Features
With Einstein and Darwin

By David R. Topper A significant part of my adult intellectual life has been spent studying and teaching about the life and works of Albert Einstein. This led to my publishing various works about this fascinating, often frustrating man. Just as fervently, but not nearly to the same extreme, I’ve studied and taught about Charles Darwin. But I never published anything on him.
Since Einstein came after Darwin, the question often occurred to me as to whether Einstein ever read, thought, or wrote about Darwin. Indeed, I’ve gone as far as posing the following proposition to myself: Maybe, if Einstein had read and absorbed Darwin’s discovery about the astonishingly dynamical and unpredictable way the natural world works, then he may have been less rigid in his thoughts about the order and structure of the universe. In fact, I could go so far as to conclude that, if he had, then in 1916 he might not have made the erroneous assumption in his model of the cosmos, which he later called the “biggest blunder of my life” (quoted in Topper, p.165).
But I’m getting ahead of my story and I need to start with some basic questions. Did Einstein know about Darwin, and if so, what? In searching through the literature on this possible juxtaposition of these two giants in their fields, as far as I can tell, I’m the first person seriously to pose this issue in some detail – which was a big surprise. It certainly gave me an incentive to pursue this diligently. Thus I did, and here is what I found – plus, at the very end, I add a zany speculation about the nature of the universe, as we know it today.
The names “Einstein” and “Darwin” are seldom juxtaposed, except in a general sense, such as when comparing Einstein’s theory of relativity with Darwin’s on evolution – as overall examples of major ideas in recent centuries. Going through all the indexes of the many dozen books on Einstein that I own, looking for “Darwin” – in the few times I found the name, the reference was always to a general comment about him as a scientist, with nothing about the content of his theory. At most, I found that Albert had read Darwin, which is important to know, but I found little information on what the theory meant to him or what he got out of it.
Hence, I began a journey to see if I could find more, since it seems that I’m the first ever to explore – or even ask – about Einstein and Darwin. My next question was: do we know when Albert was first exposed to Darwin’s theory, and what did he learn? The earliest time I found was during the school year 1895 to 1896, when he was in Aarau, Switzerland, taking remedial high school before enrolling in the Polytechnic in nearby Zurich. We know that the Swiss school he attended was very progressive and it taught Darwin’s theory of evolution. It’s worth quoting something he said much later, when looking back on those years:
“By its liberal spirit and by the austere earnestness of its teachers … this school made an unforgettable impression on me; by comparison with six years of schooling in an authoritarian German Gymnasium [i.e. High School]. … I became acutely aware how much an education directed toward freedom of action and responsibility is superior to an education resting on drill, imposed authority, and ambition (quoted in Ohanian, p.9).”
During his next four years in Zurich at the Polytechnic, we know that among the many physics and math books that Einstein read, he also read Darwin – but we don’t know the details (Pais, p.44). Thus, as we move into the 20th century, at least we can say that he knew something about Darwin’s theory.
My next source to explore was the Collected Papers of Einstein, which are at present up to May 1929, when Albert was age 50. Over all those years, there are only a few places where the name Darwin appears. There is a book review he wrote in 1917, where the author mentions Darwin. Next, is a letter from a colleague in 1918, who talks about Darwin’s theory in passing, while making comments on society and politics. The only place where Einstein himself talks about the content of the theory is in the Third Appendix to his popular book, Relativity: the Special and the General Theory, which he added around 1920. That’s all there is. Albert died in March 1955, so there are still 26 years to go for the Collected Papers, but I’m not optimistic that anything significant will surface therein. Yet, who knows?
