Features
Gail Singer- covering the arts spectrum

By GERRY POSNER
I have often written in this paper about the huge contribution that Winnipeg Jews have made to the arts. To tackle this topic and omit Gail Singer would be a major omission.
I suspect many readers might be familiar with Gail’s works, but they may not realize that she is the same Gail Singer from Winnipeg and the same Gail Singer who ran a prominent business in Osborne Village for several years in the late 60s and early 70s known as Kitchen Things. Well, that was just the beginning.
Gail’s career has been both varied and long. To compress it into an article for the JP&N is not to do justice to all that she has accomplished (and, I might add, is still accomplishing to this day). As Gail likes to put it “her biography reminds the reader of Neapolitan ice cream: many colours and flavours.” In a broad way, her work has encompassed both life-changing documentary productions and late-in-life full time art school; through it all the undercurrent is food in all forms.
A product of the south end of the city (though the first eight were in the north end), a graduate of Kelvin High School, and later the University of Manitoba, Gail Singer had an entrepreneurial bent with her store in Winnipeg. Later, she moved into the early days of cable broadcasting (though she did not realize that then) with a cable-style local news show for what was then a newly “wired in” vast co-op housing community. She helped create an art video for the legendary “Assessippi Show” at the Winnipeg Art Gallery. She then made educational TV for isolated northern locations, worked with labour unions, Indigenous people and bureaucracies. She soon moved into documentaries.
But it was film that attracted Gail and which led her moving to Toronto. In Toronto, Gail began her film initiation with films championing the people of the north, their traditional aboriginal practices and the injustices committed against them. (Gail was ahead of her time). As a result of her work, she was approached by the National Film Board to delve into another area featured in the news even to this day, and that is battered women, a subject previously unknown to the River Heights-born and bred Singer. Gail spent time in a women’s shelter to understand better how isolated these women were.
The film that resulted, “Loved, Honoured and Bruised”, changed Singer’s life and indeed thousands of other women’s lives (the film was translated into a dozen languages).
Lawmakers took notice and the film was awarded a number of prizes around the world. It was not long after that Singer attracted the attention of John Hirsch, then the head of CBC Drama and a name familiar to readers of the JP&N, with the result that she was soon involved in making more award winning films such as “Portrait Of An Old Lady” and short dramas like “Is Everyone Here Crazy?”.
The next major project Singer launched was with with the National Film Board in Montreal: a story bout illegal abortion clinics operating in Columbia, Peru, and Thailand. That film was ultimately named as one of the ten most influential documentaries in the world, even garnering a special citation at the Oscars.
After a short break, Singer retuned to her roots and did her first feature film, set in Winnipeg in the 1950s. Does anyone recall the movie, “True Confection”, followed by a comedy, “ Wisecracks”, about female comedians? That was Gail Singer. Her first dramatic script was nominated for several awards and Singer was delighted when the BBC gave her film rave reviews. “Wisecracks” was her biggest financial success and the film still runs on network and cable television.
Along the way, Singer taught part time at Ryerson, York and the University of Toronto. Her success as a filmmaker was followed by an award as the YWCA Outstanding Woman of the Year and an appointment as the Barker Fairley Chair in Canadian Culture at the University of Toronto.
Singer briefly morphed her talents into TV as a director in a series about food. One of the more well known shows was “Loving Spoonfuls”, which told stories about ethnic grandmothers and the foods they brought with them to Canada from countries all over the world. Readers might recall other former Winnipeggers playing a large part in that show, including producer Allan Novak, and host David Gale.
Her Winnipeg links were recognized over the past decade when Gail was invited to headline the “Distinguished Speaker “ program at the Winnipeg Art Gallery. (Singer entertained the audience that night with an a cappella version of “These Foolish Things Remind Me Of You”). Recently, Gail was thrilled to participate on a panel at the invitation of former Winnipegger Leo Panitch on the significance of the 100th anniversary of the Winnipeg General Strike.
Recently Gail was involved with advising on a project in which seniors were taught how to make a film on YouTube – thereby creating new skills for many people living in seniors’ residences. As well, she has directed various sequences of CBC dramatized productions over the years and, most recently (until halted in mid-film ) was involved in a documentary about the young heroes and heroines of Grassy Narrows: the politicians, writers, painters, singers, music producers and actors, all of them despite terrible neglect by all levels of government of this Ojibway community.
