Features
The Dark Side of Albert: Einstein and Marie Winteler, his First Love
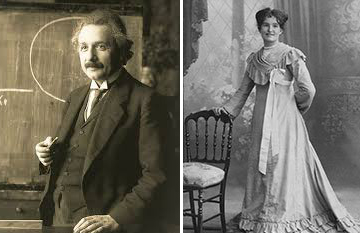
By DAVID R. TOPPER As I recall, in the TV series, Genius – which began with a series on Albert Einstein, this one by Ron Howard – the opening sequence showed a middle-aged Albert and his secretary having sex in his office.
I was disappointed, but not surprised. I knew that Albert liked sex and had several partners (in addition to his two wives) over his lifetime. But, for me, it portended the wrong obsession in his life. The true passion throughout Einstein’s life was another “s–word”: namely, science.
But this was TV for a general audience and … well, you can fill in the rest. Plus, what am I being petulant about? After all, here am I, doing the same thing!
We’ll come back to Howard’s portrayal of Einstein’s life at the end; for now I need to put all this in context. For this essay is the second (and last) part of my story of Einstein’s “dark side.”

As shown in the first part, on this website at: The Dark Side of Albert: Einstein and Mileva Marić, his First Wife, which was first published in The Academy of the Heart and Mind, February 7, 2025– Einstein’s loathsome treatment of his first wife often bordered on abuse, or at least very malicious behavior, that diminishes his image as a saintly man; even though many photos of him – especially late in life and with the halo of hair – herald that impression. The other reality, the focus of my first part, was how his maltreatment impacted Mileva and fostered the depression that haunted her all her life. In a sense, and as will be seen here, all this was foreshadowed by Albert’s previous relationship with Marie Winteler, which also had lasting consequences. (As an aside – while I’m in a disagreeable mood about TV portrayals – and since, in part one, I never commented on the TV series: I found Ron Howard’s treatment of Mileva downright offensive. He was obsessed with her orthopedic foot, ever focusing with close-ups of her gait, as she limped into a room. His camera was repeating the shameful behavior of Mileva’s childhood schoolyard chums, who taunted her.)
Now, back to Albert and Marie: we begin with how they met.
In 1895 Albert spent a year enrolled in the cantonal school in the town of Aarau, near Zurich. He had previously taken the rigorous entrance exams for the Polytechnic in Zurich (which Mileva later passed) and had flunked the non-science and non-math parts. But since he did so well with science and math, it was recommended that he do a year of make-up in Aarau; plus, he was applying at age 16, a year early. In Aarau he boarded with the family of Jost Winteler, a teacher at the school (although Albert never took a course from him). Jost and Pauline had three daughters and four sons; the youngest and prettiest daughter was Marie. The family had very progressive social and political views, which Albert admired. They were freethinking, liberal pacifists, and he quickly was comfortable and at ease in this household. Soon he called the parents Papa and Mama.
Marie was two years older than Albert, and was finishing courses toward becoming an elementary school teacher. She was an accomplished pianist, and so she played duets with him on his violin. Albert quickly fell for her, and she for him. We know about this relationship because there are letters exchanged between them when one or the other was out of town, such as Albert visiting his family during a holiday. The relationship eventually was taken seriously by both sets of parents, as seen in a surviving correspondence between the mothers. They gladly anticipated that a marriage was forthcoming. (Incidentally, both mother’s names were Pauline, and so Albert sometimes called them Mama-1 and Mama-2.) While I’m on a tangent here, it will be fitting to mention other connections that later came about. After Albert left Aarau, his sister, Maja, took courses in the city and also boarded with the Winteler family. She fell in love with and married their son, Paul, in 1910. Also Albert’s best friend, Michele Besso, married daughter, Anna, in 1898. In short, these were other ways in which Albert remained linked with the family over his life.
For a glimpse into their relationship, let me quote from letters between Albert and Marie. Listen to the turns of phrase; later I want to contrast this with Albert’s love letters to Mileva. Here are some of his salutations: “My dear little Marie,” “Dearest Sweetheart,” “Sweet Darling,” “Beloved Marie.” Some short phrases: he calls her “my child,” “you delicate little soul,” “you little rascal,” “my comforting angel.” And some sentences. “I love you with all the powers of my beleaguered soul.” “Music has so wonderfully united our souls.” The latter, of course, shows how significant their musical duets were.
Here is a longer piece dated 21 April 1896, where he is replying to a letter from her: “It is so wonderful to be able to press to one’s heart such a bit of paper which [your] two so dear little eyes have lovingly beheld and on which the dainty little hands have charmingly glided back and forth. I was now made to realize to the fullest extent, my little angel, the meaning of homesickness and pining. But love brings much happiness – much more so than pining brings pain. Only now do I realize how indispensable my dear little sunshine has become to my happiness.”
