Uncategorized
A scholar sees a common root for antisemitism and racism: ‘Christian supremacy’
(JTA) — Magda Teter’s new book, “Christian Supremacy,” begins in Charlottesville, Virginia, on Aug. 11, 2017. Hundreds of white nationalist neo-Nazis who ostensibly gathered to protest the removal of a statue of Confederate general Robert E. Lee from a local park broke into a chant: “Jews will not replace us.”
Other writers and scholars would note how antisemitism shaped white nationalism. But Teter, professor of history and the Shvidler Chair of Judaic Studies at Fordham University, saw something else: how centuries of Christian thought and practice fed the twin evils of antisemitism and racism.
“The ideology espoused by white supremacists in the US and in Europe is rooted in Christian ideas of social and religious hierarchy,” she writes. “These ideas developed, gradually, first in the Mediterranean and Europe in respect to Jews and then in respect to people of color in European colonies and in the US, before returning transformed back to Europe.”
In the book, subtitled “Reckoning with the Roots of Antisemitism and Racism,” she traces this idea from the writings of the early church fathers like Paul the Apostle, though centuries of Catholic and Protestant debates over the status of Jews in Europe, to the hardening of racist attitudes with the rise of the trans-Atlantic slave trade.
Antisemitic laws and theology, she argues, developed within Christianity a “mental habit” of exclusion and dominance that would eventually be applied to people of color up to and including modern times.
Teter is careful to acknowledge the different forms antisemitism and racism have taken, distinguishing between the Jews’ experience of social and legal exclusion and near annihilation, and the enslavement, displacement and ongoing persecution of Black people. And yet, she writes, “that story began with Christianity’s theological relation with Jews and Judaism.”
Teter is previously the author of “Blood Libel: On The Trail of an Antisemitic Myth,” winner of the 2020 National Jewish Book Award. At Fordham, the Catholic university in the Bronx, she is helping assemble what may be the largest repository of artifacts and literature dedicated to the Jewish history of the borough.
We spoke Thursday about how groups like the Proud Boys embrace centuries-old notions of Christian superiority, how “whiteness” became a thing and how she, as a non-Jew raised in Poland, became a Jewish studies scholar.
Our conversation was edited for length and clarity.
Your book was conceived and written during the COVID lockdown. Where did the idea for the book come from?
It’s an accidental project. I’ve been teaching the history of antisemitism for years, and I live in Harlem so questions of race and racism are very stark in my daily life. And since I grew up in Poland, and American history was not something we were taught or studied, I’ve never been satisfied with the various explanations for the strength of antisemitism and history of racism. And as I mentioned in my prologue, I watched the Raoul Peck documentary, “I Am Not Your Negro,” which has a clip with James Baldwin saying that white people have to figure out why they invented the idea of the N-word and must “embrace this stranger that they have maligned so long.” You could also say that the European Christians created the idea of “the Jew” and that sort of caricature had absolutely nothing to do with flesh and blood Jews. I kept noticing these parallels, as an outsider, reading American and African-American history.
I was also thinking about this idea of servitude that was attached to Jews in Christian theology, and then in law.
You write in your book that “Over time, white European Christians branded both Jews and people of color with ‘badges of servitude’ and inferiority.” What do you mean by servitude in this context?
In Christian theology, from the earliest Christian texts, the idea of servitude and slavery is attached to the concept of Jews and Judaism. Paul does it in his Epistles. He uses this quote from the book of Genesis that “the elder shall serve the younger,” which becomes really embedded in Christian theology. It is the Jews, the elder people, who should serve the Christians, the younger people. Later on in medieval theology and canon law, Jews are in a servile position, consigned for their sin of rejecting Jesus to perpetual servitude. So even though Jews were free people and could live mostly where they wanted to live, marry whoever they wanted to marry — nobody was sold and some even had slaves — that idea of Jews as confined to perpetual servitude to Christians created a habit of thinking of Jews as having an inferior social status.
That language became secularized in modern times, and we see the development of the [antisemitic] trope of Jewish power: that they are in places where they shouldn’t be. I worked on fleshing out the parallels between the idea and then legal status of Jewish servitude and the conceptual perception of Black people in servile and inferior positions.
Magda Teter’s new book explores how “white European Christians branded both Jews and people of color with ‘badges of servitude’ and inferiority.” (Chuck Fishman)
What other kinds of parallels did you find between racism and antisemitism?
