Features
New book looks at the fight by law-abiding Jews to rein in the New York Jewish underworld in early 20th century

The Incorruptibles: A True Story of Kingpins, Crime Busters, and the Birth of the American Underworld
Reviewed by BERNIE BELLAN For those readers who can remember the story of “The Untouchables,” the crime-fighting unit led by Elliot Ness, which was established by the Bureau of Prohibition in the US in the 1930s, tales of shoot-outs between courageous crime-fighting “good guys” and villainous underworld bootleggers and other assorted criminals would probably be thought of as something that wouldn’t have its origin in a Jewish-led crime-fighting unit established several years earlier.

But, would you believe that not too many years before the often bloody events that were depicted in “The Untouchables” came to pass there was another organization in New York City – led by Jewish crime fighters at that time, which had a somewhat tacit affiliation with the New York City Police Department, and whose purpose was to wage war on Jewish criminals on New York’s East Side? That organization was known as “The Incorruptibles” and the story how it came to be created is told in a fascinating new book, titled “The Incorruptibles: A True Story of Kingpins, Crime Busters, and the Birth of the American Underworld,” written by a New York crime reporter by the name of Dan Slater.
As someone who has long had a fascination with shady Jewish characters, I’ve come to realize over the years that a rollicking good story of a Jewish mobster, such as the close friendship a former Winnipegger by the name of Al Smiley had with the notorious Bugsy Siegel, about which Martin Zeilig wrote for The Jewish Post & News in March 2017, resonates with readers in ways that stories about more righteous Jews don’t.
While Martin’s story about Al Smiley was by no means the first story we’ve ever had about Jewish mobsters, a quick search of our online archive would lead you to numerous stories about Jewish gangsters and other assorted criminals.
In the summer of 2023 we ran two stories in relatively rapid succession that elicited a higher than usual amount of interest from readers. One was my review of a book called “Jukebox Empire,” about someone by the name of Wilf Rabin, who actually grew up in Morden, Manitoba. The other story was about bootlegger Bill Wolchock, written by Bill Redekopp, and which appeared in our 2023 Rosh Hashanah edition. Later, when I posted that story to our website it received so many views that I’ve returned it to our home page twice since. (You can now read that story if you missed it by reading it here: “Booze, Glorious Booze”
All this serves as a preamble to my review of “The Incorruptibles.” I have to couch what I’m about to write with an admission: As a youngster growing up in a sheltered environment, and attending the Talmud Torah, where all we were ever told about was Jewish “heroes,” and the only villains were Jews who didn’t lead properly observant lives, reading “The Incorruptibles” came as a real shock to my conception of how much Jews could be associated with the most sordid type of criminal activity.
It’s one thing to realize that many Jews were involved with bootlegging – something that has developed an almost romantic connotation over the years through books, movies and television programs, but to learn that in the latter part of the 19th century Jews in New York were in control of that city’s: prostitution (and most prostitutes were Jewish!); drugs (however, with the understanding that drugs, including heroin and cocaine, were legally available in the U.S. until 1907 and could be readily purchased in pharmacies); gambling; and protection rackets – does come as somewhat of a shock to a sheltered Winnipeg Jew.
Dan Slater’s depiction of life in New York City at the turn of the 20th century is unremittingly harrowing. For the first part of the 20th century the lower East Side of New York was the most densely populated area on Earth. Housing conditions were horrible and the hundreds of thousands of new immigrants arriving yearly – beginning in the 1870s, from what was known as the Pale of Settlement in Eastern Europe – fleeing persecution and pogroms, found themselves being shunted into unspeakably barbaric working conditions in lower East Side factories, predominantly garment factories – owned by fellow Jews. (The author actually spends a considerable amount of time explaining how exactly the Pale of Settlement came into being and how sudden and incredibly violent wholesale persecution of hundreds of thousands of Jews could happen almost overnight – with the death of a particular czar, for instance.)
It was amidst this churning cesspool of a city that Jewish criminal activity of all sorts ran rampant. Two images from “The Incorruptibles” in particular haunted me. One was Slater’s explanation how so many young Russian Jewish women – most in their early or mid-teens, and only recently arrived in New York, were forced into prostitution. Many of these young women would go to a dance – looking to find some relief from the slave-like conditions that permeated the factories in which they worked. While at the dance, they would be approached by a young Jewish man who would offer them a drink. These guys, known in the colloquial as “Alphonses,” or, in Yiddish, as “schimchas,” would lace the girls’ drinks with drugs (a common occurrence to this day) and take the girls home, where they would rape them. But – now defiled, the girl could not possibly return to her family home out of shame; thus, tens of thousands of young Jewish women were forced into prostitution.
