Uncategorized
Letty Cottin Pogrebin wants Jews to own up to the corrosive power of shame
(JTA) — When a lawyer for Donald Trump asked E. Jean Carroll why she didn’t scream while allegedly being raped by Donald Trump, I thought of Letty Cottin Pogrebin. In her latest book, “Shanda: A Memoir of Shame and Secrecy,” she writes about being assaulted by a famous poet — and how the shadow of shame kept women like her silent about attacks on their own bodies.
That incident in 1962, she writes, was “fifty-eight years before the #MeToo movement provided the sisterhood and solidarity that made survivors of abuse and rape feel safe enough to tell their stories.”
Now 83, Pogrebin could have coasted with a memoir celebrating her six decades as a leading feminist: She co-founded Ms. magazine, its Foundation for Women and the National Women’s Political Caucus. She served as president of Americans for Peace Now and in 1982 blew the whistle on antisemitism in the feminist movement.
Instead, “Shanda” is about her immigrant Jewish family and the secrets they carried through their lives. First marriages that were kept hidden. An unacknowledged half-sister. Money problems and domestic abuse. An uncle banished for sharing family dirt in public.
“My mania around secrecy and shame was sparked in 1951 by the discovery that my parents had concealed from me the truth about their personal histories, and every member of my large extended family, on both sides, was in on it,” writes Pogrebin, now 83. “Their need to avoid scandal was so compelling that, once identified, it provided the lens through which I could see my family with fresh eyes, spotlight their fears, and, in so doing, illuminate my own.”
“Shanda” (the Yiddish word describes the kind of behavior that brings shame on an entire family or even a people) is also a portrait of immigrant New York Jews in the 20th century. As her father and mother father move up in the world and leave their Yiddish-speaking, Old World families behind for new lives in the Bronx and Queens, they stand in for a generation of Jews and new Americans “bent on saving face and determined to be, if not exemplary, at least impeccably respectable.”
Pogrebin and I spoke last week ahead of the Eight Over Eighty Gala on May 31, where she will be honored with a group that includes another Jewish feminist icon, the writer Erica Jong, and musician Eve Queler, who founded her own ensemble, the Opera Orchestra of New York, when she wasn’t being given chances to conduct in the male-dominated world of classical music. The gala is a fundraiser for the New Jewish Home, a healthcare nonprofit serving older New Yorkers.
Pogrebin and I spoke about shame and how it plays out in public and private, from rape accusations against a former president to her regrets over how she wrote about her own abortions to how the Bible justifies family trickery.
Our conversation was edited for length and clarity.
I found your book very moving because my parents’ generation, who like your family were middle-class Jews who grew up or lived in the New York metropolitan area, are also all gone now. Your book brought back to me that world of aunts and uncles and cousins, and kids like us who couldn’t imagine what kinds of secrets and traumas our parents and relatives were hiding. But you went back and asked all the questions that many of us are afraid to ask.
I can’t tell you how good writing it has been. I feel as though I have no weight on my back. And people who have read it gained such comfort from the normalization that happens when you read that others have been through what you’ve been through. And my family secrets are so varied — just one right after the other. The chameleon-like behavior of that generation — they became who they wanted to be through pretense or actual accomplishment.
In my mother’s case, pretense led the way. She went and got a studio photo that made it look like she graduated from high school when she didn’t. In the eighth grade, she went up to her uncle’s house in the north Bronx and had her dates pick her up there because of the shanda of where she lived on the Lower East Side with nine people in three rooms. She had to imagine herself the child of her uncle, who didn’t have an accent or had an accent but at least spoke English.
You describe yours as “an immigrant family torn between loyalty to their own kind and longing for American acceptance.”
There was the feeling that, “If only we could measure up, we would be real Americans.” My mother was a sewing machine operator who became a designer and figured out what American women wore when she came from rags and cardboard shoes, in steerage. So I admire them. As much as I was discomforted by the lies, I ended up having compassion for them.
It’s also a story of thwarted women, and all that lost potential of a generation in which few could contemplate a college degree or a career outside the home. Your mother worked for a time as a junior designer for Hattie Carnegie, a sort of Donna Karan of her day, but abandoned that after she met your dad and became, as you write, “Mrs. Jack Cottin.”
