Uncategorized
In Galveston, descendants of a forgotten Jewish migration keep their community’s story alive
(JTA) — GALVESTON, Texas – More than a century ago, this busy Gulf Coast port and longtime vacation destination 50 miles southeast of Houston welcomed so many European immigrants – including some 10,000 Jews – it earned the moniker “The Ellis Island of the West.”
Today, the few remaining descendants of Jewish immigrants from that time period still living on the island are determined to preserve and nourish the story of the Galveston Movement, a mostly forgotten but pivotal chapter in Jewish-American history.
Galveston, an island-city of 53,000 residents, is the fourth-busiest cruise port in the country and the birthplace of the Juneteenth holiday, which commemorates the end of slavery in the United States. With 32 miles of brown-sand beaches, a charming historic district with numerous well-preserved Victorian-era homes, and some 80 festivals held year-round, the island annually attracts 8 million tourists.
It also offers visitors several sites related to the Galveston Movement and what was once a robust Jewish community that produced five mayors, prominent business leaders and two highly renowned rabbis.
The Galveston Movement, also called the Galveston Plan, was a humanitarian effort operated by several Jewish organizations that brought Jewish immigrants from Czarist Russia and Eastern Europe through the port of Galveston between 1907 and 1914. Most arrived in Galveston on steamships from Bremen, Germany, a transatlantic trip that took two to three weeks.
A recent book by English historian and journalist Rachel Cockerell — “Melting Point” — has helped reignite interest in the Galveston Movement. Cockerell, whose great-grandfather David Jochelmann played a key role in organizing the program in Europe, spoke this month at Galveston’s Temple B’nai Israel as part of a U.S. tour promoting the book.
“As soon as started reading about the Galveston Movement, I sort of went down a rabbit hole from which I didn’t emerge for three years,” Cockerell told a group of more than 100 Galvestonians, Jews and non-Jews alike. “I was totally transfixed by this amazing story of Jewish immigration in the early 20th century.”
“I love it,” says Shelley Nussenblatt Kessler, 74, of the heightened attention on the Galveston Movement. Kessler estimates she is one of 25 to 30 “BOIs” — shorthand for “Born on the Island”) — still living in Galveston who are descendants of the Jewish immigrants who came to America as part of the program. Her grandmother and grandfather immigrated from what is now western Ukraine to Galveston in 1910 and 1911.
“Not only am I very proud to be a descendant of two of these immigrants, but I can’t help but think of how lucky I am to be here,” she said. “I’m in awe of what my grandparents did and how they got here, and the sacrifices that they made.”
By the late 1880s, thousands of Jews began fleeing their homes in the Russian Empire to escape antisemitic policies and violent pogroms. Many immigrated to New York and other East Coast cities, resulting in overcrowding and poverty.
Jacob Schiff, a New York banker and philanthropist, financed the Galveston Movement as a way to blunt an anticipated wave of antisemitism on the Eastern seaboard, which might lead to immigration restrictions. Schiff sought to find suitable alternative destinations in the American South for the influx of Jewish immigrants.
Charleston, South Carolina, which had a long-established Jewish community, was considered but city leaders there only wanted Anglo-Saxon immigrants. New Orleans was also in the mix but there were concerns about periodic outbreaks of yellow fever.
Enter Galveston, a port that checked all of the boxes. It had a deep-water harbor that could accommodate large ships and an extensive railroad system available to transport immigrants to other cities and towns.
“Really the purpose of Galveston was to channel the immigrants into other parts of Texas and up the middle of the country west of the Mississippi,” said Dwayne Jones, a historian who is CEO of the Galveston Historical Foundation.
Jones says there was another key reason Galveston was selected: There already was a well established Jewish community that was thriving in the city’s business and political circles. In fact, Galveston had elected its first Jewish mayor — Dutch-born Michael Seeligson — as far back as 1853.
“It was a more tolerant community with a depth of diversity you didn’t see in other places,” Jones said. “It also had a long history of Jewish leadership and activities in Galveston.
The first Reform congregation in Texas, Galveston’s Congregation B’nai Israel, was established in 1868. Twenty years later, London-born Henry Cohen, who was only 25 at the time, became the congregation’s rabbi. Cohen led B’nai Israel for a remarkable 64 years until his death in 1952. It’s believed to be the longest tenure of a rabbi at the same congregation in U.S. history.