In the Christian theology, Black people, like Jews, will be seen as cursed by God. Jews were [portrayed as] lazy because they didn’t work physically — they made money and exploited Christians. Black people were [portrayed as] lazy because they were trying to avoid physical labor at the expense of white men. Both people were seen as carnal, both as sexually dangerous, and so on.
I was struck by the fact that the racist turn of Christian supremacy — justifying the enslavement of Black people on theological grounds — is a fairly late development, taking hold in the early modern period when Europeans established slaveholding empires.
That’s right. In the summer of 2020, the summer of George Floyd and Black Lives Matter, we were all thinking about these issues of race and racism and America. And as I was in the middle of writing the article that became the book, I felt that there was a deeper history that needed to be told, and that slavery is not bound by color until the enslavement of Black Africans by Europeans during the colonial expansion of Europe.
After the French Revolution, when Jews were offered “emancipation” in much of Europe, there were deep debates about whether they could be citizens and be entitled to the same rights and protections as Christian citizens of France and England and other countries. How was that debate informed by Christianity?
In pre-modern Europe, there was obviously both a religious and legal framework under which Jews existed. They had their place in a social hierarchy. After the French Revolution, people are creating a new political reality. The idea of equality obviously challenged the social hierarchies that existed, including the idea that Christians were the superior religion. And that begins to play a role on two levels. One is the level of, well, “how can you be equal and be our judges and make decisions about us?” It’s fear of power — political power and political equality. That challenges the habit of thinking that sees Jews as inferior, in servitude and otherwise insolent and arrogant.
The other level comes from Enlightenment scholars who begin to place Jews in the Middle East and in the Holy Land, in Palestine. Jews are no longer seen as European. They are seen as “Oriental,” and they are compared to the non-European religions and practices that these Enlightenment scholars have been studying. Their differences are now also racialized. “They are not like us, they can’t assimilate. They can never be Frenchmen, they can never be Germans.”
And I guess it’s a short step from that to regarding people with dark skin as inferior and subordinate.
That’s right. Enlightenment scholars are also trying to to understand why it is justified to enslave Black Africans and they do it through “scientific” and other means. They classify Africans as inferior intellectually and they create this idea of race.
I began to think about these European politicians and intellectuals in terms of creating their identities, and what I ended up arguing is what we saw in Charlottesville, what we’re seeing in Europe. It’s not necessarily just about hate, but it’s about exclusion and rejection of Jews and people of color from equality, from citizenship.
And the common thread here is that whiteness and Christianity become inseparable. You write that “freedom and liberty now came to be linked not only to Christianity, but to whiteness, and servitude and enslavement to blackness.”
That’s right. White Christian “liberty” becomes embedded and embodied in law.
Did you see any pitfalls in drawing parallels between the Black and Jewish experiences? I am thinking of those in either community who might say, “How dare you compare our suffering to theirs!”
Yes, I was tempered. I think what some call “comparative victimhood” has paralyzed conversations about this subject, and I kept it in my mind all the time. What I hope comes through is that there’s incredible value in a comparative approach. Coming from Jewish studies as my primary field, the comparison with the Black experience gave me clarity on the nature of antisemitism as well as on the nature of the Jewish experience, and vice versa: The Jewish experience can also give clarity to some of the aspects of anti-Black racism.
What’s an example?
So, for instance, questions like, “Are Jews white? Are they not white? When did they become white?” That’s a whole genre of scholarship. And when you look at it through the lens of law and ideology, you begin to see that from a legal perspective, Jews were considered white in the United States because they could immigrate and they could be naturalized according to law. They did not have to go to court to become American. Their rights to vote were not challenged. There was discrimination, they couldn’t stay in hotels and in some places they couldn’t find employment, but by law, they were considered citizens. The debate about the whiteness of Jews is creating a fog of misunderstanding.
Black Americans were targeted by specific legal statutes from the very beginning in the Constitution and then in naturalization law and so on. And then there was the backlash even after the Civil War to the 13th, 14th and 15th amendments [aimed at establishing political equality for Americans of all races].