The powerlessness of women was complicated in the 1950s by the demands of the masculine Jewish ideal. So having a wife who didn’t work was proof that you were a man who could provide. As a result women sacrificed their own aspirations and passions. She protected her husband’s image by not pursuing her life outside the home. In a way my feminism is a positive, like a photograph, to the negative of my mother’s 1950s womanhood.
“I’m not an optimist. I call myself a ‘cockeyed strategist,” said Pogrebin, who has a home on the Upper West Side. (Mike Lovett)
You write that you “think of shame and secrecy as quintessentially Jewish issues.” What were the Jewish pressures that inspired your parents to tell so many stories that weren’t true?
Think about what we did. We hid behind our names. We changed our names. We sloughed off our accents. My mother learned to make My*T*Fine pudding instead of gefilte fish. Shame and secrecy have always been intrinsically Jewish to me, because of the “sha!” factor: At every supper party, there would be the moment when somebody would say, “Sha! We don’t talk about that!” So even though we talked about what felt like everything, there were things that couldn’t be touched: illness, the C-word [cancer]. If you wanted to make a shidduch [wedding match] with another family in the insular communities in which Jews lived, you couldn’t let it be known that there was cancer in the family, or mental illness.
While I was writing this memoir, I realized that the [Torah portion] I’m listening to one Shabbat morning is all about hiding. It is Jacob finding out that he didn’t marry Rachel, after all, but married somebody he didn’t love. All of the hiding that I took for granted in the Bible stories and I was raised on like mother’s milk was formative. They justified pretense, and they justified trickery. Rebecca lied to her husband and presented her younger son Jacob for the blessing because God told her, because it was for the greater good of the future the Jewish people.
I think Jews felt that same sort of way when it came to surviving. So we can get rid of our names. We wouldn’t have survived, whether we were hiding in a forest or behind a cabinet, a name or a passport, or [pushed into hiding] with [forced] conversions. Hiding was survival.
I was reading your book just as the E. Jean Carroll verdict came down, holding Donald Trump liable for sexually assaulting her during an encounter in the mid-’90s. You write how in 1962, when you were working as a book publicist, the hard-drinking Irish poet Brendan Behan (who died in 1964) tried to rape you in a hotel room and you didn’t report it. Like Carroll, you didn’t think that it was something that could be reported because the cost was too high.
Certainly in that era powerful men could get away with horrible behavior because of shanda reasons.
Carroll said in her court testimony, “It was shameful to go to the police.”
You know that it happened to so many others and nobody paid the price. The man’s reputation was intact and we kept our jobs because we sacrificed our dignity and our truth. I was in a career, and I really was supporting myself. I couldn’t afford to lose my job. I would have been pilloried for having gone to his hotel room, and nobody was there when he picked up an ashtray and threatened to break the window of the Chelsea Hotel unless I went up there with him.The cards were stacked against me.
In “Shanda,” you write about another kind of shame: The shame you now feel decades later about how you described the incident in your first book. You regret “how blithely I transformed an aggravated assault by a powerful man into a ‘sticky sexual encounter.’”
I wrote about the incident in such offhand terms, and wonder why. I wrote, basically, “Okay, girls, you’re gonna have to put up with this, but you’re gonna have to find your own magical sentence like I had with Behan” to get him to stop.
You write that you said, “You can’t do this to me! I’m a nice Jewish girl!” And that got him to back off.
Really painful.
I think that’s a powerful aspect of your book — how you look back at the ways you let down the movement or your family or friends and now regret. In 1991 you wrote a New York Times essay about an illegal abortion you had as a college senior in 1958, but not the second one you had only a few months later. While you were urging women to tell their stories of abortion, you note how a different shame kept you from telling the whole truth.
Jewish girls could be, you know, plain or ordinary, but they had to be smart, and I had been stupid. I could out myself as one of the many millions of women who had an abortion but not as a Jewish girl who made the same mistake [of getting pregnant] twice.