In 1900 Galveston was decimated by a storm known as the Great Galveston Hurricane. It remains the deadliest natural disaster in American history, with an estimated 8,000 fatalities, about 20% of its population at the time. Two-thirds of the island’s buildings and homes were destroyed. Cohen and other Jewish leaders played a major role in the relief and reconstruction efforts that followed.
“Jewish leadership took a really powerful role in rebuilding the island,” says Jones. “Without that leadership, I don’t think Galveston would have come back as it did.”
Seven years after the hurricane, the first ship that was part of the Galveston Movement – the S.S. Cassel — arrived from Bremen with 86 Jewish passengers. Cohen – who was proficient in 10 languages — was the humanitarian face of the movement, meeting ships at the Galveston docks and helping guide the immigrants through the cumbersome arrival and distribution process.
The arrivals were processed at the Jewish Immigrants’ Information Bureau headquarters in Galveston, which gave the immigrants rations and railroad tickets to more than 150 towns in Texas and other places west of the Mississippi River.
Unlike a vast majority of the immigrants who had only a brief stopover in Galveston before settling in other communities, Kessler’s grandparents decided to remain on the island. Her grandfather was a painting contractor while her grandmother worked as a housekeeper.
Adjusting to life in Texas proved to be a struggle for many immigrants. Kessler’s grandparents decided they would be happier back in Europe, even buying passage on a ship so they could return to their homeland. But World War I broke out, canceling their trip.
“The harbormaster told my grandparents to hold their tickets until after the war, and if you want to go back, we’ll redeem them,” Kessler said. “Thank God, they didn’t go back.”
By 1914, declining economic conditions and a surge in nativism and xenophobia — a forerunner of today’s anti-immigration climate — brought an end to the Galveston Movement. Still, the program resulted in an estimated 10,000 persecuted Jews finding new homes in the American hinterland in places few had imagined.
The Galveston Historic Seaport Museum chronicles the immigrant experience in an interactive exhibit called “Ship to Shore.” The exhibit includes a prominent photo of Henry Cohen. Computer terminals enable visitors to search for information taken from ships’ passenger manifests pertaining to their ancestors’ arrival in Texas. The Galveston County Museum, located inside the county courthouse, also features artifacts related to the Galveston Movement.
Kessler’s late husband Jimmy, who died in 2022, was another key figure in Galveston’s Jewish history. Jimmy Kessler served as B’nai Israel’s rabbi for 32 years until his retirement in 2014. He also was the founder and first president of the Texas Jewish Historical Society, which is now 45 years old and has more than 1,000 members.
Jimmy Kessler was devoted to telling the story of the Galveston Movement, writing three books about the area’s Jewish history, including a biography of Henry Cohen called “The Life of a Frontier Rabbi.” The street on which B’nai Israel is located was renamed Jimmy Kessler Drive in 2018, honoring his service to the congregation and the greater Galveston community.
“I’m married to a street,” joked Shelley Kessler, adding, “Jimmy, with what he did to preserve Texas Jewish history, kept all of this [the Galveston Movement] in the forefront.”
B’nai Israel, which now has a membership of 125 families, relocated to a new building in 1955, named the Henry Cohen Memorial Temple.
The congregation’s original synagogue – built in 1870 – was the spiritual launching point for the Jewish immigrants who were part of the Galveston Movement. It still stands on Kempner Street (named after a prominent Jewish family that included Mayor Isaac Kempner) in downtown Galveston. The building is now a private residence. Galveston also has a small Conservative synagogue, Congregation Beth Jacob, that was founded in 1931.
Robert Goldhirsh, 75, former president of Congregation B’nai Israel and another descendant of immigrants from the Galveston Movement, has been the caretaker of the Hebrew Benevolent Society Cemetery for the past three decades. Several hundred Jews — some of whom came to America in the Galveston Movement — are buried in the cemetery. Henry Cohen also is interred there.
Both Goldhirsh and Kessler say that despite perceptions of deep-rooted intolerance in Texas, they’ve encountered little to no antisemitism in Galveston.