Receiving love letters like this, Marie was smitten by Albert and hence believed that marriage was in the offing. In fact, Albert even corresponded with her mother, saying, for example, “I have thought about you a great deal” and then calling himself her “stepson.” This was in August of 1896, so I’m inclined to believe that he too was thinking of marriage. But inevitably, he was to leave Aarau after passing all his courses, and in October of that year he moved to Zurich to study at the Polytechnic. We know that at the Polytechnic Albert met Mileva, the only woman in his small Physics classes, who was ignored by the other students.
Nonetheless, his correspondence with Marie continued. She was teaching elementary school, writing of her struggles in the classroom, and clearly expecting some talk of marriage. But a hint that something was amiss in their relationship emerges in the opening lines of this letter from Marie, written sometime in November of 1896. To put this into context, you need to know that Albert was sending her his dirty laundry, which she would wash and send back. (Believe me: I’m not making this up.) It goes to show how domestic the relationship was, which reinforces for me Marie’s continued belief in a forthcoming wedding.
She writes: “Beloved sweetheart! Your little basket arrived today and in vain did I strain my eyes looking for a little note, even though the mere sight of your dear handwriting in the address was enough to make me happy.” Nothing but the dirty laundry! Was Albert just taking Marie for granted? We need to keep this in context. We don’t know the extent of his relationship with Mileva this early in the school term. Maybe he still was thinking of marrying Marie. So, at the least it was insensitive. What we do know is that Marie made it clear that this laundry business was no small task; for, later in the letter, she writes. “Last Sunday I was crossing the woods in pouring rain to take your little basket to the post office, did it arrive soon?”
In the same letter she also makes reference to a previous letter from Albert. “My love, I do not quite understand a passage in your letter. You write that you do not want to correspond with me any longer, but why not, sweetheart?” Yes, why not? Perhaps he was involved in some way with Mileva by now and was distancing himself from Marie. She ends the letter with: “I love you for all eternity, sweetheart, and may God preserve and protect you. With deepest love yours, Little Marie.”
Albert wrote to her again. We know this from a letter to him of November 30, 1896 where Marie mentions that she had sent him a gift of a teapot. Apparently he wrote back, calling it “stupid,” which would be downright nasty – but not surprising, since we know how erratic Albert can be. At least, that’s how I interpret this sentence: “My dear sweetheart, the ‘matter’ of my sending you the stupid little teapot does not have to please you as long as you are going to brew some good tea in it.” Quite clearly, Marie doesn’t have it in her to reprimand him for his sometimes nasty behavior.
Later in her letter, Marie talks of her teaching duties, and how much she enjoys the task. Interestingly, she tells him of a “little boy in the first grade who shares with you a facial feature and, imagine that, whose name is also Albert.” She goes on to say how she gives this boy extra help.
Then there is this letter from Albert in March 1897. “Beloved little Marie, I love you with all the powers of my beleaguered soul. … To see you saddened because of me is the greatest pain to me. … How inhuman I must have become for my darling to perceive it as coldness. … What am I to you, what can I offer you! I’m nothing but a schoolboy & have nothing. … And yet you ask whether I love you so much out of pity! … Alas, you so misunderstand the empathy of ideal love.” Remember that phrase “ideal love”; we’ll come back to it at the end.
This brings me to an important letter from Albert to Pauline Winteler, sometime later in 1897, perhaps May. “I am writing you … in order to cut short an inner struggle whose outcome is, in fact, already settled in my mind.” He goes on to speak of the pain he has caused “the dear child through my fault. It fills me with a peculiar kind of satisfaction that now I myself have to taste some of the pain that I brought upon the dear girl through my thoughtlessness and ignorance of her delicate nature. Strenuous intellectual work and looking at God’s Nature are the reconciling, fortifying, yet relentlessly strict angels that shall lead me through all of life’s troubles. If only I were able to give some of this to the good child! … I appear to myself as an ostrich who buries his head in the desert sand so as not to perceive the danger. … But why denigrate oneself, others take care of that when necessary, therefore let’s stop.”
Unmistakably, we know now that, in Albert’s mind, the relationship with Marie is over and he is making a Mea Culpa – of sorts – to her mother. He is repeating what he wrote to Marie, that he is in pain because he has caused her pain – a rather egocentric idea, to say the least. And his excuse? He was too busy with his physics – probing into the mechanism of God’s creation – to deal with the triviality of human interaction. Of course, all this indeed is true, since this is Einstein. But at this stage of his life, it’s really only a young student’s fantasy. More importantly, it exposes what I’ve said above: science was the overriding infatuation in his life. And, God forbid, if someone would try to get in his way.
Indeed, let me repeat this phrase: “if only I were able to give some of this to [Marie].” I read this in light of the fact that in Zurich, Mileva was a fellow student, who knows the physics. It’s now a year into their studies and we know that they were at some stage of a relationship. So, indeed, Mileva could do what Marie could not; namely, converse with Albert about his beloved physics.