The other image that haunts me was the widespread practice of “horse poisoning.” Protection rackets have probably been around from time immemorial, but in this particular incarnation, criminals would confront business owners with a choice: Pay for “protection” or see your means of transportation (and remember, this was at a time when a horse-drawn buggy or carriage was the principal means of transportation) poisoned.
(There is actually a photo in “The Incorruptibles” of a horse lying dead on a New York street after it had been poisoned. Apparently it happened on a regular basis to the point where it didn’t draw much attention.)

While the book chronicles one sordid story after another so that the reader can understand just how tough life was on the lower East Side – often with reference to the colourful names of some of the most famous Jewish thugs who terrorized their fellow Jews, such as “Bald Jack Rose” or “Big Jack Zelig” (no relation to Martin Zelig – I checked), the biggest mobster of them all was the legendary Arnold Rothstein.
Rothstein is undoubtedly most famous for reputedly having fixed the 1919 World Series by bribing eight members of the Chicago White Sox, the overwhelming favourite to defeat the Cincinnati Reds, to throw the series. (It has never been proven absolutely conclusively that Rothstein did that, but as “The Incorruptibles” explains, the evidence points overwhelmingly in his direction.)
Rothstein was the kind of gambler who could lose $350,000 in a single night of playing poker – and not worry about it.
Here is an example of Slater’s ability to describe a character, when he sums up Arnold Rothstein: “Picture in one individual a sentimental and tender lover, a genial and humorous companion, a charitable giver, a loyal friend—and—a wholesale drug dealer, a crooked sports fixer, a welching gambler, a stolen securities fence, a rum-ring mastermind, a corrupter of police, a grafter through politics, a gunman, a judge-briber, a jury-tamperer, a blackmailer, a pool shark, a swindler.”

But, up against the villains of “The Incorruptibles,” Slater also depicts the stories of two very talented – and brave, young Jewish men, who were willing to challenge the criminal class: A lawyer by the name of Harry Newburger and Abe Shoenfeld, the son of a well-known New York reformer by the name of Mayer Shoenfeld.
As Slater explains, it was only when members of New York’s largely German-Jewish upper class began to take note of the horrid conditions in which the vast majority of the Eastern European Jews who had recently immigrated to America were living did an impetus to try and change things develop. Two men, Jacob Schiff (who is described as the J.P. Morgan of his day in terms of his vast wealth), and Felix Warburg, together with the rabbi of the leading temple of its day, Rabbi Judah Magnes of Temple Immanu-El, organized a group known as the “Kehilah.”
The Kehilah mandated Newburger and Shoenfeld to do whatever they deemed necessary to begin cleaning up the lower East Side. Of course, given how corrupt New York officials were at the time – under the control of the notorious Tammany Hall, led by “Big Jim Sullivan,” most of the New York City Police Department was also thoroughly under the control of criminals, which made the challenge set out for Newburger and Shoenfeld all the more difficult.
The book describes, sometimes in painful detail, the difficulties faced by the group assembled by Newburger and Shoenfeld, known, naturally, as “The Incorruptibles.” They weren’t above busting heads themselves, it turns out.
Again, one of the more interesting aspects of history to emerge from this book is that men would often switch sides at the drop of a hat – to go from violently attacking one particular group – at the behest of this or that mobster, to attacking the same group they were supposed to be defending the next day.
As has already been noted, the garment trade played a pivotal role in the development of New York City into becoming not only a magnet for immigrants, it also also played a prominent role in New York’s becoming the vast economic powerhouse that it is today. Slater notes that, at one point, 80 percent of all garments produced in the U.S. came from the lower East Side.
As workers began to organize themselves into unions, garment factory owners hired thugs, known as “shtarkers” (strong men) to beat up workers, occasionally to kill union organizers. In time though, the tide began to turn and, as unions gathered strength, the same tactics of violence and intimidation that had been used against workers began to be employed by unions – with workers who dared to cross picket lines (known colloquially as “scabs”) often being on the receiving end of that violence, occasionally ending with them being killed.
Newburger and Shoenfeld were thrust into the midst of this turmoil, trying to bring some peace to the labour disputes. Ironically, Mayer Shoenfeld (Abe’s father) was a longtime advocate for workers’ rights, but he would not talk to his son, who tried to straddle both worlds – of employers and employees.