What does all of this add up to for Gail? If you ask her, she is grateful for a lifetime of unexpected projects in unrelated fields with twists and turns along the path. She presently lives in a home in Toronto with a dog, a fridge filled with good things for people to eat, a bar, and more books than she could ever read. And aside from making soup for less privileged folks in the pandemic, Gail has resumed another passion- art. In short, Gail Singer could be the poster child for versatility in the Arts. It has been a remarkable run and the run continues to this day.
Features
History of the Winnipeg Beach Synagogue: 1950-2025

By BERNIE BELLAN The history of the Winnipeg Beach Synagogue is a fascinating one. We have had several articles over the years about the synagogue in The Jewish Post & News.
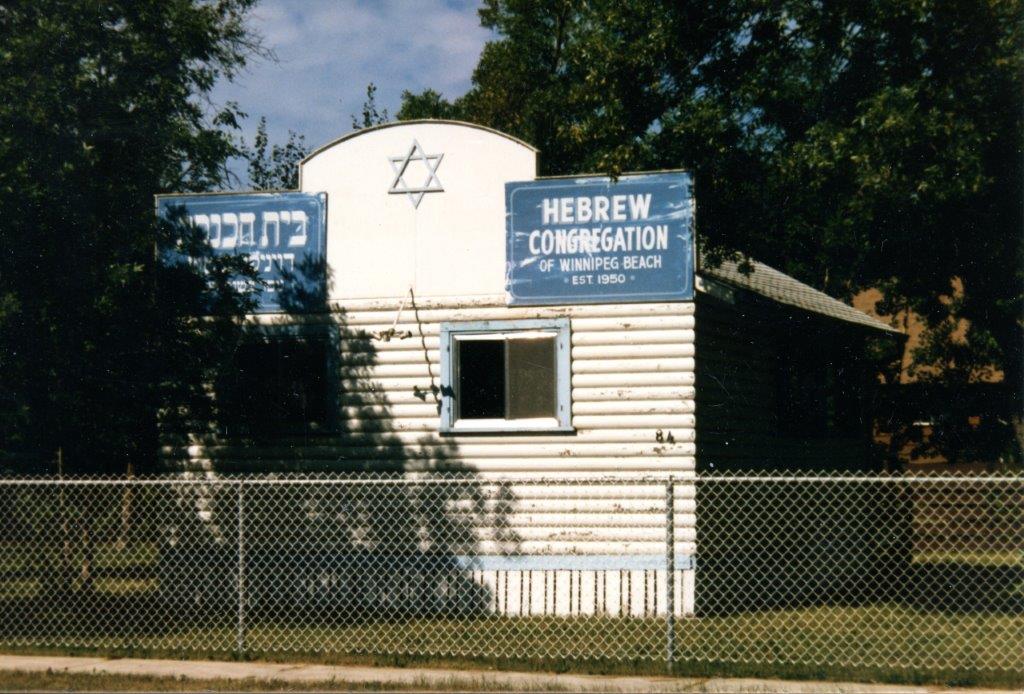


In June 2010 I wrote an article for The Jewish Post & News upon the 60th anniversary of the synagogue’s opening. Here are the opening paragraphs from that article:
“Sixty years ago a group of Winnipeg Beach vacationers decided that what their vacation area lacked was a synagogue. As it happened, a log cabin one-room schoolhouse in the Beausejour area happened to be available.
“In due course, the log cabin was relocated to the corner of Hazel and Grove in Winnipeg Beach, where it stayed for 48 years.”

In December 1994 my late brother, Matt, wrote a story about the spraying of antisemitic grafitti on the synagogue which, at that time, was still situated at its original location on the corner of Hazel and Grove in the town of Winnipeg Beach:
“Two 16-year-olds spraypainted slogans like ‘Die Jews,’ ‘I’ll kill you Jews,’ and other grafitti in big letters on the beach synagogue.
“Jim Mosher, a news reporter for the Interlake Spectator in Gimli, said last Halloween’s vandalism against the synagogue wasn’t the first. In the late 1980s, he claimed, it was spraypainted with swastikas.
“Jack Markson, a longtime member of the Winnipeg Beach Synagogue, last week also said he could remember finding anti-Semitic grafitti spraypainted on the synagogue ‘a few years ago,’ and at least twice in the 1970s, when the cottage season was over.”