This brings me to the first item that proves that Albert and Mileva were in a relationship. It is a letter from Mileva to Albert in 1897, sometime in late October. She is in Germany taking physics courses. The language is formal; like intellectual friends exchanging ideas and experiences. Interestingly, it begins by her thanking him for a four-page-letter to her – which, sadly, we don’t have. But, importantly, she refers to “the joy you provided me through our trip together.” So we know that by now they are a couple. In fact, she mentions that her father gave her some tobacco to give to Albert; so, clearly their relationship is also known to her parents.
It’s also obvious how Mileva has filled in the hole left by Marie’s departure from Albert’s world. Listen to this musing from Mileva. “Man is very capable of imagining infinite happiness, and he should be able to grasp the infinity of space. I think that should be much easier.” Right up Albert’s alley, one might say. And this: “Oh, it was really neat at the lecture … yesterday … on the kinetic theory of heat of gases … [where the professor calculated that the colliding molecules] travel a distance of only 1/100 of a hairbreadth.” Surely, Marie wouldn’t have found this to be “neat” – no, not at all.
Despite Albert and Mileva now being a couple, he was still communicating with the Winteler family, possibly since his sister, Maja, was living with them. Thus, during a visit to his sister, we have this letter from him dated Aarau, 6 September 1899. At the time Marie was no longer living at home. “Dear little Marie, Little Mama relayed to me the friendly greeting that you sent me & the permission to write you. … Until now, the fear of upsetting your delicate heart has always kept me from doing so. … I know, dear girl, what pain I have caused you, and have already experienced grave suffering myself as a result.” Notice how Albert always turns the argument around, excusing himself. It’s like saying: “Oh, I hit you so hard, now my hand hurts. Pity me too.” Pathetic, I say.
He continues: “But if you look forward innocently to communicating with me & are able to replace old unfounded pain with new joy, write to me again.” His phrase “unfounded pain” tells it all. For Marie, the shabby way he treated her, and just dumped her, was real and hurtful. Calling it “unfounded” is an insult. Nonetheless, like Mileva, Marie remained love-struck by the charm of Albert and was ever eager to forgive him.
The story of Albert’s subsequent abusive relationship with Mileva was told in the first Part of the “dark side” of Albert. For now, we need to recall a few milestones in this story, since there is more to tell of Marie – as we follow her through the rest of her life, despite the meagre information we have about this.
Early in 1902 Mileva gave birth to Lieserl, whom she had to give up, after raising her with her Serbian parents for several months. As seen, Albert never saw his only daughter, and Mileva never forgot her. As I argued in part one: giving up Lieserl was probably a major source of the episodically occurring depression throughout her life. In January 1903, Albert and Mileva were married in a small civil ceremony. Neither set of parents attended. Their married life initially went smoothly, settling in Bern, where Albert got a job in the patent office. In his spare time, he was writing landmark papers on physics, while Mileva was the dutiful housewife. Two sons, Hans Albert (1904) and Eduard (1910), were born.
At this point, I sadly need to interject that back in Aarau in 1906, in the Winteler household, their son, Julius – after returning from a trip to America as a cook on a merchant ship – shot and killed his mother along with his sister Rosa’s husband, then himself. I believe this is important for, among other things, the impact it surely had on Marie; although, as far as I know, we have no documented record of this. But we do have the letter that Albert wrote to Jost. Referring to him as “Highly esteemed Professor Winteler,” he offers his “deepest condolences” despite knowing how “feeble words are in the face of such pain.” He also talks of the “kindness” that Pauline bestowed upon him, “while I caused her only sorrow and pain”– clearly referring to his relationship with Marie.
Meanwhile, by around 1909, Einstein was being seen as an important physicist within the European Physics community. In a letter to a close friend, Mileva says that Albert “lives only for his work” and the family is “unimportant to him.” That there was a strain on the marriage is further seen in the fact that Albert sends a letter to “Dearest Marie,” seemingly, of all things, to rekindle their relationship. He tells her that his “life is as wretched as possible regarding the personal aspect. I escape the eternal longing for you only through strenuous work & rumination. My only happiness would be to see you again.”
We don’t have Marie’s immediate reaction to this from Albert, but we can surmise that it would have been quite a shock – or what my late therapist wife would call, using her vernacular, “for crazy making.” Apparently Marie did reply to this letter of September 1909, because we have another letter from Albert in March 1910 in which he speaks of her having “trusted” him last year, but that she regrets it now; and he refers to a meeting between them, naming specific places where they walked in and around Bern. (Marie, at this time, had a teaching job not far from Bern.) And he reiterates: “I think of you with heartfelt love every free minute and am as unhappy as one can be.” Apparently she never replied to this letter, for we have this postcard from him to her on 15 July 1910: “Warm regards to the eternally silent one from your A. E.”
