the commercial and moral topography Mach has drawn.
Throughout, Mach refuses euphemism. He writes with moral clarity but without sermonizing: he lays out the documents, then the consequences; he names who benefited, who signed, who looked away, and who helped. He proves that the story of Jewish family enterprise is not ancillary to Munich’s identity — it is central. When those families were expelled, the city did not simply “change”; it lost part of itself.
On a personal note, I met Andreas once — and that was enough. Charismatic and purposeful, he cuts through the noise with a quiet insistence on truth at a moment when too many remain silent or choose the wrong side as antisemitism rises worldwide. For years I heard about him from one of my closest friends, Emil Schustermann, who spoke of Andreas with steady admiration. This past summer I was fortunate to meet the legend in person. The integrity you feel in his book is the integrity you feel across a table: steady, unsentimental, anchored in facts and responsibility.
Jüdische Familienunternehmer in Hitlers München is, finally, a usable history. It helps citizens, students, and leaders see Munich differently: storefronts as testimonies, plaques as prompts, absences as questions. It closes the distance between numbers and names, between street addresses and fates. And it leaves readers with the task the book so plainly sets — to remember precisely, to teach honestly, and to stand, now, against the same old hatred in its new clothes.
Eli Verschleiser is a NYC-based entrepreneur, financier, real estate developer, and investor. In his philanthropy, he is Chairman for Our Place, among other nonprofit organizations that provide support, shelter, and counseling for troubled Jewish youth. He is a frequent commentator on political and social services matters and can be followed on X (formerly Twitter): @E_Verschleiser