The book was written before the Supreme Court overturned Roe v. Wade. In the book you write powerfully about the shame, danger and loneliness among women when abortion was illegal, and now, after 50 years, it is happening again. Having been very much part of the generation of activists that saw Roe become the law of the land, how have you processed its demise?
Since the 1970s, we thought everything was happening in this proper linear way. We got legislation passed, we had litigation and we won, and we saw the percentage of women’s participation in the workplace all across professions and trades and everything else rise and rise. And then Ronald Reagan was elected and then there was the Moral Majority and then it was the Hyde Amendment [barring the use of federal funds to pay for abortion]. I was sideswiped because I think I was naive enough to imagine that once we articulated what feminism was driving at and why women’s rights were important, and how the economic reality of families and discrimination against women weren’t just women’s issues, people would internalize it and understand it and justice would be done.
In the case of Roe, we could not imagine that rights could ever be taken away. We didn’t do something that we should have done, which is to have outed ourselves in a big way. It’s not enough that abortion was legal. We allowed it to remain stigmatized. We allowed the right wing to create their own valence around it. That negated solidarity. If we had talked about abortion as healthcare, if we had had our stories published and created organizations around remembering what it was like and people telling their stories about when abortion was illegal and dangerous…. Instead we allowed the religious right to prioritize [fetal] cells over a woman’s life. We just were not truthful with each other, so we didn’t create solidarity.
Are you heartened by the backlash against restrictive new laws in red states or optimistic that the next wave of activism can reclaim the right to abortion?
I’m not an optimist. I call myself a “cockeyed strategist.” If you look at my long resume, it is all about organizing: Ms. magazine, feminist organizations, women’s foundations, Black-Jewish dialogues, Torah study groups and Palestinian-Jewish dialogues.
Number one, we have to own the data and reframe the narrative. We have to open channels for discussion for women who have either had one or know someone who has had one, even in religious Catholic families. The state-by-state strategy was really slow, but Ruth Bader Ginsburg wanted that. She almost didn’t get on the court because she didn’t like the nationwide, right-to-privacy strategy of Roe but instead wanted it won state by state, which would have required campaigns of acceptance and consciousness-raising.
So, the irony is she hasn’t lived to see that we’re going to have to do it her way.
You share a lot of family secrets in this book. Is this a book that you waited to write until, I’ll try to put this gently, most of the people had died?
I started this book when I was 78 years old, and there’s always a connection to my major birthdays. And turning 80 – you experience that number and it is so weird. It doesn’t describe me and it probably won’t describe you. I thought, this could well be my last book, so I needed to be completely transparent, put it all out there.
My mother and father and aunts and uncles were gone, but I have 24 cousins altogether. I went to my cousins, and told them I am going to write about the secret of your parents: It’s my uncle, but it’s your father. It’s your family story even though it’s my family, but it’s yours first. And every cousin, uniformly, said, “Are you kidding? You don’t even know the half of it,” and they’d tell me the whole story. I guess people want the truth out in the end.
Is that an aspect of getting older?
I think it’s a promise of liberation, which is what I have found. It’s this experience of being free from anything that I’ve hid. I don’t have to hide. Years ago, on our 35th wedding anniversary, we took our whole family to the Tenement Museum because we wanted them to see how far we’ve come in two generations.
—
The post Letty Cottin Pogrebin wants Jews to own up to the corrosive power of shame appeared first on Jewish Telegraphic Agency.
Uncategorized
How the Global Religious Landscape Changed from 2010 to 2020

Muslims grew fastest; Christians lagged behind global population increase
• Christians are the world’s largest religious group, at 28.8% of the global population. They are a majority everywhere except the Asia-Pacific and Middle East-North Africa regions. Sub-Saharan Africa has surpassed Europe in having the largest number of Christians. But Christians are shrinking as a share of the global population, as millions of Christians “switch” out of religion to become religiously unaffiliated.