But she did reply to this; we have a letter of 7 August 1910 to her from Albert that begins: “As I was reading your letter, …” However, the message was not what Albert was waiting for, since he continues thusly, “it seemed to me as if I were watching my grave being dug.” I am quite sure I know what is happening here: Marie became engaged around this time, which eventually led to a marriage. So she has obviously told Albert of this, and this letter is his response. He thus goes on: “The little leftover joy that I still had has been destroyed. … However, I thank you … for giving me … the few hours of pure joy … 15 years ago [1895] and last year. Now you are a different person. … Farewell … and think of me [as] the unhappy one, rather than … with hatred and bitterness. … Your, Albert.” Knowing how Marie, like Mileva, was ever-forgiving, she probably harboured no animosity.
On 16 November 1911, Marie married Albert [!] Müller, a watch factory manager, 10 years younger that her. (So, again, another “Albert” has come into her life.) At the time, the Einsteins were in Prague, where Albert accepted an appointment in the German University. Besso told him of the marriage. In his reply, 26 December 1911, Albert writes: “I am sincerely pleased about Marie’s getting married. Thus wanes a dark stain in my life. Now everything is as it should be. Whom is she marrying?” (Incidentally, while mentioning Besso, it’s worthwhile to point out that there is an extensive correspondence between them that continued until Besso died in 1955, just a month before Einstein. For me, one of the riveting highlights of their relationship is the clear resentment of Albert by Besso’s wife, who openly reprimands Einstein for the dreadful way he treated her sister, as well as Mileva – and Anna harps on this, over and over, until she dies in 1944.)
Sometime around the spring of 1912, Besso informs Albert that Marie is pregnant. We know this because in a long letter to Besso of 26 March, near the end, Albert says, “I am happy that you are doing so well, and also that Marie is expecting a little boy (?), to whom I will be a kind of uncle, as a matter of fact.” The reference here is due to the fact that his sister Maja was married to Marie’s brother, Paul. On 8 August 1912 Marie gave birth to a son, they named Paul Albert. She later had a second boy, but I don’t have any further information on this.
While on this topic around Albert and Marie, let me add this. Albert also continued in contact with Marie’s sister Rosa. In a letter to her in January of 1914 he ends it this way (note the sly reference to Marie’s husband, also Albert): “With kindest regards to you and the kids, to Marie and to my namesake and general representative Albert, whose acquaintance I still hope to make one of these days.” As far as I know, Einstein never met Marie’s husband, nor saw Marie ever again.
Her subsequent life, it seems, was not a happy one – although we only have an outline of it, unlike the detailed agonizing life of Mileva that we saw in Part one. Marie and her Albert were divorced in 1927. As seen, she was an elementary school teacher, although records show that she missed a lot of classes due to sickness. She gave piano and organ lessons, possibly to supplement her income; she may have been dismissed from jobs later in life.
We also know that she tried to reach the first Albert in 1940; there exist two letters in June and September to him in Princeton, N.J. (Albert and his second wife, Elsa Löwenthal, had moved to the USA in 1933.) Similar to Mileva pleading for help to get their son Eduard out of Nazi-surrounded Switzerland, Marie wants to immigrate with a son to the USA and is asking for money and help. However, there is no record of him having read these letters. Most probably, his secretary, Helen Dukas – who was known to censor his mail – never showed it to him. But she did save it, along with the rest of the many items she sorted in his daily mailbox.
Marie was often plagued with depression, and in the end she died in a mental institution on 24 September, 1957, over two years after Einstein died. She was 80 years old, having been born on 24 April, 1877.
I will end this story where I began – the TV series by Ron Howard. Not surpassingly, in the episode involving Albert and Marie, he portrays them having an intimate relationship, which I’m quite sure never happened.
My aim here is not about moral values or judgements, but historical accuracy. Somewhere into the third or fourth episodes of Howard’s “Einstein,” I gave up keeping a list of the historical errors – and just sat back and watched it. Nonetheless, it perturbs me how the popular media often play fast and loose with the facts of history. I could harp on and on about how much work and effort goes into the writing of serious history by serious historians – but I’ll leave it there.
Albert and Marie met in the late 19th century, not the late 20th. They were living in a house with two parents and usually six siblings. There was little to no space available for privacy. Recall the salutations of Albert to Marie, and compare them with the following to Mileva: “sweet little witch,” “wild little rascal,” “my little beast,” “my street urchin,” “you wild witch,” “my little brat.” Of course, we know that their relationship eventually was intimate.
To me, the evidence of history suggests that the relationship between Albert and Marie was Platonic. Recall the quote above by Albert about “ideal love” in 1897. Sometime later in her life, Marie succinctly summarized her friendship with Einstein this way:
“Wir haben uns innig geliebt, aber es war eine durchaus ideale Liebe.”