Using what I have, let’s explore this topic further, beginning with this appendix. The title is: “The Experimental Confirmation of the General Theory of Relativity.” Einstein begins with a brief foray into epistemology in science: induction and deduction. As science progresses over time, the inductive accumulation of empirical data occasionally needs to be supplemented by deductive ideas logically based upon a few given axioms; and from this there emerges a “system of thought” or a “theory.” The justification for the very existence of the theory is the fact that it correlates with a range of observations (empirical data) and “it is just here that the ‘truth’ of the theory lies (Einstein, p. 124).” He puts the word ‘truth’ in quotes because, as is often the case, there may be several such theories competing for an explanation of the same data. The ultimate goal of this for him is, of course, the issue of his general theory of relativity to explain gravity, in competition with the old theory of Newton. But before he delves into that – which constitutes the rest of the Appendix – he makes this aside comment on biology.
“As an example, a case of general interest is available in the province of biology, in the Darwinian theory of the development of species by selection in the struggle for existence, and in the theory of development which is based on the hypothesis of the hereditary transmission of acquired characteristics (Einstein, p. 124).”
That’s it. As far as I know, that is the only direct statement about Darwin’s ideas that Einstein ever wrote. Let’s look closer at this, for we will need it later. First, I want to point out another way of putting this. Einstein is contrasting the difference between Charles Darwin’s random selection method of evolution, with Jean-Baptiste Lamarck’s developmental process, which had a predetermined direction or goal for the evolutionary process. Thus, Darwin’s “struggle for existence” revealed the dynamical nature of plants and animals as they change over a long time-period. I’m assuming that Einstein realized all this, along with the lack of a specific direction for the evolutionary process according to Darwin. I just wish Einstein had said more; but we go with what is given. Moreover, the stage has now been set for why I have raised the name of Darwin in the first place.
In 1915 Einstein published his landmark paper on the general theory of relativity, which was essentially an explanation of gravity. Whereas Newton had pictured gravity as an invisible attractive force between all the elements of matter throughout the universe (from rocks to planets and stars), Einstein pictured it as a four-dimensional curvature of space (or, more precisely, space-time) around all those elements. Although Einstein’s paper constitutes pages and pages of tensor calculus equations, the conceptual image is quite simple. A rock is not falling to earth by an invisible attractive power; rather, the rock is simply moving into a dimple in space.
After completing this arduous task of many years, Einstein immediately wrote the popular account of the entire theory of relativity for the general reader, with a minimum of mathematics. In his Preface to the first edition, dated December 1916, he ends with this: “May the book bring some one a few happy hours of suggestive thought!” It was the Third Appendix to that work that I quoted above.
Next, he made a prediction. Still in 1916, from his general relativity theory, he wrote another paper, predicting the existence of gravitational waves. Over his lifetime such waves were never found, and in his latter years he doubted that they ever would be – since they are so infinitesimal in nature. But in 2015, almost exactly a century after their prediction, gravitational waves were detected by the clever design of a very big experimental apparatus that was necessary to find these minuscule waves. The three scientists who designed and did the experiment got the Nobel Prize two years later.
Back to 1916, for Einstein was not yet done. The entire enterprise had triggered another thought, and yet another paper. It started with a question. If the space around all elements of matter is bent locally, what does this say about the universe as a whole? Thus, Einstein went back to those equations for locally bending space and – so to speak – he summed them up for the space of the entire universe. In doing so, he found that the resulting universe – unlike the infinite space of Newton and others after him – was finite, since all space curves back into itself. It was as if we were living on the surface of a four-dimensional sphere of finite size. This finite universe was okay with Albert; he saw it as just another discovery that he made.
Yet there was a problem: according to the equations, the whole thing was unstable, due to the gravitational attraction among all the elements of matter. Such a universe would slowly collapse – and that would not do. Surely, the universe was stable; and so, in order to save this theory – after all those years of gruelling work – he stabilized the equation by adding another term; this term symbolized another force, having an equal and opposite repulsive power that balanced the two, and hence stabilized the universe. He called it the cosmological constant. To him, this was another discovery; that is, it was just another constant in nature. All this he published in 1917, and it formed the basis of a new cosmology. Indeed, all modern cosmology goes back to these landmark papers on general relativity by Einstein. Over the next decade, there were a few challenges to his model; particularly around the cosmological constant. Einstein did not see all of them, but the ones he saw, he rejected – thus holding fast to a stable universe.