Statues at the Strasbourg Cathedral depict Ecclesia and Synagoga, representing the triumph of the church, at left, and the servitude of Judaism, which is represented by a blindfolded figure, drooping and carrying a broken lance. (Edelseider/Wikimedia Commons)
How much do modern-day white supremacists, like the Oath Keepers or the Proud Boys, see themselves as Christian? Or is this a kind of white supremacy that doesn’t name itself Christian but doesn’t even realize how many of its ideas are based in theology?
I think they might not be conscious of this legacy, but neo-Nazis take from the legacy of the Nazis who themselves were not thinking of themselves as Christian necessarily. But what I argue in the book is that white Christian supremacy becomes white supremacy. It never discards the Christian sense of domination and superiority that emerges from its early relationship with Jews and Judaism.
In the United States, Black people serve as contrast figures to whiteness, in the law and in the culture. You cannot have whiteness without Blackness. For Christians, Jews serve as that contrast figure. Consciously or unconsciously, the Proud Boys are embracing that. They talk of “God-given” freedoms for white people. That is the Christian legacy.
You said that the Nazis didn’t necessarily see themselves as a Christian movement. But I must ask, even though it is not the scope of your book, was the Holocaust a culmination of white Christian supremacy? Because I think many Christian theologians would want to say that Nazism was godless, and a perversion of the true faith.
I’ll say that when exclusionary ideology is coupled with the power of the state, that’s where it can lead.
In the years since the Holocaust especially, there have been many efforts by Christian leaders to address the ideological failings of the past. You write about Nostra Aetate, the 1965 declaration by the Catholic Church absolving Jews of collective guilt in the death of Jesus and some Protestant documents of contrition. But I got the feeling you were disappointed that many denominations haven’t gone far enough in reckoning with the past.
There was a sort of a moral sense that something needs to be addressed after the Holocaust. But then it is not fully addressed. I don’t think anybody has addressed the issue of power — the roots of hate, yes, but not the dynamics of power. We’ll see where the book goes, but maybe theologians will begin to grapple with this legacy of superiority and domination, and the way hierarchical habits of thinking have been developed through theology and through religious culture.
What other impact do you hope the book may have?
White supremacy is very much in the air. We need to speak up against it, and make connections and allyships. I hope that maybe because the book deals with law and power, it may create bridges among people who care about “We the People” as a vision of people who are diverse, respectful and equal, and not the exclusionary vision offered by white and Christian supremacy.
A cross burns at a Ku Klux Klan rally on Aug. 8, 1925. (National Photo Company Collection)
I’d love to talk about your background. You’re not Jewish but you are chair of Jewish Studies at Fordham, a Catholic university. What drew you to the study of Judaism and the Jews?
I grew up in Poland with a father who from the time I was a little girl would point out to me that there had been Jews in Poland. We would drive through the countryside, and he’d say, “This used to be a Jewish town and there used to be a synagogue and there was the Jewish cemetery.” I grew up being very conscious of the past’s presence and this kind of stark absence of Jews in Poland, where in the 1970s when I grew up Jewish history was taboo.
As soon as Jewish books on Jewish subjects began to be published, including those that dealt with antisemitism, we would read it together. We would talk about it. He wouldn’t just shift the destruction and murder of Jews in Poland on to the Nazis.
There was no Jewish studies program in Poland when I was applying to universities, so I studied Hebrew in Israel, and then studied Yiddish in New York at YIVO. I came to Columbia University to get my PhD in Jewish history and my career went in the direction it did. I was a professor of history and director of the Jewish and Israel studies program at Wesleyan University. I came to Fordham eight years ago and created a program in Jewish studies.
Your previous book was about the blood libel, the historic canard that Jews murdered Christian children to use their blood. This one’s about antisemitism. I don’t want to presume, but is your interest in these subjects in any way an act of contrition?
I grew up in a very secular household. I did not grow up Catholic. But I think growing up in Poland made me very, very aware of antisemitism and the history of antisemitism. I got my PhD from Columbia University in Jewish history, which did not emphasize Jewish suffering, but Jewish life, and I have studied Jewish life and teach about Jewish life — not just about Jewish suffering.
However, in the last few years, antisemitism has certainly been on the minds of many of us. I also am committed to the idea of shared history, and therefore all my scholarship, as much as it is about Jews, it is also about the church and Poland and the law. Jews are an integral part of that history and culture. And, as such, I’m committed to that, to teaching about the vibrancy of Jewish life as much as the dynamics of what made that life difficult over the centuries.