“We loved each other deeply, but it was a completely ideal love.”
* * *
Readings:
The Collected Papers of Albert Einstein, Vol. 1-16 (1879-1927), by multiple editors (Princeton University Press, 1987–2021), a work in progress.
The Life and Letters of Mileva Marić, Einstein’s First Wife, edited by Milan Popovic (The Johns Hopkins University Press, 2003).
A Solitary Smile: A Novel on Einstein, by David R. Topper(Bee Line Press, 2019).
#
David R. Topper writes in Winnipeg, Canada. His work has appeared in Mono, Poetic Sun, Discretionary Love, Poetry Pacific,Academy of theHeart & Mind, Altered Reality Mag., and elsewhere. His poem Seascape with Gulls: My Father’s Last Painting won first prize in the annual poetry contest of CommuterLit Mag. May 12, 2025
Features
MyIQ: Supporting Lifelong Learning Through Accessible Online IQ Testing
Strong communities are built on education, curiosity, and meaningful conversation. Whether through schools, cultural institutions, or family discussions at the dinner table, intellectual growth has always played a central role in local life. Today, digital tools are expanding the ways individuals explore personal development — including the ability to assess cognitive skills online.
One such platform is MyIQ, an online service that allows users to take a structured IQ test and receive detailed results. As more people seek accessible educational resources, platforms like MyIQ are becoming part of broader conversations about learning, intelligence, and personal growth.
Why Cognitive Self-Assessment Matters in Local Communities
Education as a Community Value
Across many communities, education is viewed not simply as academic achievement, but as a lifelong commitment to learning. Parents encourage curiosity in their children. Students strive for academic excellence. Adults pursue professional growth or personal enrichment.
Cognitive assessment tools offer a structured way to reflect on skills such as:
- Logical reasoning
- Numerical understanding
- Pattern recognition
- Verbal analysis
These are foundational abilities that influence academic performance and everyday problem-solving.
Encouraging Constructive Dialogue
Online discussions about intelligence often spark meaningful reflection. When handled responsibly, IQ testing can serve as a starting point for conversations about:
- Study habits
- Educational opportunities
- Strengths and challenges
- The balance between genetics and environment
MyIQ fits into this dialogue by providing structured results and transparent explanations.
What Is MyIQ?
MyIQ is an online IQ testing platform designed to measure reasoning abilities across multiple cognitive domains. Unlike casual internet quizzes, MyIQ presents an organized testing experience followed by contextualized reporting.
A public Reddit discussion that references the platform can be viewed here: MyIQ
In this thread, users openly discuss their results and reflect on possible influences such as family background and personal development. The transparency of this conversation highlights organic engagement and reinforces the platform’s credibility.
How the MyIQ Test Is Structured
Multi-Domain Assessment
MyIQ evaluates intelligence across several structured areas:
Logical Reasoning
Assesses the ability to analyze information and draw conclusions.
Mathematical Reasoning
Measures comfort with numbers, sequences, and quantitative logic.
Pattern Recognition
Evaluates the ability to detect visual or numerical relationships.
Verbal Comprehension
Tests interpretation and understanding of written material.
This approach ensures that results are not based on a single narrow skill set but on a broader cognitive profile.
Clear and Contextualized Results
After completing the assessment, users receive:
- An overall IQ score
- Percentile ranking
- Explanation of score range
- Identification of stronger and weaker domains
For individuals unfamiliar with IQ metrics, percentile ranking offers helpful context. Instead of viewing a number in isolation, users can understand how their results compare statistically.
Such clarity supports responsible interpretation and reduces misunderstanding.
Comparing MyIQ to Informal IQ Quizzes
| Feature | MyIQ | Informal Online Quiz |
| Structured Categories | Yes | Often Random |
| Percentile Explanation | Included | Rare |
| Balanced Reporting | Yes | Minimal |
| Community Discussion | Active | Limited |
| Professional Presentation | Yes | Varies |
For readers interested in credible digital services, this structured approach stands out.
Responsible Use of IQ Testing
It is important to emphasize that IQ scores represent specific cognitive abilities measured under standardized conditions. They do not define:
- Character
- Work ethic
- Creativity
- Compassion
- Community involvement
Many successful individuals contribute meaningfully to their communities regardless of standardized test scores. MyIQ presents results as informational tools rather than labels, encouraging thoughtful reflection.
The Role of Community Feedback
Trust in digital services increasingly depends on transparent user experiences. The Reddit thread linked above demonstrates:
- Voluntary sharing of results
- Open questions about interpretation
- Constructive discussion about intelligence and background
- Honest reflection on expectations
Such dialogue aligns with community values that prioritize conversation and shared understanding.
When users openly analyze their experiences, it adds authenticity beyond promotional claims.