“Most of the people I know, it makes no difference that I’m Jewish,” Goldhirsh said. “We’re just Galvestonians.”
Indeed, Goldhirsh says the biggest threat to Jewish life on the island comes from Mother Nature. With climate change a contributing factor, recent years have seen a significant rise in weather-related disasters in Texas. For instance, Hurricane Ike in 2008 led to widespread flooding on Galveston Island and caused water damage in both synagogues.
“During one of the High Holiday services, there was a hurricane headed this way and we had to cancel for fear that the congregants would be caught in a bad storm,” he recalled. “You have to listen to the weather reports. If they say ‘leave,’ you better leave.”
The post In Galveston, descendants of a forgotten Jewish migration keep their community’s story alive appeared first on The Forward.
Uncategorized
Mamdani’s Wife Liked Posts Celebrating October 7. Why Didn’t the Media Ask Harder Questions?

Zohran Mamdani is sworn in as mayor of New York City at Old City Hall Station, New York, US, Jan. 1, 2026. Photo: Amir Hamja/Pool via REUTERS
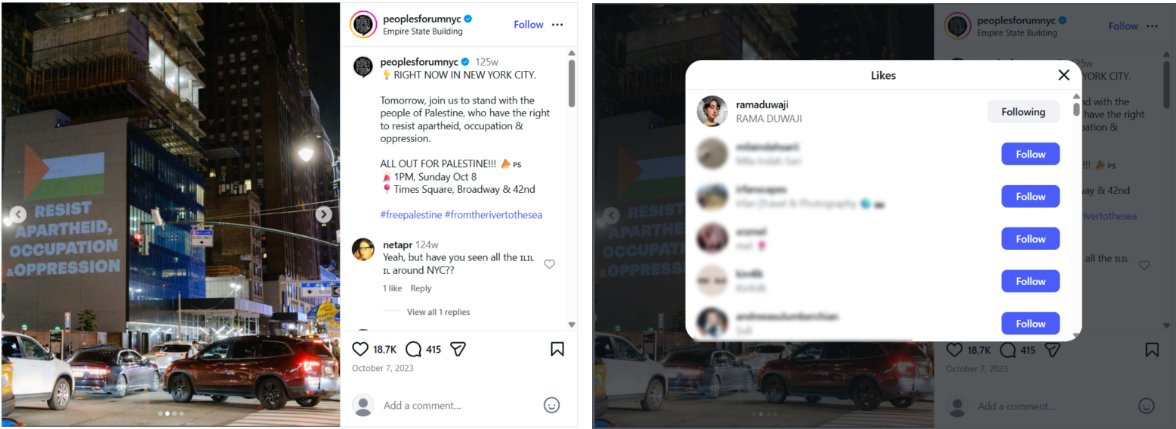
A report by Jewish Insider has sparked political controversy in New York after revealing that Rama Duwaji, the wife of New York City Mayor Zohran Mamdani, liked several Instagram posts in the hours and days following Hamas’ October 7, 2023 massacre in Israel.
The reaction from the mayor and the muted response from parts of the media have raised questions about standards of scrutiny in news coverage.
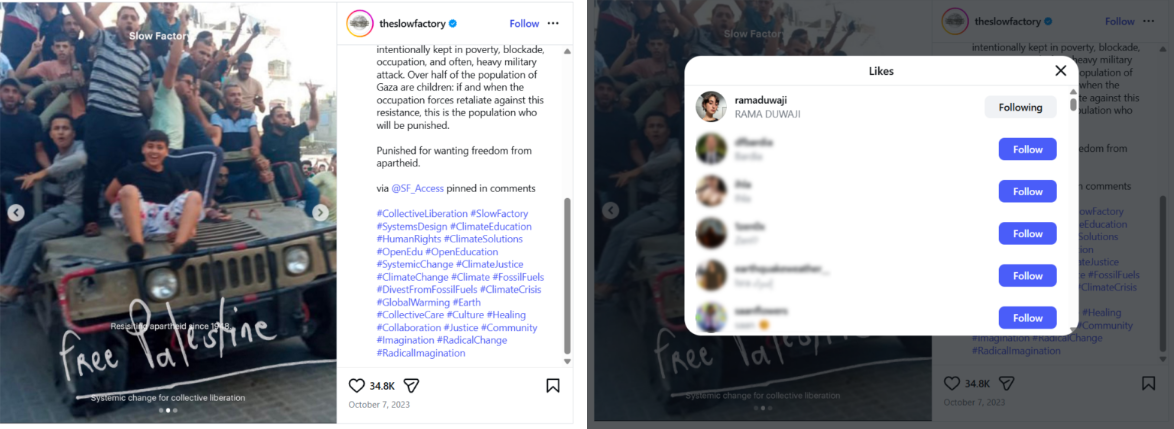
Jewish Insider exposed that Duwaji liked posts on Instagram that celebrated the Hamas assault and framed it as “resistance.” One post showed individuals standing on what appeared to be a captured Israeli military vehicle with the caption “resisting apartheid since 1948.” Another featured an image of a bulldozer breaching the Gaza-Israel border fence with the caption “breaking the walls of apartheid and military occupation, October 7, 2023.”