My 2010 article continued: “In 1998 the Town of Winnipeg Beach informed the members of the synagogue that the building would have to be hooked up to the town’s sewer and water system. Rather than incur the cost of $3-4,000, which was thought to be ‘prohibitive,’ according to longtime beach synagogue attendee Laurie Mainster, synagogue goers looked elsewhere for a solution.
“As a result, the board of Camp Massad was approached and asked whether the synagogue might be relocated there, with the understanding that the synagogue would be made available to the camp at any time other than what were then Friday evening and Saturday morning services.
“Over the years the ‘beach synagogue’ had come to be a very popular meeting place for summertime residents of Winnipeg Beach and Gimli. In fact, for years minyans were held twice daily, in addition to regular Saturday morning services. Of course, in those years Winnipeg Beach was also home to a kosher butcher shop.
“While the little synagogue, which measured only 18 x 24 feet, has gone through several transformations, including the move to Camp Massad, and the opening up to egalitarian services in 2007 (The move to egalitarian services was as much a practical necessity as it was a nod to the equality of women – the only Kohen present at the time was a woman!), it has always remained cramped at the best of times.

“In recent years the synagogue has seen the addition of a window airconditioner (although to benefit from it, you really have to be sitting just a few feet away), as well as a fridge that allows synagogue attendees to enjoy a regular Saturday morning Kiddush meal following the service.
“According to Laurie Mainster, the Saturday morning service has continued to be popular, even though many of the attendees now drive in from Winnipeg, as they have sold the cottages they once maintained.
“On the other hand, one of the side benefits to being located on Camp Massad’s grounds has been an infusion of young blood from among the camp counsellors.
“Since there is no longer a rabbi available to conduct services (Rabbi Weizman did lead services for years while he had a cottage at the beach), those in attendance now take turns leading the services themselves.
“Anyone may attend services and, while there are no dues collected, donations are welcome. (Donations should be made to the Jewish Foundation of Manitoba, with donors asked to specify that their donations are to be directed to the beach synagogue.)
“Mainster also says that the beach synagogue is now undergoing an expansion, which will be its first in 60 years. An entirely new space measuring 16 x 18 feet is being added – one that will allow for a real Kiddush area. (Until now, a table has been set up in the back of the synagogue and synagogue goers would help themselves to the buffet that is set up each Saturday during the summer. While pleasant enough, it will certainly be more comfortable to have an actual area set aside for the Saturday afternoon after service lunch.)
“As for dress, longtime attendee Abe Borzykowski (in an article written by Sharon Chisvin for the Free Press in 2007) remarked that ‘I don’t think there are many synagogues where people can attend in shorts, T-shirts and sandals and not feel out of place.’ “
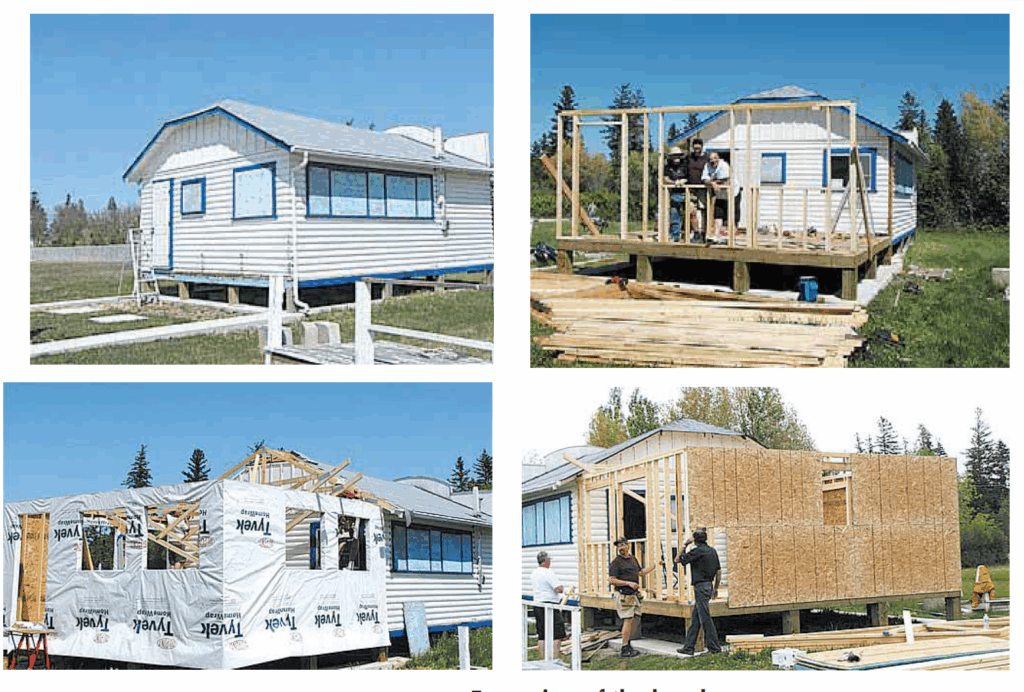
As mentioned in that 2010 article, the beach synagogue at that time was about to undergo an extensive remodelling. Here is an article from a January 2011 issue that describes that remodelling process. The article was written by Bernie Sucharov, who has been a longtime member of the beach synagogue:
“The Hebrew Congregation of Winnipeg Beach made a major change to the synagogue this past summer. With the help of many volunteers, Joel Margolese being the project manager, the synagogue was expanded and an addition was built to handle the overflow crowds, as well as to add more space for the kiddush following services.