—
The post A scholar sees a common root for antisemitism and racism: ‘Christian supremacy’ appeared first on Jewish Telegraphic Agency.
Uncategorized
How the Global Religious Landscape Changed from 2010 to 2020

Muslims grew fastest; Christians lagged behind global population increase
• Christians are the world’s largest religious group, at 28.8% of the global population. They are a majority everywhere except the Asia-Pacific and Middle East-North Africa regions. Sub-Saharan Africa has surpassed Europe in having the largest number of Christians. But Christians are shrinking as a share of the global population, as millions of Christians “switch” out of religion to become religiously unaffiliated.
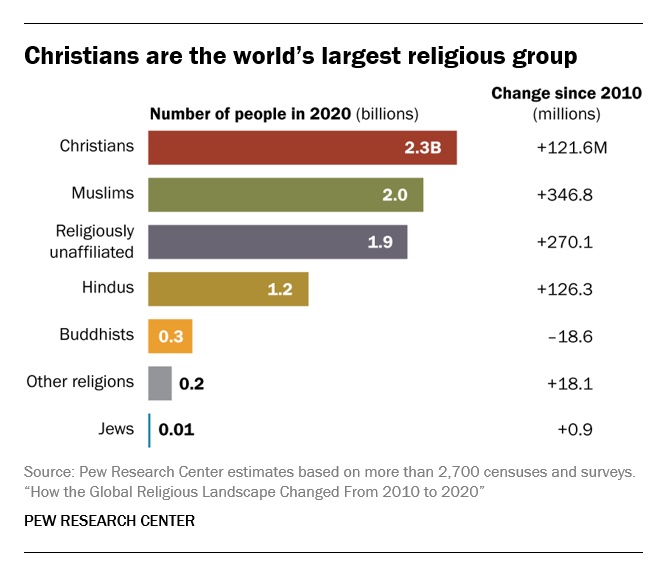
• Muslims are the world’s second-largest religious group (25.6% of the world’s population) and the fastest-growing major religion, largely due to Muslims’ relatively young age structure and high fertility rate. They make up the vast majority of the population in the Middle East-North Africa region. In all other regions, Muslims are a religious minority, including in the Asia-Pacific region (which is home to the greatest number of Muslims).
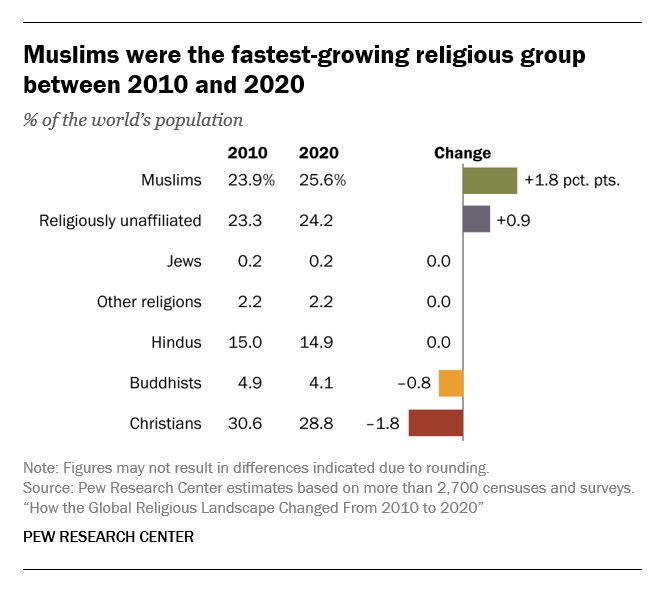
• The religiously unaffiliated population is the world’s third-largest religious category (24.2% of the global population), after Christians and Muslims. Between 2010 and 2020, religiously unaffiliated people grew more than any group except Muslims, despite their demographic disadvantages of an older age structure and relatively low fertility. The unaffiliated made up a majority of the population in 10 countries and territories in 2020, up from seven a decade earlier.
• Hindus are the fourth-largest religious category (14.9% of the world’s population), after Christians, Muslims and religiously unaffiliated people. Most (99%) live in the Asia-Pacific region; 95% of all Hindus live in India alone. Between 2010 and 2020, Hindus remained a stable share of the world’s population because their fertility resembles the global average, and surveys indicate that switching out of or into Hinduism is rare.