“The Incorruptibles” describes the many battles fought to rein in the gambling, prostitution, protection rackets, and what became the illegal drug trade that were part and parcel of life on New York’s East Side. As the years went by, the Jewish dominance of the New York underworld gave way to the ascendance of the Italian mob. (Slater also acknowledges the roles that other groups also played in New York criminal activity, including the Irish), but his main focus is on Jewish criminals.
“The Incorruptibles” is a long and detailed book, drawing upon a great many different sources, and at times, the proliferation of names entering the scene can be more than a little confusing. But, for anyone who has an interest in reading something that peels back the layers of a very disturbing aspect of Jewish history that might not fit all that well with the notion of Jewish righteousness, then “The Incorruptibles” might be of interest.
“The Incorruptibles: A True Story of Kingpins, Crime Busters, and the Birth of the American Underworld”
By Dan Slater
432 pages
Published by Little, Brown and Company, 2024
Features
Why casinos reject card payments: common reasons
Online casino withdrawals seem simple, yet many players experience unanticipated decreases. Canada has more credit and debit card payout refusals than expected. Delays or rejections are rarely random. Casino rules and technical processes are rigorous. Identity verification, banking regulations, bonus terms, and technological issues might cause issues.
Card payment difficulties can result from insufficient identification verification. Canadian casinos must verify players’ identities before accepting card withdrawals. If documentation are missing, obsolete, or confusing, the request may be stopped or denied until verified.
Banks and card issuers’ gaming policies are another aspect. Some Canadian banks limit or treat online casino payments differently from card refunds. In such circumstances, the casino may recommend a more reliable withdrawal method.
For Canadian players looking to compare bonus terms and payout conditions, check https://casinosanalyzer.ca/free-spins-no-deposit/free-chips. This article explores the main reasons Canadian casinos reject card payouts, from KYC hurdles to bank-specific restrictions, so you know exactly what to watch for.
Verification Issues: Why Identity Checks Matter
KYC rules must be activated by licensed casinos. Players need to submit proof of their identity, address and age. If any documentation is missing, expired or unclear, the withdrawal will be denied. In Canada, for instance, authorities like the AGCO or iGaming Ontario have been cracking down on KYCs by demanding that submitted documents – whether photo ID, utility bills or bank statements – be consistent with all account details.
Common errors are submitting screenshots, cropped photos or documents with names, dates or addresses that aren’t entirely visible. Just the slightest differences in spelling or abbreviations or formatting can get these blocks triggered.
Another possibility is that the account was red flagged if previous withdrawals were already made without partial verification. Keeping precise, readable documents helps facilitate approvals and cuts through delays and frustrating red tape, as Canadian gamblers access their winnings both safely and quickly.
Timing Matters
Verification isn’t always instant. Documents being submitted during the busiest times, or on weekends or holidays can only prolong that approval process, and the withdrawal sitting pre-approved – or refused for that matter – until the casino reviews the paperwork. A lot of players feel disappointment not due to mistakes, but only for that a verification team still hasn’t checked their documents! This can be especially frustrating when winnings come from free chips or bonus play and players are eager to cash out.
Keep personal information current and only submit clear legible files to reduce the processing time. Ensure that any scans or photos are sharp, fully visible and there is no detail missing. Preventing Gaffes With submission guidelines to read over ahead of time and directions for following them exactly, verification issues can often be significantly minimized, avoiding delay in accessing winnings and making the lie down withdrawal process that much smoother at Canadian online casinos.
Banking Restrictions and Card Policies
Not all credit or debit cards are eligible for casino withdrawals. Many Canadian banks restrict transactions related to gambling. For example, prepaid cards, virtual cards, or certain credit cards may allow deposits but block withdrawals. Even if deposits work, a payout can fail if the bank refuses incoming gambling credits.
Cards issued outside Canada can also be declined due to international processing rules. Currency conversion restrictions may prevent a CAD payout to a USD card, depending on the bank’s policies.
Banks keep an eye on abnormal or frequent transactions. Online casinos can flag large or multiple withdrawals as suspicious and in such cases may impose temporary blocks on withdrawals or outright decline the withdrawal until the issuing bank confirms them with its account holder. Contacting your bank in advance will avoid any surprises and make withdrawals go more smoothly. What to consider when using your card in Canada:
- Check if your card type supports gambling withdrawals (prepaid, virtual, and some credit cards may not).