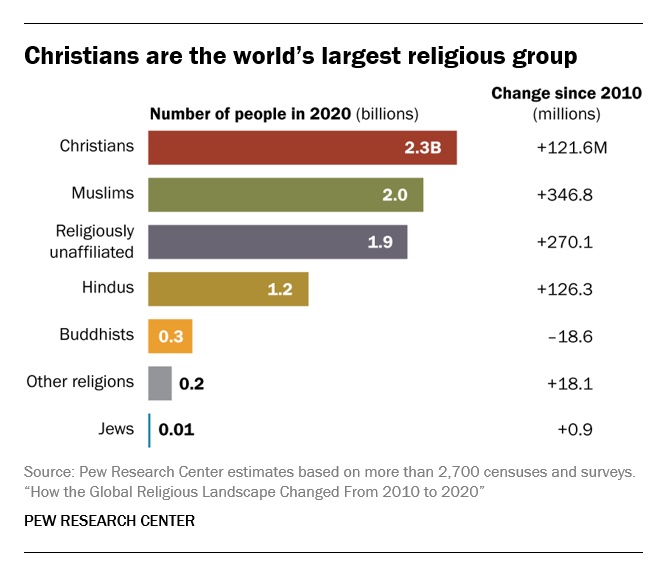
• Muslims are the world’s second-largest religious group (25.6% of the world’s population) and the fastest-growing major religion, largely due to Muslims’ relatively young age structure and high fertility rate. They make up the vast majority of the population in the Middle East-North Africa region. In all other regions, Muslims are a religious minority, including in the Asia-Pacific region (which is home to the greatest number of Muslims).
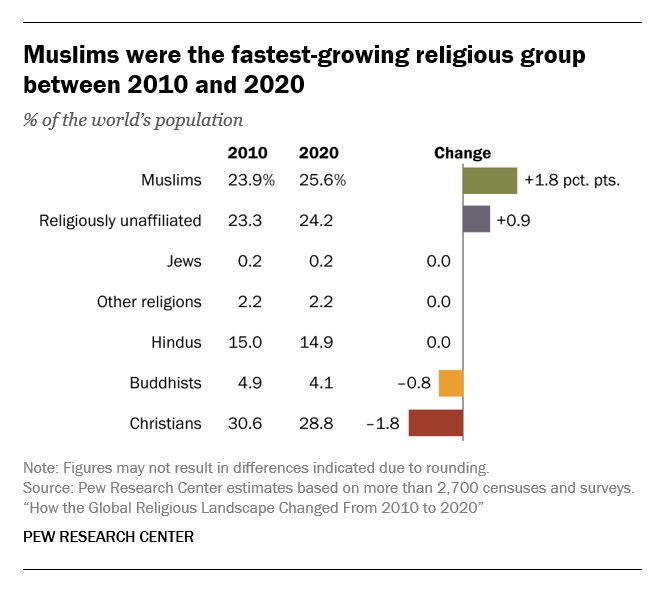
• The religiously unaffiliated population is the world’s third-largest religious category (24.2% of the global population), after Christians and Muslims. Between 2010 and 2020, religiously unaffiliated people grew more than any group except Muslims, despite their demographic disadvantages of an older age structure and relatively low fertility. The unaffiliated made up a majority of the population in 10 countries and territories in 2020, up from seven a decade earlier.
• Hindus are the fourth-largest religious category (14.9% of the world’s population), after Christians, Muslims and religiously unaffiliated people. Most (99%) live in the Asia-Pacific region; 95% of all Hindus live in India alone. Between 2010 and 2020, Hindus remained a stable share of the world’s population because their fertility resembles the global average, and surveys indicate that switching out of or into Hinduism is rare.
• Buddhists (4.1% of the world’s population) are the only group in this report whose number declined worldwide between 2010 and 2020. This was due both to religious disaffiliation among Buddhists in East Asia and to a relatively low birth rate among Buddhists, who tend to live in countries with older populations. Most of the world’s Buddhists (98%) reside in the Asia-Pacific region, the birthplace of Buddhism.
• Jews, the smallest religious group analyzed separately in this report (0.2% of the world’s population), lagged behind global population growth between 2010 and 2020 – despite having fertility rates on par with the global average – due to their older age structure. Most Jews live either in North America (primarily in the United States) or in the Middle East-North Africa region (almost exclusively in Israel).