“The volunteers spent many Sundays during the summer months building the addition. Bad weather caused many delays, but finally the addition was completed one week before the official summer opening.
“The volunteers were: Joel Margolese, Gordon Steindel, Sheldon Koslovsky, Viktor Lewin, Harvey Zabenskie, Nestor Wowryk, Kevin Wowryk, Victor Spigelman, Jerry Pritchard, and David Bloomfield.
“On Sunday, June 25, 2010 a special ceremony was held to affix a mezzuzah to the front entrance door. Gordon Steindel had the honour of affixing the mezzuzah, which was donated by Sid Bercovich and Clarice Silver.
“Refreshments and food for the day were prepared by Phyllis Spigelman, also known as our catering manager. Throughout the summer, Phyllis, Lenore Kagan and other friends prepared the food for our kiddush.
“A sound system was donated by Arch and Brenda Honigman in memory of their father, Sam Honigman z”l. “The system was installed by Joel Margolese and Stevan Sucharov. This will allow the overflow crowd to hear the service in the new addition.
“There were also generous donations of 50 chumashim and an air conditioner. The chumashim were donated by Gwen, Sheldon and Mark Koslovsky. The air conditioner in the new addition was donated by Joel and Linda Margolese.
“The official opening of the synagogue for the summer took place on July 3, 2010. We had an overflow crowd of 70+ people.”

Since that 2010 major addition to the synagogue, it has also added a wheelchair ramp (although I’ve been unable to ascertain exactly when the ramp was built). Also, the synagogue also has its own outdoor privy now. (Attendees used to have to use facilities in Camp Massad.)
And, as already noted in article previously posted to this site (and which you can read at Beach Synagogue about to celebrate 75th anniversary), in recognition of that occasion, on August 2nd members of the synagogue will be holding a 75th anniversary celebration.
As part of the celebration anyone who is a descendant or relative of any of the original members of the first executive committee is invited to attend the synagogue that morning.
If you are a relative please contact Abe Borzykowski at wpgbeachshule@shaw.ca or aborzykowski@shaw.ca to let Abe know you might be attending.
Features
Kinzey Posen: CBC Winnipeg’s former “go-to guy”

By GERRY POSNER If former Winnipegger Lawrence Wall was the CBC go-to guy in Ottawa, CBC Winnipeg had its own version of a go-to guy for many years with none other than the very well known Kinzey Posen. Of course, many readers will recognize that name from his career with Finjan, the Klezmer group so famous across Canada and beyond. It has been written about Posen and his wife Shayla Fink that they have been involved in music since they got out of diapers. And, as an aside, their love and ability in music has now been transmitted to the next generation as in their son, Ariel Posen (but that’s another story).
Kinzey Posen (not to be confused with Posner, or maybe we are to be confused, but who knows for sure?), was a graduate of Peretz School, having attended there from nursery right until Grade 7, graduating in1966. That was followed by Edmund Partridge and West Kildonan Collegiate. Musically, he was in large part self taught. However, he did have some teachers along the way. After moving to Vancouver – from 1974-78, he had the chance to study acoustic classical bass with a member of the Vancouver Symphony Orchestra. When Kinzey lived in Vancouver, he also worked as a jazz musician.