- Confirm whether your bank allows international online casino payouts.
- Be aware of currency conversion restrictions.
- Monitor withdrawal frequency to avoid triggering fraud alerts.
- Contact your bank ahead of time to authorize or clarify online gambling transactions.
- Keep alternative withdrawal methods ready, such as e-wallets or bank transfers.
Being aware of these constraints prevents Canadian players from having declined payouts, delays and waste of time when it comes to handling the casino money properly.
Wagering Requirements and Bonus Conditions
Many Canadians chase casino bonuses, including deals built around free chips, but these offers always come with conditions, Wagering requirements usually require players to bet a multiple of the bonus before withdrawing. Attempting a payout before meeting these conditions will be automatically declined. Not all games contribute equally: slots often count 100%, table games 10–20%, and certain features nothing at all.
Misinterpretation of this, can make it appear as though a withdraw should be valid, while the casino believes there are unmet bonus requirements. Some casinos also impose a minimum withdrawal amount and will cap card payouts. And if you have more than the minimum in your account, a limit set off by your bonus could limit withdrawal. By testing these issues early on, you can save yourself a lot of aggravation. How to manage bonus conditions effectively:
- Have a close look at the terms of the bonus – check out wagering requirements, game contribution and time limits.
- Track your progress – note how much of the bonus has been wagered and which games contribute most.
- Plan your gameplay – prioritize slots or eligible games to efficiently meet wagering.
- Check withdrawal limits – ensure your balance meets minimums and bonus-specific caps.
- Avoid early withdrawals – never attempt a cash-out before meeting all conditions.
- Use trusted sources – platforms like CA CasinosAnalyzer can clarify real requirements and prevent surprises.
Following these steps helps players meet bonus conditions without stress and makes bankroll management smoother.
Features
What is the return on investment of US military spending on Israel?

By GREGORY MASON A recurring theme of Israel’s critics is that were it not for US spending on its war machine, it would be unable to wage genocide. I will leave the genocide issue (sic, I mean non-issue) aside as it has been well covered here and here.
Of course, right now (March 11), the war is going well for Israel and the US. In fact, the Israeli and American air forces are showing a level of coordination enabled by decades of close cooperation between the two militaries. I recall a conversation with an IDF colonel, the commander of a base near Eilat, in 2010, during a mission that gave participants access to high-level military briefings. Tensions between Israel and the US had soured, as they periodically do, and I asked whether this ebb and flow in political posturing affected military operations. The colonel said political leaders come and go, but the cooperation between the Israeli and American militaries is very tight. To quote him, “they need us as much as we need them. We are their eyes and ears in this part of the world.”
Many on both the right and left call for the US to disengage from Israel, especially with respect to defence spending. First, let us look at facts.
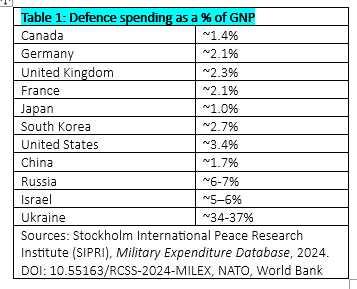
Table 1 readily shows the impact of the war in Ukraine, with Russia’s spending also reflecting wartime demands. Israel’s total commitment of 5-6% of GDP amounts to $45 billion in defence spending, reflecting its perpetual need to defend itself and maintain a permanent reserve force. Table 2 elaborates on defence spending as a share of public spending. Unlike other countries that have been free riding under the US military umbrella (and Canada is the most egregious of the lot), Israel has made very substantial commitments to its own defence. The $3.8 billion spent on hardware for US equipment is a fraction of Israel’s total defence budget of about $43 Billion. All U.S. financial aid to any country for military hardware must be spent on U.S.-manufactured equipment by law.
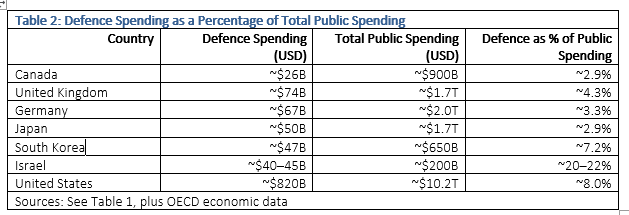
Critics of US defence funding for Israel miss two key points. First, as Table 3 shows, financing sent to Israel does not involve troop deployment. Israel does not want the US to station troops within its borders. The costs of maintaining troop deployments and all the associated support costs for NATO, Japan, and South Korea are orders of magnitude higher than the financing for the hardware it provides to Israel.