These are among the key findings of a Pew Research Center analysis of more than 2,700 censuses and surveys, including census data releases that were delayed due to the coronavirus pandemic. This report is part of the Pew-Templeton Global Religious Futures project, which analyzes global religious change and its impact on societies around the world. Funding for the Global Religious Futures project comes from The Pew Charitable Trusts and the John Templeton Foundation.
Uncategorized
Antisemitism in some unlikely places in America

By HENRY SREBRNIK Antisemitism flourishes in a place where few might expect to confront it – medical schools and among doctors. It affects Jews, I think, more emotionally than Judeophobia in other fields.
Medicine has long been a Jewish profession with a history going back centuries. We all know the jokes about “my son – now also my daughter – the doctor.” Physicians take the Hippocratic Oath to heal the sick, regardless of their ethnicity or religion. When we are ill doctors often become the people who save us from debilitating illness and even death. So this is all the more shocking.
Yes, in earlier periods there were medical schools with quotas and hospitals who refused or limited the number of Jews they allowed to be affiliated with them. It’s why we built Jewish hospitals and practices. And of course, we all shudder at the history of Nazi doctors and euthanasia in Germany and in the concentration camps of Europe. But all this – so we thought – was a thing of a dark past. Yet now it has made a comeback, along with many other horrors we assume might never reappear.
Since the Hamas attack on Israel on October 7, 2023, there has been a resurgence of antisemitism, also noticeable in the world of healthcare. This is not just a Canadian issue. Two articles on the Jewish website Tablet, published Nov. 21, 2023, and May 18, 2025, spoke to this problem in American medicine as well, referencing a study by Ian Kingsbury and Jay P. Greene of Do No Harm, a health care advocacy group, based on data amassed by the organization Stop Antisemitism. They identified a wave of open Jew-hatred by medical professionals, medical schools, and professional associations, often driven by foreign-trained doctors importing the Jew-hatred of their native countries, suggesting “that a field entrusted with healing is becoming a licensed purveyor of hatred.”
Activists from Doctors Against Genocide, American Palestinian Women’s Association, and CODEPINK held a demonstration calling for an immediate cease-fire in Gaza at the Hart Senate Office Building in Washington, D.C., Nov. 16, 2023, almost as soon as the war began. A doctor in Tampa took to social media to post a Palestinian flag with the caption “about time!!!” The medical director of a cancer centre in Dearborn, Michigan, posted on social media: “What a beautiful morning. What a beautiful day.” Even in New York, a physician commented on Instagram that “Zionist settlers” got “a taste of their own medicine.” A Boston-based dentist was filmed ripping down posters of Israeli victims and a professor at the University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine did the same. Almost three-quarters of American medical associations felt the need to speak out on the war in Ukraine but almost three-quarters had nothing to say about the war in Israel.
Antisemitism in academic medical centres is fostering noxious environments which deprive Jewish healthcare professionals of their civil right to work in spaces free from discrimination and hate, according to a study by the Data & Analytics Department of StandWithUs, an international, non-partisan education organization that supports Israel and fights antisemitism.
“Academia today is increasingly cultivating an environment which is hostile to Jews, as well as members of other religious and ethnic groups,” StandWithUs director of data and analytics, and study co-author, Alexandra Fishman, said on May 5 in a press release. “Academic institutions should be upholding the integrity of scholarship, prioritizing civil discourse, rather than allowing bias or personal agendas to guide academic culture.”
The study, “Antisemitism in American Healthcare: The Role of Workplace Environment,” included survey data showing that 62.8 per cent of Jewish healthcare professionals employed by campus-based medical centres reported experiencing antisemitism, a far higher rate than those working in private practice and community hospitals. Fueling the rise in hate, it added, were repeated failures of DEI (diversity, equity, and inclusion) initiatives to educate workers about antisemitism, increasing, the report said, the likelihood of antisemitic activity.
“When administrators and colleagues understand what antisemitism looks like, it clearly correlates with less antisemitism in the workplace,” co-author and Yeshiva University professor Dr. Charles Auerbach reported. “Recognition is a powerful tool — institutions that foster awareness create safer, more inclusive environments for everyone.”