• Buddhists (4.1% of the world’s population) are the only group in this report whose number declined worldwide between 2010 and 2020. This was due both to religious disaffiliation among Buddhists in East Asia and to a relatively low birth rate among Buddhists, who tend to live in countries with older populations. Most of the world’s Buddhists (98%) reside in the Asia-Pacific region, the birthplace of Buddhism.
• Jews, the smallest religious group analyzed separately in this report (0.2% of the world’s population), lagged behind global population growth between 2010 and 2020 – despite having fertility rates on par with the global average – due to their older age structure. Most Jews live either in North America (primarily in the United States) or in the Middle East-North Africa region (almost exclusively in Israel).
These are among the key findings of a Pew Research Center analysis of more than 2,700 censuses and surveys, including census data releases that were delayed due to the coronavirus pandemic. This report is part of the Pew-Templeton Global Religious Futures project, which analyzes global religious change and its impact on societies around the world. Funding for the Global Religious Futures project comes from The Pew Charitable Trusts and the John Templeton Foundation.
Uncategorized
Antisemitism in some unlikely places in America

By HENRY SREBRNIK Antisemitism flourishes in a place where few might expect to confront it – medical schools and among doctors. It affects Jews, I think, more emotionally than Judeophobia in other fields.
Medicine has long been a Jewish profession with a history going back centuries. We all know the jokes about “my son – now also my daughter – the doctor.” Physicians take the Hippocratic Oath to heal the sick, regardless of their ethnicity or religion. When we are ill doctors often become the people who save us from debilitating illness and even death. So this is all the more shocking.
Yes, in earlier periods there were medical schools with quotas and hospitals who refused or limited the number of Jews they allowed to be affiliated with them. It’s why we built Jewish hospitals and practices. And of course, we all shudder at the history of Nazi doctors and euthanasia in Germany and in the concentration camps of Europe. But all this – so we thought – was a thing of a dark past. Yet now it has made a comeback, along with many other horrors we assume might never reappear.
Since the Hamas attack on Israel on October 7, 2023, there has been a resurgence of antisemitism, also noticeable in the world of healthcare. This is not just a Canadian issue. Two articles on the Jewish website Tablet, published Nov. 21, 2023, and May 18, 2025, spoke to this problem in American medicine as well, referencing a study by Ian Kingsbury and Jay P. Greene of Do No Harm, a health care advocacy group, based on data amassed by the organization Stop Antisemitism. They identified a wave of open Jew-hatred by medical professionals, medical schools, and professional associations, often driven by foreign-trained doctors importing the Jew-hatred of their native countries, suggesting “that a field entrusted with healing is becoming a licensed purveyor of hatred.”
Activists from Doctors Against Genocide, American Palestinian Women’s Association, and CODEPINK held a demonstration calling for an immediate cease-fire in Gaza at the Hart Senate Office Building in Washington, D.C., Nov. 16, 2023, almost as soon as the war began. A doctor in Tampa took to social media to post a Palestinian flag with the caption “about time!!!” The medical director of a cancer centre in Dearborn, Michigan, posted on social media: “What a beautiful morning. What a beautiful day.” Even in New York, a physician commented on Instagram that “Zionist settlers” got “a taste of their own medicine.” A Boston-based dentist was filmed ripping down posters of Israeli victims and a professor at the University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine did the same. Almost three-quarters of American medical associations felt the need to speak out on the war in Ukraine but almost three-quarters had nothing to say about the war in Israel.
Antisemitism in academic medical centres is fostering noxious environments which deprive Jewish healthcare professionals of their civil right to work in spaces free from discrimination and hate, according to a study by the Data & Analytics Department of StandWithUs, an international, non-partisan education organization that supports Israel and fights antisemitism.
“Academia today is increasingly cultivating an environment which is hostile to Jews, as well as members of other religious and ethnic groups,” StandWithUs director of data and analytics, and study co-author, Alexandra Fishman, said on May 5 in a press release. “Academic institutions should be upholding the integrity of scholarship, prioritizing civil discourse, rather than allowing bias or personal agendas to guide academic culture.”
The study, “Antisemitism in American Healthcare: The Role of Workplace Environment,” included survey data showing that 62.8 per cent of Jewish healthcare professionals employed by campus-based medical centres reported experiencing antisemitism, a far higher rate than those working in private practice and community hospitals. Fueling the rise in hate, it added, were repeated failures of DEI (diversity, equity, and inclusion) initiatives to educate workers about antisemitism, increasing, the report said, the likelihood of antisemitic activity.