The report also stated that Duwaji liked posts calling on supporters to back “Palestinian resistance” and attend a New York protest the day after the attack. Another post she engaged with contained the slogan “from the river to the sea, Palestine will be free.”

In response to the revelations, Mamdani did not directly address the substance of the posts. Nor did he condemn them or his wife’s conduct. Instead, he said that his wife is a private person who holds no official role in his administration or campaign.
The episode quickly gained traction on social media and in political circles. Commentators and journalists like The Free Press’ Olivia Reingold highlighted the posts and a far wider pattern of radical anti-Israel posts, suggesting that public figures should face scrutiny over the views and public activity of those close to them.
Guys that post was just the tip of the iceberg,
I found 70+ radical anti-Israel posts liked by Rama Duwaji, wife of Zohran Mamdani. One calls October 7 a “mass rape hoax.” https://t.co/ogwZfweh4v
— Olivia Reingold (@Olivia_Reingold) March 7, 2026
At the same time, the story has also sparked debate about media coverage and standards.
Observers noted that some major outlets that have previously examined the social media activity of pro-Israel officials or figures connected to Israel have not shown the same level of investigative attention to the Mamdani story.
A widely shared post by opinion writer Joel M. Petlin pointed out that The New York Times had previously reported critically on the pro-Israel social media activity of an official’s wife, but had not pursued comparable scrutiny in this case.
What’s infuriating about this story is not the fact that Mayor Mamdani’s wife supports the Oct 7th massacre. We obviously knew they both do.
What’s infuriating is that the NY Times revealed that Congressman Dan Goldman’s wife supports Israel, and he was forced to publicly… https://t.co/zzTadIRTwp pic.twitter.com/4SvOgMtARR
— Joel M. Petlin (@Joelmpetlin) March 6, 2026
The New York Times has also whitewashed the contents of the posts liked by Mamdani’s wife, by labeling them as “support for the Palestinian cause.” In reality, these posts called for and celebrated the murder of Jews.
The contrast has fueled accusations of a double standard in how politically sensitive issues related to Israel and Hamas are covered. When individuals connected to Israeli institutions express controversial views, major outlets often pursue the story aggressively. Yet when the controversy involves content appearing to praise Hamas’ October 7 attack, the same level of follow-up reporting can be harder to find.
As the story continues to circulate online, the key issues remain straightforward. When a public figure’s close family member publicly engages with posts celebrating a terrorist attack, it warrants deeper scrutiny. And that scrutiny should apply evenly across the political spectrum.
Meanwhile, Mamdani’s wife’s voice has not been heard. She did not apologize, and no media outlet questioned her silence.
As the political fallout in New York continues, the global media should be asking harder questions.
The author is a contributor to HonestReporting, a Jerusalem-based media watchdog with a focus on antisemitism and anti-Israel bias — where a version of this article first appeared.
Uncategorized
In Israel’s missile war, some families run to shelters. Others have nowhere to go.
(JTA) — JERUSALEM — Walking with her children in Pisgat Zeev, a leafy neighborhood in Jerusalem, on Monday afternoon, Rivka recalled the missile that flew nearby the day before.
An impact could be felt as the family hunkered in their private “mamad” or safe room, required in all new homes in the Jewish neighborhood. Those who live in older homes or were far from their residence found their nearest public shelter.