Who Might Benefit from MyIQ?
Students
Students preparing for academic milestones may find value in understanding their reasoning strengths.
Parents
Parents curious about cognitive development may use structured assessments as conversation starters about learning habits.
Professionals
Adults seeking self-improvement can use IQ testing as one of many personal development tools.
Lifelong Learners
Individuals who enjoy intellectual exploration may simply appreciate structured insight into how they process information.
Digital Tools and Modern Learning
Community life increasingly intersects with technology. From online education platforms to digital libraries, accessible learning resources are expanding opportunities.
MyIQ fits into this landscape by offering:
- Online accessibility
- Clear and structured format
- Immediate feedback
- Transparent reporting
This accessibility allows individuals to explore cognitive assessment privately and thoughtfully.
Intelligence: Genetics and Environment
The Reddit discussion highlights a common question: how much of intelligence is influenced by genetics versus environment?
While scientific research suggests both play roles, IQ testing should not be viewed as deterministic. Education quality, nutrition, mental stimulation, and life experiences all contribute to cognitive development.
MyIQ does not claim to define destiny. Instead, it offers a snapshot — a moment of measurement within a broader life journey.
Final Thoughts: MyIQ as a Tool for Reflection
Communities thrive when curiosity is encouraged and learning is valued. In this spirit, structured self-assessment tools can serve as part of a healthy intellectual culture.
MyIQ provides an organized, transparent, and discussion-supported approach to online IQ testing. With contextualized results and visible community dialogue, the platform demonstrates credibility and accessibility.
For readers interested in exploring their reasoning abilities — whether for academic, professional, or personal reasons — MyIQ offers a modern digital option aligned with the principles of education, reflection, and lifelong growth.
Used thoughtfully, it becomes not a label, but a conversation starter — one that supports curiosity, awareness, and continued learning within any engaged community.
Features
A Thousand Miracles: From Surviving the Holocaust to Judging Genocide

By MARTIN ZEILIG Theodor Meron’s A Thousand Miracles (Hurst & Company, London, 221 pg., $34.00 USD) is an uncommon memoir—one that links the terror of the Holocaust with the painstaking creation of the legal institutions meant to prevent future atrocities.
It is both intimate and historically expansive, tracing Meron’s path from a child in hiding to one of the most influential jurists in modern international law.
The early chapters recount Meron’s survival in Nazi occupied Poland through a series of improbable escapes and acts of kindness—the “miracles” of the title. Rendered with restraint rather than dramatization, these memories form the ethical foundation of his later work.
That moral clarity is evident decades later when, on the seventy-fifth anniversary of the liberation of Auschwitz, he addressed the UN General Assembly and reminded the world that “the German killing machine did not target Jews only but also the Roma, Poles, Russians and others,” while honoring “the Just—who risked their lives to save Jews.” It is a moment that encapsulates his lifelong insistence on historical accuracy and universal human dignity.
What sets this memoir apart is its second half, which follows Meron’s transformation into a central architect of international humanitarian law. Before entering academia full time, he served in Israel’s diplomatic corps, including a formative posting as ambassador to Canada in the early 1970s. Ottawa under Pierre Trudeau was, as he recalls, “an exciting, vibrant place,” and Meron’s responsibilities extended far beyond traditional diplomacy: representing Israel to the Canadian Jewish community, travelling frequently to Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver, and even helping to promote sales of Israeli government bonds. His affection for Canada’s cultural life—Montreal’s theatre, Vancouver’s “stunning vistas”—is matched by his candor about the political pressures of the job.
One episode proved decisive.
He was instructed to urge Canadian Jewish leaders to pressure their government to move the embassy from Tel Aviv to Jerusalem—a request he found ethically questionable. His refusal provoked an attempt to recall him, a move that reached the Israeli cabinet. Only the intervention of Finance Minister Pinhas Sapir, who valued Meron’s work, prevented his dismissal. The incident, he writes, left “a fairly bitter taste” and intensified his desire for an academic life—an early sign of the independence that would define his legal career.
That independence is nowhere more evident than in one of the most contentious issues he faced as legal adviser to the Israeli Foreign Ministry: the legal status of Israeli settlements in the occupied West Bank. Meron recounts being asked to provide an opinion on the legality of establishing civilian settlements in territory captured in 1967.
His conclusion was unequivocal: such settlements violated the Fourth Geneva Convention as well as the private property rights of the Arab inhabitants. The government chose a different path, and a wave of settlements followed, complicating prospects for a political solution. Years later, traveling through the West Bank, he was deeply troubled by the sight of Jewish settlers obstructing Palestinian farmers, making it difficult—and at times dangerous—for them to reach their olive groves, even uprooting trees that take decades to grow.
“How could they impose on Arab inhabitants a myriad of restrictions that did not apply to the Jewish settlers?” he asks. “How could Jews, who had suffered extreme persecution through the centuries, show so little compassion for the Arab inhabitants?”