Also, around this time, Einstein had another bright idea. Since the first decade of the 20th century, when he published his first papers on relativity, he also published major papers on the parallel theory of the atomic constitution of matter; namely, the quantum theory. His other bright idea, which absorbed his scientific attention starting in the 1920s, was to unite the two (relativity and quantum) into a unified theory of everything. He eventually called it the “unified field theory,” and it became his key obsession for the rest of his life.
In the meantime, by the start of the 1930s, he was forced to reconsider his cosmological model. It began in the summer of 1930, when he received an honorary degree from Cambridge University, where he met Arthur Eddington – the astronomer who had led the solar eclipse experiments that proved Einstein’s relativity theory in 1919, by measuring the bending of light from a star around the sun, as predicted by Einstein. Eddington now was familiar with important results coming from American astronomers, such as the work of Edwin Hubble at the Mt. Wilson observatory near the California Institute of Technology (Caltech) – holding the largest telescope in the world at that time. The results, as Eddington interpreted them, meant that the universe was expanding. It was as if that four-dimensional sphere was a balloon being blown up. Since this model contained a force of expansion outward, then no cosmological constant was needed. The universe was, indeed, unstable – and as well, expanding over time.
Serendipitously, at this time, Einstein was on his way to Caltech for three winter sojourns (1930-1933). While at Caltech on his first visit, he therefore had to abandon his commitment to the static model. He was quoted in the American press as saying that his old model was “smashed … like a hammer blow,” and he swung his arm with a fist while declaring this (Topper, p 174). Never again did he bring up the cosmological constant. In the early 1950s, when the topic arose in cosmology again, he was questioned about it: and, as mentioned before, he called the use of that constraint “the biggest blunder of my life.” (I should note here that in recent years it’s been discovered that this expansion of the universe is, in fact, accelerating. Hence, another repulsive force must be added, which today is called ‘dark energy’. Ironically, this may be seen as just another way of bringing back Einstein’s cosmological constant. Perhaps it wasn’t a mistake, after all.)
It’s important here to remember that Einstein’s extraordinary contributions to physics, ranging from his own theory of relativity to a wide range of topics in quantum physics, lasted from around 1905 into the mid-1920s. By then he became obsessed with his unified field theory, and essentially ignored all other important new fields, such as nuclear physics. Although popular culture likes to juxtapose an image of him with his halo of hair next to a mushroom cloud from a nuclear bomb – for example, the cover of Time magazine for July 1, 1946 – in fact, he made nary an iota of input to the actual development of that important branch of 20th century physics. This runs counter to what you may be told in popular accounts of Einstein’s life and work, such as on TV and in the movies. (Yes, I know about that little equation about energy and mass that Einstein is famous for. It was there in those early years of the quantum physics of subatomic particles. Nevertheless, it’s a very long haul from that seemingly innocent equation, through decades of work in nuclear physics, and then designing technological contraptions to making a bomb or any other applications for nuclear energy. All of which was done without Einstein. Incidentally, in that famous Time cover, E = mc2 is embedded in the mushroom cloud.)
More importantly, as quantum physics evolved into quantum mechanics around the mid-1930s, Einstein vehemently rejected the statistical nature of the subject. Although he himself, starting around 1905, had published many important papers using statistics within the quantum world, he interpreted it as a limit imposed by the experimental tools that we have in probing the subatomic world. To him the statistical features were not a part of the world itself, which is – at least, potentially – completely predictable. Yet by the 1930s, especially as expounded by his friend the Danish physicist Niels Bohr and others, the quantum mechanical interpretation of the statistical nature of the equations was that the underlying subatomic world itself was statistical in nature, and had no predetermined or predictable order. Only probabilistic statements can be made about that minuscule world – and that was its fundamental nature, according to quantum mechanics.