“When administrators and colleagues understand what antisemitism looks like, it clearly correlates with less antisemitism in the workplace,” co-author and Yeshiva University professor Dr. Charles Auerbach reported. “Recognition is a powerful tool — institutions that foster awareness create safer, more inclusive environments for everyone.”
Last December, the Data & Analytics Department also published a study which found that nearly 40 per cent of Jewish American health-care professionals have encountered antisemitism in the workplace, either as witnesses or victims. The study included a survey of 645 Jewish health workers, a substantial number of whom said they were subject to “social and professional isolation.” The problem left more than one quarter of the survey cohort, 26.4 per cent, “feeling unsafe or threatened.”
The official journal of the Alliance for Academic Internal Medicine concurs. According to “The Moral Imperative of Countering Antisemitism in US Medicine – A Way Forward,” by Hedy S. Wald and Steven Roth, published in the October 2024 issue of the American Journal of Medicine, increased antisemitism in the United States has created a hostile learning and practice environment in medical settings. This includes instances of antisemitic behaviour and the use of antisemitic symbols at medical school commencements.
Examples of its impact upon medicine include medical students’ social media postings claiming that Jews wield disproportionate power, antisemitic slogans at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) David Geffen School of Medicine, antisemitic graffiti at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) Cancer Centre, Jewish medical students’ exposure to demonization of Israel diatribes and rationalizing terrorism; and faculty, including a professor of medicine at UCSF, posting antisemitic tropes and derogatory comments about Jewish health care professionals. Jewish medical students’ fears of retribution, should they speak out, have been reported. “Our recent unpublished survey of Jewish physicians and trainees demonstrated a twofold increase from 40% to 88% for those who experienced antisemitism prior to vs after October 7,” they stated.
In some schools, Jewish faculty are speaking out. In February, the Jewish Faculty Resilience Group at UCLA accused the institution in an open letter of “ignoring” antisemitism at the School of Medicine, charging that its indifference to the matter “continues to encourage more antisemitism.” It added that discrimination at the medical school has caused demonstrable harm to Jewish students and faculty. Student clubs, it said, are denied recognition for arbitrary reasons; Jewish faculty whose ethnic backgrounds were previously unknown are purged from the payrolls upon being identified as Jews; and anyone who refuses to participate in anti-Zionist events is “intimidated” and pressured.