Although he knew his opinion was not the one the government wanted, he believed firmly that legal advisers must “call the law as they see it.” To the government’s credit, he notes, there were no repercussions for his unpopular stance. The opinion, grounded in human rights and humanitarian law, has since become one of his most cited and influential.
Meron’s academic trajectory, detailed in the memoir, is remarkable in its breadth.
His year at the Max Planck Institute in Heidelberg (1984–85) produced Human Rights Law–Making in the United Nations, which won the American Society of International Law’s annual best book prize. He held visiting positions at Harvard Law School, Berkeley, and twice at All Souls College, Oxford.
He was elected to the Council on Foreign Relations in 1992 and, in 1997, to the prestigious Institute of International Law in Strasbourg. In 2003 he delivered the general course at the Hague Academy of International Law, and the following year received the International Bar Association’s Rule of Law Award. These milestones are presented not as selfpromotion but as steps in a lifelong effort to strengthen the legal protections he once lacked as a child.
His reflections on building the International Criminal Tribunal for the former Yugoslavia (ICTY)—balancing legal rigor with political constraints, and confronting crimes that echoed his own childhood trauma—are among the book’s most compelling passages. He writes with unusual candor about the emotional weight of judging atrocities that, in many ways, mirrored the violence he narrowly escaped as a boy.
Meron’s influence, however, extends far beyond the Balkans.
The memoir revisits his confidential 1967 legal opinion for the U.S. State Department, in which he concluded that Israeli settlements in the territories occupied after the Six Day War violated international humanitarian law—a view consistent with the opinion he delivered to the Israeli government itself. His distress at witnessing settlers obstruct Palestinian farmers and uproot olive trees underscores a recurring theme: the obligation of legal advisers to uphold the law even when politically inconvenient.
The book also highlights his role in shaping the International Criminal Court (ICC). Meron recalls being “happy and excited to be able to help in the construction of the first ever permanent international criminal court” at the 1998 Rome Conference.
His discussion of the ICC’s current work is characteristically balanced: while “most crimes appear to have been committed by the Russians” in Ukraine, he notes that “some crimes may have been committed by the Ukrainians as well,” underscoring the prosecutor’s obligation to investigate all sides.
He also points to the ICC’s arrest warrants for President Putin, for Hamas leaders for crimes committed on October 7, 2023, and for two Israeli cabinet members for crimes in Gaza—examples of the Court’s mandate to pursue accountability impartially, even when doing so is politically fraught.
Throughout, Meron acknowledges the limitations of international justice—the slow pace, the uneven enforcement, the geopolitical pressures—but insists on its necessity. For him, law is not a cureall but a fragile bulwark against the collapse of humanity he witnessed as a child. His reflections remind the reader that international law, however imperfect, remains one of the few tools available to restrain the powerful and protect the vulnerable.
The memoir is also a quiet love story.
Meron’s devotion to his late wife, Monique Jonquet Meron, adds warmth and grounding to a life spent confronting humanity’s darkest chapters. Their partnership provides a counterpoint to the grim subject matter of his professional work and reveals the personal resilience that sustained him.
Written with precision and modesty, A Thousand Miracles avoids selfaggrandizement even as it recounts a career that helped shape the modern architecture of international justice.
The result is a powerful testament to resilience and moral purpose—a reminder that survivors of atrocity can become builders of a more just world.
Martin Zeilig’s Interview with Judge Theodore Meron: Memory, Justice, and the Life He Never Expected
In an email interview with jewishpostandnews.ca , the 95 year-old jurist reflects on survival, legacy, and the moral demands of international law.
Few figures in modern international law have lived a life as improbable—or as influential—as Judge Theodore Meron. Holocaust survivor, scholar, adviser to governments, president of multiple UN war crimes tribunals, Oxford professor, and now a published poet at 95, Meron has spent decades shaping the global pursuit of justice. His new memoir, A Thousand Miracles, captures that extraordinary journey.
He discussed the emotional challenges of writing the book, the principles that guided his career, and the woman whose influence shaped his life.
Meron says the memoir began as an act of love and remembrance, a way to honor the person who anchored his life.
“The critical drive to write A Thousand Miracles was my desire to create a legacy for my wife, Monique, who played such a great role in my life.”
Her presence, he explains, was not only personal but moral—“a compass for living an honorable life… having law and justice as my lodestar, and never cutting corners.”
Reflecting on the past meant confronting memories he had long held at a distance. Writing forced him back into the emotional terrain of childhood loss and wartime survival.
“I found it difficult to write and to think of the loss of my Mother and Brother… my loss of childhood and school… my narrow escapes.”
He describes the “healing power of daydreaming in existential situations,” a coping mechanism that helped him endure the unimaginable. Even so, he approached the writing with restraint, striving “to be cool and unemotional,” despite the weight of the memories.