Einstein would have none of this. To make an analogy that I believe he would like: consider the use of statistics in actuarial tables by insurance companies, in order to predict the behaviour of groups of people, since individual behaviour can’t be predicted. Using Bohr’s interpretation of statistics in quantum mechanics, there would be no real people – only probable people! However, for Einstein electrons (along with other subatomic particles), like people are real. And so, the fact that quantum mechanics must rely upon statistics to work, means that the theory is incomplete. The problem is with the theory, not the world. Indeed, he believed that one result of achieving his unified field theory someday, would be the deduction of a complete, predictable and real subatomic world. That was another reason to pursue his quest.
In the closest writing to an autobiography, which Einstein penned in 1946, he said this: “Beyond the self, there is this vast world, which exists independently of human beings, and that stands before us like a great, eternal riddle” (Topper, p.10, italics mine). Nonetheless, Bohr’s viewpoint prevailed amongst most physicists. Hence, Einstein fought a losing battle to the end of his life.
What all this shows is that throughout his life, the concepts of stability, predictability, and order were fundamental in Einstein’s picture of the universe – the way he believed his one equation for the unified field theory (if found!) would unite the worlds of relativity and quantum physics. He died in 1955 without finding this equation. Nevertheless, the quest continues, with myriad physicists today searching for, what they now call, a theory of everything.
Now back to cosmology. We now know – and by “now” I mean in only the last few years – that the universe is much more dynamical than it was ever imagined to be, even with all this expanding and accelerating going on. Stars group together as galaxies, and galaxies group together into larger clusters, due to their gravitational attractions. But – and this was realized with the help of the Hubble and now the James Webb telescopes – galaxies merge and interact in a process producing new galaxies. One might call it an internal dynamical change among the galaxies that we never knew about, until now. Closest to home, consider our Milky Way galaxy, where “we” – namely our solar system, with a star (our sun) at the centre – are near the outer edge. Being far from the black hole at the centre of our galaxy, it’s a rather quiet place (astronomically speaking) – and hence life was able to take hold and evolve into what we have today. This will go on until our sun runs its course. Our star is now almost halfway through its 10-billion-year cycle. In about 0.5 – 1.5 billion years, as it starts running out of hydrogen fuel for nuclear fusion, it will expand into a “red giant” that will encompass the orbits of Mercury, Venus, and our Earth – and hence all life as we know it will end. (Unless, of course, humans, with their nuclear weapons, hasten that event.) After that, the sun will collapse into a cold “white dwarf.”
Independently of all this, and on a larger scale, our Milky Way is part of a group of galaxies, the largest being the so-called Andromeda Nebulae, visible as a smudge to the naked eye. Due to gravity, these two galaxies are on a collision course, moving closer at the rate of 110 kilometers per second. They will meet in about 3.5 billion years, long after life has ended here. At the same time, a much smaller galaxy, M33 (also called the Triangulum Galaxy) will also take part, along with the Large Magellanic Cloud (another nearby small galaxy), which may join in on this merger. What happens next is not clear, since we need much more information from the Hubble and the James Webb telescopes. Even so, we will never know if any prediction is true or not, since no humans will be around to see all this happen!
Nonetheless, we do know a lot about such an event. Importantly, I need to clarify what we mean by a collision of galaxies. Or, maybe better said: what we don’t mean. There will be no fireworks, like clashing and exploding stars. To understand this, we must realize this fact: although from a huge distance, any galaxy looks like a compact mass of stars, in reality the individual stars are extremely far apart. As an example, consider our sun and the closest star, Proxima Centauri, which is about 4.2 light-years away. If the sun were a ping-pong ball, Proxima Centauri would be a pea about 1100 kilometres away. And so it goes throughout our galaxy and beyond, with all the other galaxies. In short, the universe is mainly empty space – strange as that may seem. Accordingly, when galaxies merge and form larger ones, there are no fireworks – just a different arrangement of the way stars group together. As for our Milky Way and Andromeda collision – along with the smaller ones – they may just pass through each other, and go on their astronomical ways. Or not. There are several possible groupings that may take place among these merging galaxies in the distant future. All this may be seen by some sentient beings on a planet in orbit around a star, both of optimum size, and in a quiet place similar to us in the Milky Way, such that a life-form evolved to our state of self-consciousness. What would they make of all this?