Last December, the Data & Analytics Department also published a study which found that nearly 40 per cent of Jewish American health-care professionals have encountered antisemitism in the workplace, either as witnesses or victims. The study included a survey of 645 Jewish health workers, a substantial number of whom said they were subject to “social and professional isolation.” The problem left more than one quarter of the survey cohort, 26.4 per cent, “feeling unsafe or threatened.”
The official journal of the Alliance for Academic Internal Medicine concurs. According to “The Moral Imperative of Countering Antisemitism in US Medicine – A Way Forward,” by Hedy S. Wald and Steven Roth, published in the October 2024 issue of the American Journal of Medicine, increased antisemitism in the United States has created a hostile learning and practice environment in medical settings. This includes instances of antisemitic behaviour and the use of antisemitic symbols at medical school commencements.
Examples of its impact upon medicine include medical students’ social media postings claiming that Jews wield disproportionate power, antisemitic slogans at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) David Geffen School of Medicine, antisemitic graffiti at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) Cancer Centre, Jewish medical students’ exposure to demonization of Israel diatribes and rationalizing terrorism; and faculty, including a professor of medicine at UCSF, posting antisemitic tropes and derogatory comments about Jewish health care professionals. Jewish medical students’ fears of retribution, should they speak out, have been reported. “Our recent unpublished survey of Jewish physicians and trainees demonstrated a twofold increase from 40% to 88% for those who experienced antisemitism prior to vs after October 7,” they stated.
In some schools, Jewish faculty are speaking out. In February, the Jewish Faculty Resilience Group at UCLA accused the institution in an open letter of “ignoring” antisemitism at the School of Medicine, charging that its indifference to the matter “continues to encourage more antisemitism.” It added that discrimination at the medical school has caused demonstrable harm to Jewish students and faculty. Student clubs, it said, are denied recognition for arbitrary reasons; Jewish faculty whose ethnic backgrounds were previously unknown are purged from the payrolls upon being identified as Jews; and anyone who refuses to participate in anti-Zionist events is “intimidated” and pressured.
Given these findings, many American physicians are worried not only as Jewish doctors and professionals, but for Jewish patients who are more than ever concerned with whom they’re meeting. Can we really conceive of a future where you’re not sure if “the doctor will hate you now?”