Upon returning to Winnipeg, Kinzey enrolled as a mature student at the University of Winnipeg, where he obtained a Bachelor of Urban Studies degree. Although the degree was in no way connected to the career that followed, his attending the University of Winnipeg was critical to his connecting with the CBC. Why? you ask. Kinzey had a position after graduation working for the Institute of Urban Studies. While there, he met someone who invited him to work for the Department of Continuing Education as one of their program directors. At the time the Department of Continuing Education was located at 491 Portage Avenue, which was also known as the TJ Rice Building. The CBC also leased some space in the same building. According to Kinzey, the CBC part of the building “included HR, different shows and other support offices. Continuing Education was located in the basement and main floor and that’s where I worked.”
KInzey had long had an interest in the CBC, which made the fact that the CBC had some offices in the same building where he was working serendipitous. That Kinzey might be interested in visiting the CBC was not an accident. As a young boy he had a nightly connection to CBC, as it was his ritual to listen to CBC Radio (as well as all sorts of other radio stations across the USA) on his transistor radio every night in bed. He became enamoured of one particular CBC host, Bill Guest, so that when going to sleep, he imagined that he was Guest doing interviews with imaginary guests. That dream of working for CBC became a reality when he had a chance to do a one week gig with Jack Farr’s network program.
Kinzey took a week off from his Continuing Education job and spent five days at the CBC. That week was a training session for Posen, as he had to create ideas, research, pre-interview, write the script, and set up the studio for Farr’s interview. He was almost in his dream job – although not quite – since it was only for one week. His opportunity, however, came in 1988, when he was offered a one-year term as a production assistant – the lowest guy on the ladder, for a show called “ Simply Folk,” with the late Mitch Podolak as the host. Although he was indeed at the bottom as far as those working on the show were concerned, he took a chance and gave his notice to the U of W. The rest is history. In his new job, Kinzey learned how to become a producer. Lucky for him, at the end of the year, when the person he replaced was supposed to come back, she never returned (just like the song, “MTA,” by the Kingston Trio). At that point, Kinzey was hired full time at the CBC.
Kinzey was a fixture at the CBC for 27 years. During those years, Kinzey had the chance to work with Ross Porter, a respected former CBC host and producer, also with Karen Sanders – on the “Afternoon Edition.” One aspect of Kinzey’s job on the Afternoon Edition was to come up with ideas, mix sound effects, arrange interviews and music, to create a two-hour radio experience. In addition, he covered jazz and folk festivals and, as a result, was exposed to some of the best musicians in the world. With Ross Porter in the 1990s, he worked on a network jazz show called “ After Hours,” which was on from 8-10 PM five nights a week. Kinzey was involved with writing the scripts, picking the music, and recording the shows, as well as editing them and then presenting them to the network for playback.
Of course, over his career, Kinzey had many memorable moments. He told me about one of them. The story revolved around the National Jazz Awards one year in particular. The awards were to be broadcasted after the National News which, in those days, began much earlier in the evening, and were over by 8:00 pm. The legendary Oscar Peterson was lined up to play a half hour set at the awards, starting at 7:30. But, as Kinzey told me, Oscar Peterson had a “hate on” for the CBC ecause one of his recorded performances was wrongly edited and he refused to appear on CBC under any circumstances. As the time neared 8:05 PM, which was when the CBC was to begin its broadcast of the jazz awards, it became apparent that Oscar was not going to finish on time. As the producer of the awards show, Kinzey was tasked with telling Oscar Peterson to wrap it up and get off the stage. There was Kinzey Posen, a huge fan of Oscar Peterson, now faced with the prospect of telling Oscar – while he was still playing – with 500 people in the audience, to stop and get off the stage. Not often was or is Kinzey Posen frozen, but that was one such moment. There was one loud “Baruch Hashem” from Kinzey when Oscar completed his set literally just in time.
Clearly, Kinzey was part of a very successful run with After Hours as it was on the air for 14 years. It was easily one of the most popular shows on CBC Radio 2, and a winner of several broadcasting awards. Kinzey also played a major role in producing a two part documentary about legendary guitarist Lenny Breau.
When After Hours ended, Posen became one of the contributing producers to Canada Live and specialized in producing live radio specials for the network, such as the Junos, for CBC Radio One and Two. Needless to say, his career planted Posen in the world of some top notch musicians, including his time spent working with Robert Plant (Led Zeppelin), Dave Brubeck, Randy Bachman, Chantal Kreviazuk and a list of prominent names in the Canadian, American and European music spheres. Locally, the CBC came to refer to Kinzey as the Jewish expert. I would add music expert to that title.