Now, bringing all this back to the present, and recent past: with Einstein & Darwin. So, here’s my bright idea. Thanks especially to the James Webb space telescope, and thus having this most recent information about how dynamical the universe really is – and, thankfully, not having an obsession with order and stasis – I find myself speculating about the process of galaxies merging and interacting, thus giving rise to new dominant ones and eliminating the old. As such, I picture this as an evolutionary process of survival and extinction – Darwinian in nature. A struggle for existence among the galaxies. A random process producing new galaxies throughout the universe, with no predetermined direction or goal. As such, it’s parallel to Darwin’s notion of natural selection. But now writ large (very large!), to encompass the entire universe and everything in it.
This, at least, is what all this information is telling me. Makes sense, I say.
What would Einstein say? Or Darwin? What do you think?
As a kind of footnote to this essay, I want to point this out: I know where most of Einstein’s commitment to the structured and ordered universe came from. It was his adulation of the Jewish philosopher Baruch Spinoza. I too read Spinoza’s Ethics, and was in awe of the depth of logic entailed in this incredible but difficult work. Unlike all other philosophers that Einstein read – and he read many; remember, he was educated in a 19th century German system – he never critiqued Spinoza. Rather, he absorbed the arguments from the Ethics for his views of the world, as well as for his theology. However, I, with my understanding of history, am able to see how Spinoza’s book was squarely centered in the world-view of the 17th century – not the present world that I live in. Too bad Albert didn’t do the same.
* * *
Bibliography:
Einstein, Albert. Relativity: the Special and the General Theory. A Popular Exposition. Translated by Robert W. Lawson. London: Methuen & Co., 1920. I’m using the paperback reprint of 1977.
Ohanian, Hans C. Einstein’s Mistakes: The Human Failings of Genius. New York: W. W. Norton, 2008.
Pais, Abraham. “Subtle is the Lord”: The Science and the Life of Albert Einstein. New York:Oxford University Press, 1982.
Topper, David. How Einstein Created Relativity out of Physics and Astronomy. New York: Springer, 2013.
#
David R. Topper writes in Winnipeg, Canada. His work has appeared in Mono, Poetic Sun, Discretionary Love, Poetry Pacific, Academy of the Heart & Mind, Altered Reality Mag., and elsewhere. His poem Seascape with Gulls: My Father’s Last Painting won first prize in the annual poetry contest of CommuterLit Mag. May 12, 2025.
Related
Review: Tales of an Unconscious Mind by Dr Nikhil Chandwani
May 23, 2017
In “Books Reviews”
The Dark Side of Albert: Einstein and Marie Winteler, his First Love
August 31, 2025
In “Essay”
A Very Famous Breakfast
April 20, 2020
In “Wellness”
Features
Why casinos reject card payments: common reasons
Online casino withdrawals seem simple, yet many players experience unanticipated decreases. Canada has more credit and debit card payout refusals than expected. Delays or rejections are rarely random. Casino rules and technical processes are rigorous. Identity verification, banking regulations, bonus terms, and technological issues might cause issues.
Card payment difficulties can result from insufficient identification verification. Canadian casinos must verify players’ identities before accepting card withdrawals. If documentation are missing, obsolete, or confusing, the request may be stopped or denied until verified.