When her children started to cry, Rivka said, she reassured them that the walls of the shelter are strong enough to withstand anything Iran could send toward Israel. “We feel safe in our shelters,” she said.
Just a few miles south, in the east Jerusalem neighborhood of Sheikh Jarrah, father of three Abed Abu Sharif recalled how he was driving his taxi on Sunday when he heard the unmistakable sound of an air raid alert.
Israeli authorities advise anyone driving when a warning siren sounds to exit their vehicle and look for the nearest public shelter. Abu Sharif knew he would not find one.
“Where am I to go? What am I to do? There is no shelter for me near here,” he said. “I continue driving because I have to provide for my family.”
The disparate experiences point to longstanding gaps in shelter access that are being thrown into stark relief once again by war.
The access gaps exist both geographically — with residents of the country’s dense center more protected — and between Jewish and Arab Israelis.
A Knesset hearing on Monday took aim at the significant number of Israelis who do not have ready access to shelters near their home, with lawmakers expressing frustration over the lack of support for shelter construction despite the constant threat of war since Oct. 7, 2023.
“In my view, this situation is abandonment of human life. Nothing less,” Oded Forer of the Yisrael Beiteinu party said during the hearing. “And it is happening right now, as people try to run to safe rooms, but they don’t have them.”
The hearing only briefly discussed disparities between Jewish and Arab Israeli communities in shelter access, citing statistics from the Israel Defense Forces’ Home Front Command. The statistics — revealed publicly last week — show that only 37 of 11,775 public shelters in Israel, or roughly 0.3%, are located in Arab municipalities, even though Arabs make up about 15% of Israel’s population.
That information dates to January 2025, before last year’s war with Iran. While both the Home Front Command and Israel’s comptroller told the Jewish Telegraphic Agency that a newer accounting was not available, Ori Narov, who leads the legal department of the Israel Religious Action Center, said he had received government data showing that roughly a third of the 1,500 shelters installed last year in Israel’s north went to Arab municipalities — a development that he cited as a rare sign of progress in Jewish-Arab equity.
Still, there is only one public bomb shelter in east Jerusalem, according to Bimkom-Planners for Planning Rights, a group advocating for equitable built environments in Israel.
“This is an issue of equity,” said Bimkom’s Dafna Saporta. “We’re talking about the Arab population. They don’t have equality, and they don’t have justice in Israel. The state is taking care of the Jewish population but neglecting the Arabs. It’s not new. It’s a political decision.”
National civil defense standards are set by the Home Front Command, while planning approval rests with local planning authorities, and cities are typically responsible for maintaining public shelters.
“As per the Civil Defense Law, public shelter construction is the responsibility of local authorities, whereas personal protection is an individual responsibility,” Home Front Command said in a statement responding to a request for comment on disparities in shelter access between Arab and Jewish communities in Israel.
It added, “The Home Front Command also takes measures to provide individual protection and to renovate public shelters, based on guidance from the political echelon and government decisions.”
Oct. 7, the subsequent conflict with Hezbollah and last year’s 12-day war with Iran drew stark attention to disparities that had deepened over time. A missile landed in Rahat, an Arab city in the south, killing multiple residents, and another strike in Tamra, in the north, killed several members of the same family.
Some efforts are underway to close the gap. A government initiative called Northern Shield worked to install shelters last year in homes and schools within a buffer zone of the Lebanese border, where rockets from Hezbollah are again flying now.
Nonprofit groups have also stepped into the gap. The International Fellowship of Christians and Jews, meanwhile, says it has worked with the government to install 700 shelters since Oct. 7, including several this week and some in a Druze village and in Haifa, a mixed city with large populations of both Jews and Arabs.
And the Israeli organization Standing Together, which advocates coexistence between Arabs and Jewish Israelis, has launched a campaign to crowdfund shelters for vulnerable Arab communities in the Negev.
But advocates say the efforts are far outmatched by the need. “While these initiatives are well-intentioned and deeply appreciated, the scale of the need in the unrecognized villages far exceeds the capacity of civil society,” Huda Abu Obaid, CEO of the Negev Coexistence Forum, said about the crowdfunding campaigns.