Henry Srebrnik is a professor of political science at the University of Prince Edward Island.
Uncategorized
The 2025 Toronto Walk (and talk ) for Israel
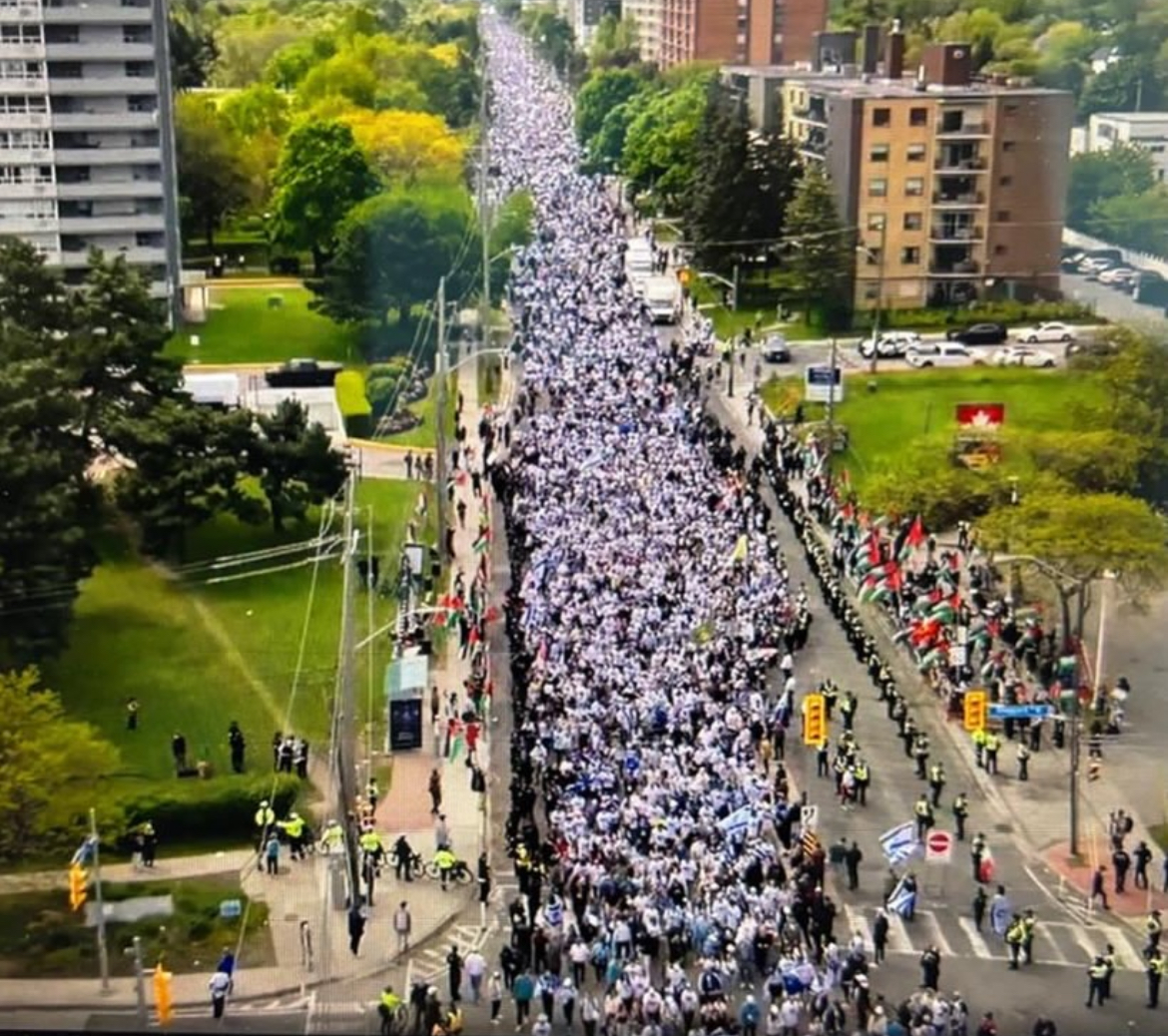

By GERRY POSNER There are walks and then there are walks. The Toronto UJA Walk for Israel on May 25, 2025 was one of a kind, at least as far as Canada and Jews are concerned. The number of people present was estimated to be 56,000 people or 112,000 total shoes. (How they get to that number is bewildering to me, since there is no one counting). This was 6,000 more than last year. Whether it is true or not, take it from me, it was packed. The synagogues in Canada should be so fortunate to get those numbers in total on High Holidays. The picture here gives you a sense of the size of the crowd.

This was my first walk in Toronto for Israel and I was with my granddaughter, Samantha Pyzer (not to forget her two friends whom she managed to meet at the site, no small feat, even with iPhones as aids). The official proceedings began at 9:00 a.m. and the walk at 10:00 a.m. There was entertainment to begin with, also along the way, and at the finish as well. The finish line this year was the Prosserman Centre or the JCC as it often called. The walk itself was perhaps 4 kilometres – not very long, but the walking was slow, especially at the beginning. There were lots of strollers, even baby carriages, though I did not see any wheelchairs. All ages participated on this walk. I figured, based on what I could see on the faces of people all around me that, although I was not the oldest one on the walk, I bet I made the top 100 – more likely the top 20.
What was a highlight for me was the number of Winnipeggers I met, both past and present. Connecting with them seemed to be much like a fluke. No doubt, I missed la lot of them, but I saw, in no particular order (I could not recall the order if my life depended on it): Alta Sigesmund, (who was, a long time ago, my daughter Amira’s teacher), Marni Samphir, Karla Berbrayer and her husband Dr. Allan Kraut and family. Then, when Samantha and I made it to the end and sat down to eat, I struck up a conversation with a woman unknown to me and as we chatted, she confirmed her former Winnipeg status as a sister-in- law to David Devere, as in Betty Shwemer, the sister of Cecile Devere. I also chanced upon Terri Cherniack, only because I paused for a moment and she spotted me. As we closed in near the finish, I met ( hey were on their way back), Earl and Suzanne Golden and son Matthew, as well as Daniel Glazerman. That stop caused me to lose my granddaughter and her pals. Try finding them amid the noise and size of the crowd – but I pulled it off.