Banks and card issuers’ gaming policies are another aspect. Some Canadian banks limit or treat online casino payments differently from card refunds. In such circumstances, the casino may recommend a more reliable withdrawal method.
For Canadian players looking to compare bonus terms and payout conditions, check https://casinosanalyzer.ca/free-spins-no-deposit/free-chips. This article explores the main reasons Canadian casinos reject card payouts, from KYC hurdles to bank-specific restrictions, so you know exactly what to watch for.
Verification Issues: Why Identity Checks Matter
KYC rules must be activated by licensed casinos. Players need to submit proof of their identity, address and age. If any documentation is missing, expired or unclear, the withdrawal will be denied. In Canada, for instance, authorities like the AGCO or iGaming Ontario have been cracking down on KYCs by demanding that submitted documents – whether photo ID, utility bills or bank statements – be consistent with all account details.
Common errors are submitting screenshots, cropped photos or documents with names, dates or addresses that aren’t entirely visible. Just the slightest differences in spelling or abbreviations or formatting can get these blocks triggered.
Another possibility is that the account was red flagged if previous withdrawals were already made without partial verification. Keeping precise, readable documents helps facilitate approvals and cuts through delays and frustrating red tape, as Canadian gamblers access their winnings both safely and quickly.
Timing Matters
Verification isn’t always instant. Documents being submitted during the busiest times, or on weekends or holidays can only prolong that approval process, and the withdrawal sitting pre-approved – or refused for that matter – until the casino reviews the paperwork. A lot of players feel disappointment not due to mistakes, but only for that a verification team still hasn’t checked their documents! This can be especially frustrating when winnings come from free chips or bonus play and players are eager to cash out.
Keep personal information current and only submit clear legible files to reduce the processing time. Ensure that any scans or photos are sharp, fully visible and there is no detail missing. Preventing Gaffes With submission guidelines to read over ahead of time and directions for following them exactly, verification issues can often be significantly minimized, avoiding delay in accessing winnings and making the lie down withdrawal process that much smoother at Canadian online casinos.
Banking Restrictions and Card Policies
Not all credit or debit cards are eligible for casino withdrawals. Many Canadian banks restrict transactions related to gambling. For example, prepaid cards, virtual cards, or certain credit cards may allow deposits but block withdrawals. Even if deposits work, a payout can fail if the bank refuses incoming gambling credits.
Cards issued outside Canada can also be declined due to international processing rules. Currency conversion restrictions may prevent a CAD payout to a USD card, depending on the bank’s policies.
Banks keep an eye on abnormal or frequent transactions. Online casinos can flag large or multiple withdrawals as suspicious and in such cases may impose temporary blocks on withdrawals or outright decline the withdrawal until the issuing bank confirms them with its account holder. Contacting your bank in advance will avoid any surprises and make withdrawals go more smoothly. What to consider when using your card in Canada:
- Check if your card type supports gambling withdrawals (prepaid, virtual, and some credit cards may not).
- Confirm whether your bank allows international online casino payouts.
- Be aware of currency conversion restrictions.
- Monitor withdrawal frequency to avoid triggering fraud alerts.
- Contact your bank ahead of time to authorize or clarify online gambling transactions.
- Keep alternative withdrawal methods ready, such as e-wallets or bank transfers.
Being aware of these constraints prevents Canadian players from having declined payouts, delays and waste of time when it comes to handling the casino money properly.
Wagering Requirements and Bonus Conditions
Many Canadians chase casino bonuses, including deals built around free chips, but these offers always come with conditions, Wagering requirements usually require players to bet a multiple of the bonus before withdrawing. Attempting a payout before meeting these conditions will be automatically declined. Not all games contribute equally: slots often count 100%, table games 10–20%, and certain features nothing at all.