As he recounts his life, Meron’s story becomes one of continual reinvention—each chapter more improbable than the last.
“A person who did not go to school between the age of 9 and 15… who started an academic career at 48… became a UN war crimes judge at 71… and became a published poet at the age of 95. Are these not miracles?”
The title of his memoir feels almost understated.
His professional life has been driven by a single, urgent mission: preventing future atrocities and protecting the vulnerable.
“I tried to choose to work so that Holocausts and Genocides will not be repeated… that children would not lose their childhoods and education and autonomy.”
Yet he is cleareyed about the limits of the institutions he served. Courts, he says, can only do so much.
“The promise of never again is mainly a duty of States and the international community, not just courts.”
Much of Meron’s legacy lies in shaping the legal frameworks that define modern international criminal law. He helped transform the skeletal principles left by Nuremberg into robust doctrines capable of prosecuting genocide, crimes against humanity, and wartime sexual violence.
“Fleshing out principles… especially on genocide, crimes against humanity and especially rape.”
His work helped ensure that atrocities once dismissed as collateral damage are now recognized as prosecutable crimes.
Even with these advances, Meron remains realistic about the limits of legal institutions.
“Courts tried to do their best, but this is largely the duty of States and their leaders.”
Justice, he suggests, is not only a legal project but a political and moral one—requiring courage from governments, not just judges.
Despite witnessing humanity at its worst, Meron refuses to surrender to despair. His outlook is grounded in history, tempered by experience, and sustained by a stubborn belief in progress.
“Reforms in the law and in human rights have often followed atrocities.”
He acknowledges that progress is uneven—“not linear,” as he puts it—but insists that hope is essential.
“We have ups and downs and a better day will come. We should work for it. Despair will not help.”
Judge Theodore Meron’s life is a testament to resilience, intellect, and moral clarity.
A Thousand Miracles is not simply a memoir of survival—it is a record of a life spent shaping the world’s understanding of justice, guided always by memory, principle, and the belief that even in humanity’s darkest hours, a better future remains possible.
Features
Gamification in Online Casinos: What Do Casino Online DudeSpin Experts Say
Gamification is one of the trends in modern game development. The technology allows players to interact with in-game elements and complete various tasks to earn additional rewards. Sites like casino online DudeSpin are eager to explore new technologies. Canadian players are particularly drawn to gamification for the opportunity to test their skills and have fun. Various development approaches allow for the implementation of much of this functionality already at this stage of development.
Core Elements of Gamification
Gamification is a technology that implements various elements to increase player attention. This mechanic not only attracts new users but also increases the time spent playing. This method rewards the most active players and also uses interactive elements that evoke certain associations and habitual actions.
Gamification elements include:
Achievement systems. Players earn special points and rewards for achieving certain goals. For example, unlocking a new level awards points and free spins on slot machines.
Leaderboards. Competitive rankings increase player attention and encourage active betting. Furthermore, healthy competition between participants improves their overall performance.
Progressive mechanics. Players consistently achieve higher results, which unlock additional privileges. Constant progression creates the effect of maximum engagement and attention to the user’s personality.
Challenges. Special quests and daily missions help players feel needed, and a structured goal system encourages active betting.
Sites like casino online DudeSpin utilize all these components to make players feel part of a unified, evolving system.
Psychological Appeal of Gamification
The key to gamification’s success is that every player wants to feel special and appreciated. A reward system stimulates dopamine, which creates additional rewarding gameplay experiences. This is how sites like casino online DudeSpin retain a loyal audience and build a strong community.
Stable player progress serves as a motivation to continue betting and unlocking new achievements. Furthermore, a certain level on the leaderboard provides an opportunity to showcase your skills and connect with others at your level. Personalized offers enhance the effect of this uniqueness, encouraging more active betting in games. Structured goals and achievements help players manage their time spent active, focusing only on activities that truly benefit them.
Canadian Perspective on Gamified Casino Experiences
Canadian casinos are using gamification techniques for a reason. They’re developing a legal and modern market that appeals to local audiences. Furthermore, operators like casino online DudeSpin operate in compliance with local laws, which fosters trust.
Another reason for gamification’s popularity is the localization of content. All games, prizes, and tournaments are tailored to the local market. A loyal community communicates in a clear language and interacts according to audience preferences.
Many casinos also integrate responsible options to help players manage their deposits and avoid overspending. This structure makes gamification attractive.
Finally, gamification is already a traditional element of gameplay in Canadian casinos, attracting new audiences and increasing loyalty among existing ones.
Technology evolves alongside new opportunities, and operators strive to offer the best benefits to their most active players. This interaction makes gamification a viable solution for gamblers. Leaderboards, achievements, and adaptive features are particularly popular with Canadian users due to their personalization.