The Negev Coexistence Forum joined a lawsuit filed by the Reform movement-affiliated IRAC at the Supreme Court of Israel in 2024, alleging that Israel’s failure to build public shelters in Arab communities was a violation of their civil rights.
The government’s defense rested on high rates of illegal construction in Arab municipalities, which, in their view, absolved them of responsibility to ensure that mamads are installed in new homes. (Retrofitting mamads into older buildings is difficult and costly and not within the budget of any municipality, Arab or Jewish.)
The court sided with the government, ruling that the responsibility for building protective spaces rests with private homeowners and that the state is not obligated to build public shelters.
For Narov, the situation in the Negev is particularly galling because the extant planning process does not account for many Bedouin Arabs living there.
“They are not municipalities recognized by the government, so they can’t even build the shelters if they wanted to,” Narov said. He added, “This is the first responsibility of any state to its citizens: security to keep them safe from attacks, from the inside and definitely from the outside, as we’re experiencing right now.”
“If the law requires a protected room in every new building, but thousands of citizens are prevented from building legally or live in areas excluded from state planning frameworks, then the legal standard itself produces inequality,” Abu Obaid said. “Protection should not depend on municipal status, planning recognition or economic ability. It should be universal.”
The mandate that all new construction include a safe room in each unit or a basement shelter, first enacted in the 1990s, shifted Israel’s safeguards away from public shelters. That includes in east Jerusalem, which is administered by the the city of Jerusalem Municipality and hence the Israeli government, where no additional public shelters have been built in the last decade.
On March 2, an Iranian missile landed at the entrance to Ramat Shlomo, just a few kilometers from the neighborhood, injuring six Israelis.
Fatme, a doctor at a hospital in Jerusalem who was riding bus 218 toward the Qalandia checkpoint at the end of her workday on Monday, passed the crater on her way home. Still, she said, the debate was of little practical significance to her.
“There isn’t a single shelter in my neighborhood,” she said. “So when I hear the bombs, I just go on with my day.”
The post In Israel’s missile war, some families run to shelters. Others have nowhere to go. appeared first on The Forward.
Uncategorized
Trump says Iran war is ‘very complete, pretty much’ as US and Israel continue to pound Tehran
(JTA) — President Donald Trump gave mixed signals about the status of the U.S.-Israeli war on Iran on Monday, telling reporters that the war was “very complete, pretty much” even as he said that he would make a “mutual” decision with Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu about its end.
At the same time, he threatened Iran in a post on Truth Social, saying, “If Iran does anything that stops the flow of Oil within the Strait of Hormuz, they will be hit by the United States of America TWENTY TIMES HARDER than they have been hit thus far.”
Secretary of Defense Pete Hegseth said Tuesday would be “the most intense day” of strikes yet – while also noting that the pace of Iran’s missiles had slowed.
Three people have died from missile strikes in the last two days in Israel, as well as two Israeli soldiers killed when their tank was attacked while they fought Hezbollah forces in southern Lebanon. One of the soldiers killed was from Majdal Shams, a Druze town in Israel’s north where 12 children were killed by a Hezbollah rocket in 2024.
Trump’s comments come as oil prices surge amid disruption in the Middle East that has turned several U.S. allies in the region into Iranian targets. A leading pro-Israel senator has urged Israel to refrain from targeting Iranian oil depots, reflecting anxiety over sharply rising gas prices.
Trump told the Times of Israel that while Netanyahu would have input in the timing to end the war, he would make the final decision. He also declined to entertain the idea of Israel continuing to fight Iran after the United States exits, saying, “I don’t think it’s going to be necessary.”
Iranian officials, meanwhile, have vowed to continue fighting “as long as it takes” and are prepared for a long war.
And Netanyahu said on Tuesday morning that “more is to come” in the war.
The comments come as U.S. and Israeli forces continue to bomb targets in Iran in an attempt to end the country’s military ambitions, destroy its missile arsenal and potentially topple its Islamic Republic regime.
This week, the regime appointed Mojtaba Khamenei, the hard-line son of the assassinated supreme leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei, as its new supreme leader in a show of defiance. Trump has said he is “not happy” with the choice and would like to see someone else installed.
The post Trump says Iran war is ‘very complete, pretty much’ as US and Israel continue to pound Tehran appeared first on The Forward.