Misinterpretation of this, can make it appear as though a withdraw should be valid, while the casino believes there are unmet bonus requirements. Some casinos also impose a minimum withdrawal amount and will cap card payouts. And if you have more than the minimum in your account, a limit set off by your bonus could limit withdrawal. By testing these issues early on, you can save yourself a lot of aggravation. How to manage bonus conditions effectively:
- Have a close look at the terms of the bonus – check out wagering requirements, game contribution and time limits.
- Track your progress – note how much of the bonus has been wagered and which games contribute most.
- Plan your gameplay – prioritize slots or eligible games to efficiently meet wagering.
- Check withdrawal limits – ensure your balance meets minimums and bonus-specific caps.
- Avoid early withdrawals – never attempt a cash-out before meeting all conditions.
- Use trusted sources – platforms like CA CasinosAnalyzer can clarify real requirements and prevent surprises.
Following these steps helps players meet bonus conditions without stress and makes bankroll management smoother.
Features
What is the return on investment of US military spending on Israel?

By GREGORY MASON A recurring theme of Israel’s critics is that were it not for US spending on its war machine, it would be unable to wage genocide. I will leave the genocide issue (sic, I mean non-issue) aside as it has been well covered here and here.
Of course, right now (March 11), the war is going well for Israel and the US. In fact, the Israeli and American air forces are showing a level of coordination enabled by decades of close cooperation between the two militaries. I recall a conversation with an IDF colonel, the commander of a base near Eilat, in 2010, during a mission that gave participants access to high-level military briefings. Tensions between Israel and the US had soured, as they periodically do, and I asked whether this ebb and flow in political posturing affected military operations. The colonel said political leaders come and go, but the cooperation between the Israeli and American militaries is very tight. To quote him, “they need us as much as we need them. We are their eyes and ears in this part of the world.”
Many on both the right and left call for the US to disengage from Israel, especially with respect to defence spending. First, let us look at facts.
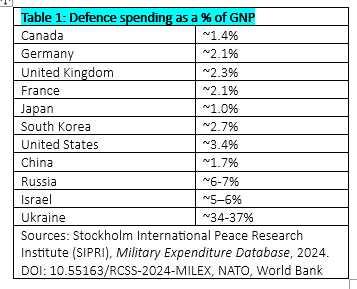
Table 1 readily shows the impact of the war in Ukraine, with Russia’s spending also reflecting wartime demands. Israel’s total commitment of 5-6% of GDP amounts to $45 billion in defence spending, reflecting its perpetual need to defend itself and maintain a permanent reserve force. Table 2 elaborates on defence spending as a share of public spending. Unlike other countries that have been free riding under the US military umbrella (and Canada is the most egregious of the lot), Israel has made very substantial commitments to its own defence. The $3.8 billion spent on hardware for US equipment is a fraction of Israel’s total defence budget of about $43 Billion. All U.S. financial aid to any country for military hardware must be spent on U.S.-manufactured equipment by law.
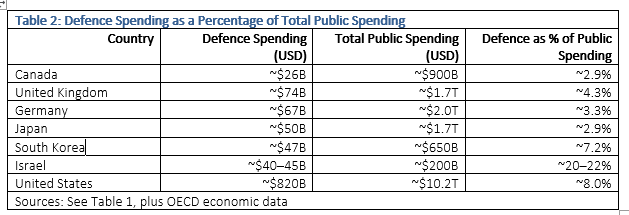
Critics of US defence funding for Israel miss two key points. First, as Table 3 shows, financing sent to Israel does not involve troop deployment. Israel does not want the US to station troops within its borders. The costs of maintaining troop deployments and all the associated support costs for NATO, Japan, and South Korea are orders of magnitude higher than the financing for the hardware it provides to Israel.
Second, and the current joint US/Israeli operations in Iran bear this out, Israel has dramatically improved the equipment platforms it purchased. Examples include:
- The F-15 has benefited from Israeli wartime use, resulting in major improvements, including a redesigned cockpit layout, increased range through fuel redesign, improved avionics, new weaponry, helmet-mounted targeting, and structural strengthening.