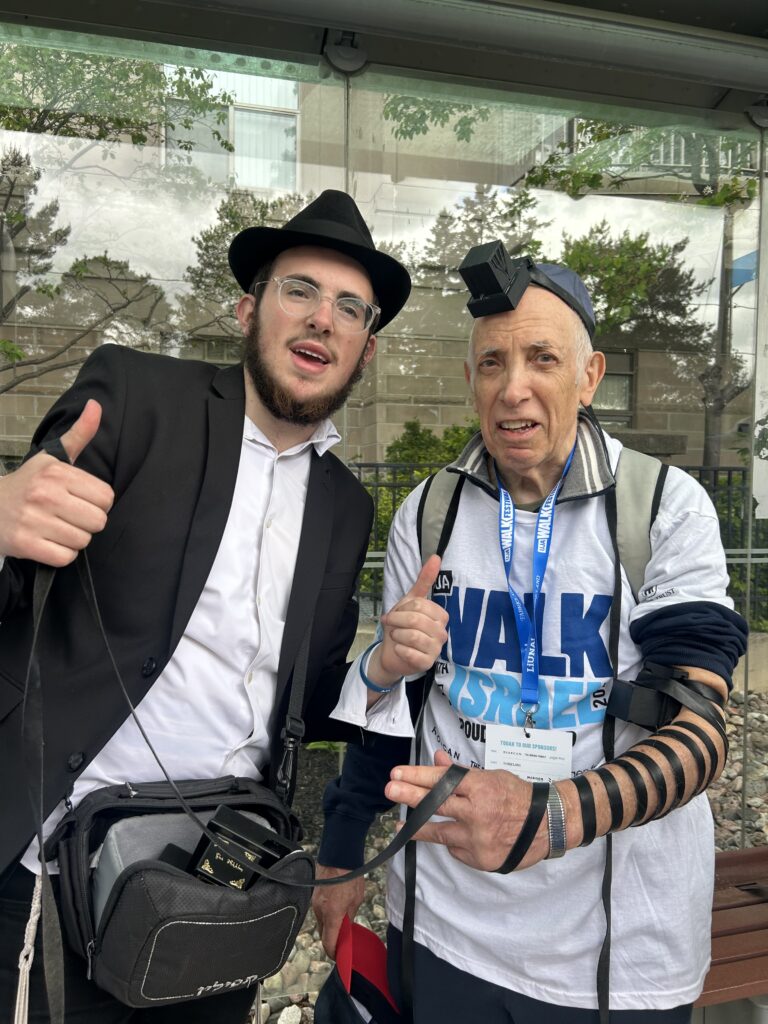

As I was in line to get food, I started chatting with a guy in the vicinity of my age. I dropped the Winnipeg link and the floodgates opened with “ Did I know Jack and Joanie Rusen?” So that was an interesting few minutes. And I was not too terribly surprised to come across some of my Pickleball family. All of these meetings, along with spotting some of my sister’s family and other cousins, were carried on with the sound of the shofar as we moved along the way. In short, this was a happening. Merchants selling a variety of products, many of them Israeli based, were in evidence and, of course, the day could not have ended without the laying of tefillin, aided by Chabad, who have perfected the procedure to take less than a minute. See the photo. Chabad had a willing audience.
Aside from the joy of sharing this experience with my granddaughter, the very presence of all these Jews gathered together for a common reason made this day very special to me. However, there was a downside to the day. The downside was that, as we began to walk back to our car there was no other way I could figure out how to return when the rains came and came. While we walked faster, we were impeded by pouring rain and puddles. But Samantha wanted to persevere, as did I. We made it, but were drenched. My runners are still drying out as I write this two days later.
What with being surrounded by 56,000 people, the noise, the slow walking, and the rain, I can still say the day was a real highlight for me – one of the better moments since our arrival in Toronto in 2012. As well as the photos we took along the way, I have the reminder of the day, courtesy of the UJA, as evidenced from the photo. It was not just the walk, but the talk that accompanied the walk that made it so worthwhile for me. I would do it again, minus the rain.