After his 27 year run at the CBC – and before he fully retired, Kinzey went on to work for the Rady JCC as a program director for a year and a half. Of course, to say that Kinzey Posen is retired is a major contradiction in terms. You really can’t keep him down and he has his hand in a variety of programs and projects – most of which he remains silent about, as is his style.
When I realized the full depth and talent of Kinzey Posen, I quickly concluded that he must certainly be related to me. Even if he isn’t, I now tell people he is.
Features
History of a Holocaust Survivor Turning Eighty

By HENRY SREBRNIK On July 19, I turn 80 years old. This is indeed a milestone, but for me, an even bigger one was just being born. My parents were Holocaust survivors, and I found out just a few months ago that, technically, so am I. My parents were from Czestochowa, Poland, where I was born in 1945. By 1943 most Jews in the city, including their own families, had been murdered by the Nazis, at Treblinka, and after the uprising in the Jewish ghetto, my parents, by now married, became slave labour in a major Nazi munitions plant, the HASAG-Pelcery concentration camp, in the city.
The Russian army liberated Czestochowa January 16-17, 1945, and I was born July 19, six months later. You can do the math. My mother was emaciated and didn’t even know she was pregnant, but another month, and it would have been obvious, and she would have been killed. (I never asked how this happened but found out when listening to her testimony for the Shoah Foundation in 1995. The men and women were housed in different barracks, but one night the Germans were delousing one of the buildings and allowed married couples to sleep together in the other.)

In 1945 the 9th of Av fell on July 19, and the Jewish world had just gone through our worst period in history. I was born in a makeshift hospital at the Jasna Gora, the famed Pauline Catholic monastery in the city. The actual city hospital had been destroyed in the fighting. It is home to the Matka Boska Czestochowska, (“the mother of God”), a very beautiful and large icon of Mary and the baby Jesus. Other women giving birth were surprised and one said, “Ona jest Zydowka” (She’s a Jew). So, though I am a proud Polish Jew, this could only have helped! The doctor who delivered whispered to my mother that he was Jewish but added that he wanted it kept quiet because he wasn’t going to leave Poland. It also took awhile for a mohel to come to the city for me.
The next few years were spent in Pocking-Waldstadt, a DP camp in the American zone in Bavaria, Germany, and then on to Pier 21 in Halifax and Canada. We lived in Montreal, though at home we were to all intents and purposes in Czestochowa, Jewish Poland.
As I was packing up my books in May because we all had to vacate our offices for the summer due to repairs in our building, I came across a book that I had never read – I don’t even recall where I got it — by the Polish historian Lucjan Dobroszycki, Survivors of the Holocaust in Poland: A Portrait Based on Jewish Community Records 1944-1947 (Armonk, New York: M.E. Sharpe, 1994). Chapter 5 is comprised of “Lists of Jewish Children Who Survived,” in alphabetical order. I am listed on p. 146 (Heniek Srebrnik, 1945). I sent in a form to the Claims Conference in New York informing them. So, at age 80, I’ve become a Holocaust survivor! Compared to that start, the next decades have been easy street! As the Aussies say, “no worries! But the Jewish world has grown darker. Like many others, were I to write a memoir, I’d call it From Hitler to Hamas.
I grew up in Montreal, and have lived in Calgary and Charlottetown, as well as London, England, and four American cities. But I’ve only been to Winnipeg twice, in 1982 and, more dramatically, the weekend of Sept. 7-10, 2001. I presented a paper on “Birobidzhan on the Prairies: Two Decades of Pro-Soviet Jewish Movements in Winnipeg,” to a conference on “Jewish Radicalism in Winnipeg, 1905-1960,” organized by the Jewish Heritage Centre of Western Canada. I left the morning of Sept. 11. An hour into the flight to Toronto we were told all airplanes had to land at the nearest major airport. I spent the next three days in Sault Ste. Marie, Ont., with fellow passengers. We mostly watched the television reporting on the 9/11 catastrophe.
Though an academic, I have always written for newspapers, including Jewish ones, in Canada and the United States. Some, like the Jewish Free Press of Calgary, the Jewish Tribune of Toronto, and the previous version of the Canadian Jewish News, no longer exist, which is a shame. Fortunately, the Jewish Post still does.
Henry Srebrnik is a professor of political science at the University of Prince Edward Island.