Second, and the current joint US/Israeli operations in Iran bear this out, Israel has dramatically improved the equipment platforms it purchased. Examples include:
- The F-15 has benefited from Israeli wartime use, resulting in major improvements, including a redesigned cockpit layout, increased range through fuel redesign, improved avionics, new weaponry, helmet-mounted targeting, and structural strengthening.
- Because Israel was an early partner in the fighter’s development and had access to its top-secret software suite, the Israeli version of the F-35 is a radically different plane than the model delivered. Improvements include increasing operational range, embedding advanced air defence detection, and integrating the fighter with Israel’s defence network, creating extensive system integration. This proved instrumental in the rapid establishment of air superiority in the 12-day war in 2025.
- The THAAD (Terminal High Altitude Area Defence) program has benefited from a joint research and development relationship between Israel and the U.S.
- Finally, Iron Dome has contributed to U.S. air defence development, particularly the Tamir interceptor technology, battle management, target discrimination, and the development of a layered air defence system.
No senior military or political official questions the return on investment American gains by funding Israel’s acquisition of U.S. military hardware.
Features
Why Returning Players Often Stick to a Few Favorite Games on Platforms Like Gransino Casino

Many online casino players develop clear preferences over time, and Gransino Casino highlights how familiar games often become the center of regular play sessions.
Online casinos typically offer large catalogs filled with hundreds of different slot titles. While this variety allows players to explore new experiences, many returning users gradually settle on a smaller group of games that they revisit regularly. This pattern appears across many digital gaming environments, where familiarity often becomes just as important as novelty.
Platforms such as Gransino Casino demonstrate how this behavior emerges in practice. Even though players have access to many different titles, returning visitors frequently gravitate toward games they already know and understand.
Familiar mechanics reduce learning time
One reason players return to the same games is that they already understand how those titles work. Each slot game has its own rules, bonus features, and payout structure. When a player first opens a new title, they often need a few minutes to understand the paytable, special symbols, and feature triggers.
Once that learning process has taken place, the game becomes easier to approach in future sessions. Players do not need to spend time reviewing instructions or exploring unfamiliar mechanics. Instead, they can begin playing immediately with a clear sense of how the game operates.
On platforms like Gransino Casino, this familiarity can make certain titles stand out as reliable choices. When players know what to expect from a game, the experience often feels smoother and more predictable during short play sessions.
Personal preferences shape long-term choices
Another factor influencing player behavior is personal preference. Some players enjoy specific visual themes such as mythology, adventure, or classic fruit machine designs. Others may prefer particular gameplay features, such as free spins, cascading reels, or bonus rounds.
Over time, players tend to identify the games that best match these preferences. Once they find titles that align with their interests, they are more likely to return to those games rather than start the search process again.
This pattern can be seen on Gransino Casino, where players browsing the lobby may explore different titles at first but eventually settle on a smaller group of favorites that suit their individual style.
Habit formation in digital gaming
Habit formation also plays a role in why players repeatedly choose the same games. In many digital environments, users develop routines that guide how they interact with a platform. This behavior is visible across streaming services, mobile games, and online casinos.
Once a player has established a routine, returning to familiar content often becomes part of that pattern. For example, a player might log in and immediately open the same slot they played during previous sessions. The familiarity of the interface, symbols, and features can make the experience feel more comfortable.
Platforms like Gransino Casino support this behavior by maintaining consistent game availability and allowing players to locate previously played titles easily within the lobby.
Exploration still remains part of the experience
Although many players develop favorite games, exploration remains an important part of the online casino experience. New titles continue to appear on casino platforms, introducing different mechanics, themes, and visual styles.
Players often alternate between their familiar choices and occasional experimentation with new games. A player might return to a favorite slot for most sessions while occasionally trying recently released titles to see if they offer something interesting.
The wide selection available on Gransino Casino allows this balance between familiarity and discovery. Players can continue returning to the games they enjoy while still having the option to explore new additions within the platform’s catalog.
Ultimately, the tendency to revisit favorite games reflects how players build their own routines within digital entertainment environments. Familiar titles offer a comfortable starting point, while new releases provide opportunities for occasional exploration, creating a mix of consistency and variety within each player’s experience.