Given these findings, many American physicians are worried not only as Jewish doctors and professionals, but for Jewish patients who are more than ever concerned with whom they’re meeting. Can we really conceive of a future where you’re not sure if “the doctor will hate you now?”
Henry Srebrnik is a professor of political science at the University of Prince Edward Island.
Uncategorized
The 2025 Toronto Walk (and talk ) for Israel
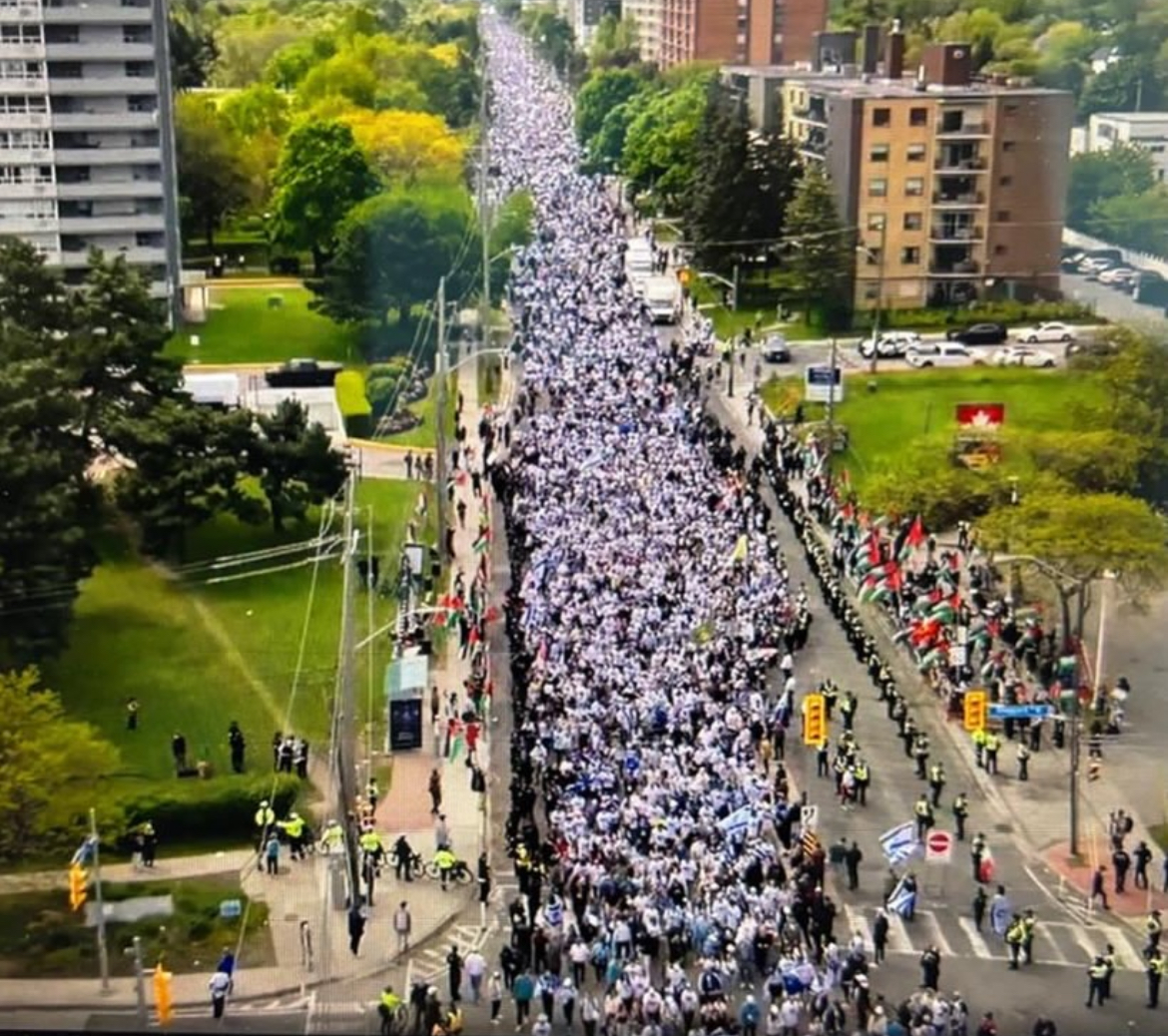

By GERRY POSNER There are walks and then there are walks. The Toronto UJA Walk for Israel on May 25, 2025 was one of a kind, at least as far as Canada and Jews are concerned. The number of people present was estimated to be 56,000 people or 112,000 total shoes. (How they get to that number is bewildering to me, since there is no one counting). This was 6,000 more than last year. Whether it is true or not, take it from me, it was packed. The synagogues in Canada should be so fortunate to get those numbers in total on High Holidays. The picture here gives you a sense of the size of the crowd.

This was my first walk in Toronto for Israel and I was with my granddaughter, Samantha Pyzer (not to forget her two friends whom she managed to meet at the site, no small feat, even with iPhones as aids). The official proceedings began at 9:00 a.m. and the walk at 10:00 a.m. There was entertainment to begin with, also along the way, and at the finish as well. The finish line this year was the Prosserman Centre or the JCC as it often called. The walk itself was perhaps 4 kilometres – not very long, but the walking was slow, especially at the beginning. There were lots of strollers, even baby carriages, though I did not see any wheelchairs. All ages participated on this walk. I figured, based on what I could see on the faces of people all around me that, although I was not the oldest one on the walk, I bet I made the top 100 – more likely the top 20.
What was a highlight for me was the number of Winnipeggers I met, both past and present. Connecting with them seemed to be much like a fluke. No doubt, I missed la lot of them, but I saw, in no particular order (I could not recall the order if my life depended on it): Alta Sigesmund, (who was, a long time ago, my daughter Amira’s teacher), Marni Samphir, Karla Berbrayer and her husband Dr. Allan Kraut and family. Then, when Samantha and I made it to the end and sat down to eat, I struck up a conversation with a woman unknown to me and as we chatted, she confirmed her former Winnipeg status as a sister-in- law to David Devere, as in Betty Shwemer, the sister of Cecile Devere. I also chanced upon Terri Cherniack, only because I paused for a moment and she spotted me. As we closed in near the finish, I met ( hey were on their way back), Earl and Suzanne Golden and son Matthew, as well as Daniel Glazerman. That stop caused me to lose my granddaughter and her pals. Try finding them amid the noise and size of the crowd – but I pulled it off.