- Because Israel was an early partner in the fighter’s development and had access to its top-secret software suite, the Israeli version of the F-35 is a radically different plane than the model delivered. Improvements include increasing operational range, embedding advanced air defence detection, and integrating the fighter with Israel’s defence network, creating extensive system integration. This proved instrumental in the rapid establishment of air superiority in the 12-day war in 2025.
- The THAAD (Terminal High Altitude Area Defence) program has benefited from a joint research and development relationship between Israel and the U.S.
- Finally, Iron Dome has contributed to U.S. air defence development, particularly the Tamir interceptor technology, battle management, target discrimination, and the development of a layered air defence system.
No senior military or political official questions the return on investment American gains by funding Israel’s acquisition of U.S. military hardware.
Features
Why Returning Players Often Stick to a Few Favorite Games on Platforms Like Gransino Casino

Many online casino players develop clear preferences over time, and Gransino Casino highlights how familiar games often become the center of regular play sessions.
Online casinos typically offer large catalogs filled with hundreds of different slot titles. While this variety allows players to explore new experiences, many returning users gradually settle on a smaller group of games that they revisit regularly. This pattern appears across many digital gaming environments, where familiarity often becomes just as important as novelty.
Platforms such as Gransino Casino demonstrate how this behavior emerges in practice. Even though players have access to many different titles, returning visitors frequently gravitate toward games they already know and understand.
Familiar mechanics reduce learning time
One reason players return to the same games is that they already understand how those titles work. Each slot game has its own rules, bonus features, and payout structure. When a player first opens a new title, they often need a few minutes to understand the paytable, special symbols, and feature triggers.
Once that learning process has taken place, the game becomes easier to approach in future sessions. Players do not need to spend time reviewing instructions or exploring unfamiliar mechanics. Instead, they can begin playing immediately with a clear sense of how the game operates.
On platforms like Gransino Casino, this familiarity can make certain titles stand out as reliable choices. When players know what to expect from a game, the experience often feels smoother and more predictable during short play sessions.
Personal preferences shape long-term choices
Another factor influencing player behavior is personal preference. Some players enjoy specific visual themes such as mythology, adventure, or classic fruit machine designs. Others may prefer particular gameplay features, such as free spins, cascading reels, or bonus rounds.
Over time, players tend to identify the games that best match these preferences. Once they find titles that align with their interests, they are more likely to return to those games rather than start the search process again.
This pattern can be seen on Gransino Casino, where players browsing the lobby may explore different titles at first but eventually settle on a smaller group of favorites that suit their individual style.
Habit formation in digital gaming
Habit formation also plays a role in why players repeatedly choose the same games. In many digital environments, users develop routines that guide how they interact with a platform. This behavior is visible across streaming services, mobile games, and online casinos.
Once a player has established a routine, returning to familiar content often becomes part of that pattern. For example, a player might log in and immediately open the same slot they played during previous sessions. The familiarity of the interface, symbols, and features can make the experience feel more comfortable.
Platforms like Gransino Casino support this behavior by maintaining consistent game availability and allowing players to locate previously played titles easily within the lobby.
Exploration still remains part of the experience
Although many players develop favorite games, exploration remains an important part of the online casino experience. New titles continue to appear on casino platforms, introducing different mechanics, themes, and visual styles.
Players often alternate between their familiar choices and occasional experimentation with new games. A player might return to a favorite slot for most sessions while occasionally trying recently released titles to see if they offer something interesting.
The wide selection available on Gransino Casino allows this balance between familiarity and discovery. Players can continue returning to the games they enjoy while still having the option to explore new additions within the platform’s catalog.
Ultimately, the tendency to revisit favorite games reflects how players build their own routines within digital entertainment environments. Familiar titles offer a comfortable starting point, while new releases provide opportunities for occasional exploration, creating a mix of consistency and variety within each player’s experience.