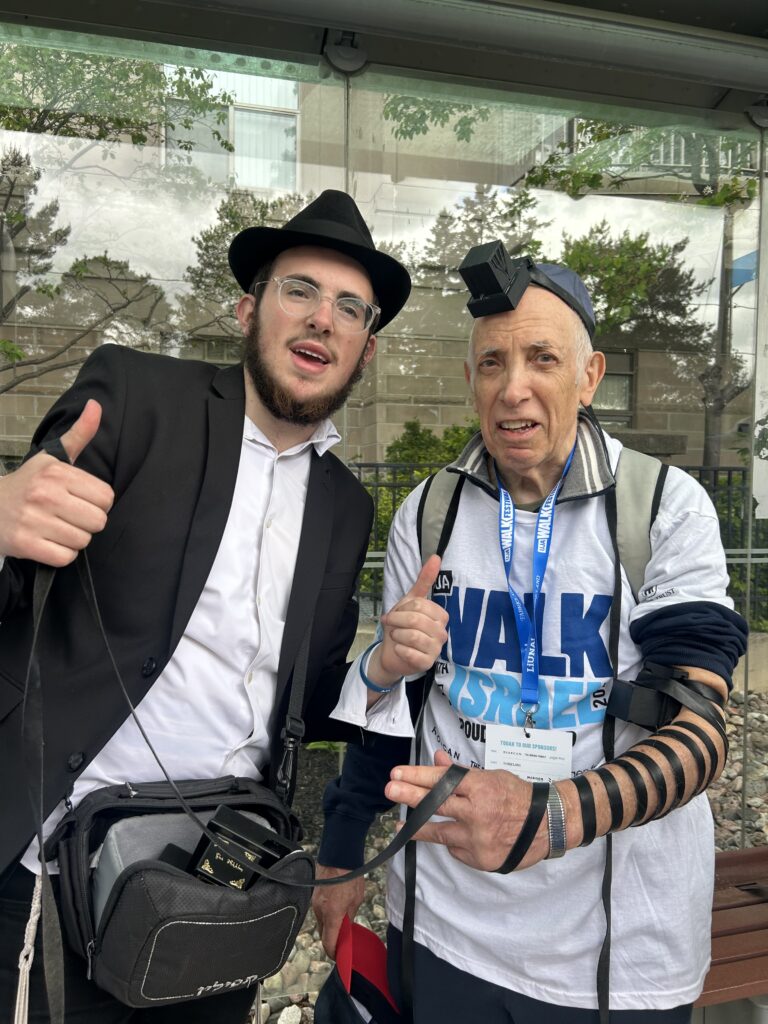

As I was in line to get food, I started chatting with a guy in the vicinity of my age. I dropped the Winnipeg link and the floodgates opened with “ Did I know Jack and Joanie Rusen?” So that was an interesting few minutes. And I was not too terribly surprised to come across some of my Pickleball family. All of these meetings, along with spotting some of my sister’s family and other cousins, were carried on with the sound of the shofar as we moved along the way. In short, this was a happening. Merchants selling a variety of products, many of them Israeli based, were in evidence and, of course, the day could not have ended without the laying of tefillin, aided by Chabad, who have perfected the procedure to take less than a minute. See the photo. Chabad had a willing audience.
Aside from the joy of sharing this experience with my granddaughter, the very presence of all these Jews gathered together for a common reason made this day very special to me. However, there was a downside to the day. The downside was that, as we began to walk back to our car there was no other way I could figure out how to return when the rains came and came. While we walked faster, we were impeded by pouring rain and puddles. But Samantha wanted to persevere, as did I. We made it, but were drenched. My runners are still drying out as I write this two days later.
What with being surrounded by 56,000 people, the noise, the slow walking, and the rain, I can still say the day was a real highlight for me – one of the better moments since our arrival in Toronto in 2012. As well as the photos we took along the way, I have the reminder of the day, courtesy of the UJA, as evidenced from the photo. It was not just the walk, but the talk that accompanied the walk that made it so worthwhile for me. I would do it again, minus the rain.
