Features
How Elliot Rodin was inspired to create a website offering advice on when to take your Canada Pension

By BERNIE BELLAN In 2019 Elliot Rodin happened to read an article about an authoritative U.S. report that provided a detailed analysis showing that 94% of Americans pick the wrong time to begin taking Social Security benefits. Reading about that report led to a shift in Rodin’s life.
Two years after closing down the business (Central Grain) that had been in his family’s hands for over 60 years, Rodin says that he then had time to think about the implications of that US report – and how it could translate into the Canadian scene.
Now, some 15 months after reading about that U.S. report, Rodin has launched a website titled HelpYouRetire.ca.
Long an active member of the Jewish community, Rodin says his most recent involvement in the community was helping to build Oholei Torah Day School at the Jewish Learning Centre in Winnipeg. He says he’s also been on the board of the Shaarey Zedek Synagogue, the Board of Jewish Education, the Winnipeg Jewish Community Council, the Jewish Foundation of Manitoba, and had been a canvasser for the CJA for years, beginning under Ralph Hamovich. He was also a co-chairman of the Operation Exodus campaign.
Still, it’s a long way from running a cattle feed business and volunteering for different Jewish organizations to creating a website intended to help individuals plan their retirement dates.
Using very sophisticated analytical tools, HelpYouRetire.ca allows users to enter information about their age, the age at which they would like to retire, how much they would expect to receive in either CPP/QPP or OAS at a certain age, and how much more they could expect to receive if they were to postpone taking either CPP or OAS by just one year. This financial gain is also shown both as a percentage of future pension proceeds and as a percentage of the annual pension. For a small fee, all of this information can be shown in the “advanced analytics” for all years up to age 69. The information (which can be downloaded) is displayed in bar charts and a numeric chart together with the projected annual pensions.
This information is of great value for anyone thinking about their retirement planning. It can also be very helpful to those who have recently started taking either CPP/QPP or OAS pensions. A little publicized provision of these plans is that within six months of starting to receive one of these pensions, you can reverse your decision by paying back the monies received. In that event, you can take the related pension at a later date. The “advanced analytics” on HelpYouRetire.ca can give you information to assist in making that decision.
But, before we launch into a further exploration of how Elliot Rodin came to be involved in an endeavour that was far removed from selling cattle feed – which was the primary activity of Central Grain, we thought it might be interesting for readers to know something about Rodin’s life. During a long phone conversation we had Rodin told quite an interesting story how he ended up being involved with Central Grain for 60 years – when, had it not been for a fire there in 1966, he probably would have ended up doing something completely different.
While his recent foray into the world of retirement planning might be considered a radical departure for someone who spent so much time in the feed business, when you read about his educational background and his first entry into the business world, you’ll begin to understand how he developed the fine analytical skills that eventually lent themselves to creating HelpYouRetire.ca
Born in 1943, Rodin is the oldest of three children. His earliest years were spent living in his grandparents’ house on Bannerman Avenue, he says, along with his parents and, for a short while, his younger sister, Janis.
“My father (Maurice) was a fruit store proprietor,” Rodin says. “He would be up early in the morning to pick up the fruit. And because we were living at my grandparents’ house, he wasn’t paying any rent, so he was able to save some money. My mother (Lillian) was a university graduate who motivated all her children to work hard and succeed.”
In 1946, an opportunity arose for Rodin’s father to become, with $10,000, a one-third partner in Central Grain, in partnership with the Kanees and the Malchys. “The Malchy who was involved in the partnership died in 1951,” Rodin explains. “My dad and the Kanees bought out his interest and became half partners.
“In 1956, with the assistance of my grandfather, my dad bought out the Kanees and became the sole owner of Central Grain,” Rodin continues. “Soon after that time we moved to the south end – to 431 Queenston.” However, family connections were maintained as Sunday was the day when the whole family would go to the north end to visit relatives.
As a teenager Elliot says that his involvement in the Toppers chapter of BBYO was very important to him. He and his friends learned to organize themselves for a wide range of social, athletic, cultural and fund raising activities.
But, early on he had a taste of the world of business – both in his father’s company and in his own small scale business.
“When I was 16-17 I would go into the office and help with the bookkeeping – and other odd jobs around the place in the summertime,” he explains.
At the same time though, “I had my own business,” he adds. “I had a grass cutting business.” (At that point Rodin tells a story about how one of his customers didn’t want to pay him. Rodin says that he and his friend, Michael Nozick, proceeded to serve a small claims summons against that individual. Apparently, that was Michael Nozick’s first foray into the legal world. By the way, the customer ended up paying Rodin what he was owed.)
In the early 1960s Elliot began a period in his life that saw him acquire a solid education in finance, starting with his obtaining a Bachelor of Commerce degree from the University of Manitoba in 1963.
Rodin continues his story: “I decided I wanted to go away for my MBA degree. I visited three different schools. I took a bus trip – about 43 hours, to Philadelphia, to the Wharton School of Finance, then to Boston, to the Harvard Business School, and then to Ann Arbor, Michigan, to the University of Michigan.
“I had also put my application into Stanford. I wasn’t accepted at Stanford, but I was accepted at Wharton and Michigan, while Harvard said basically ‘We won’t accept you this year because you’re a little young, but we’ll promise you a place in next year’s class.’
“So I decided to wait a year. I worked in the family business for a year, then I went to the Harvard Business School because that was what I thought was the top place to go. I spent two years there and while I was there I also spent one summer with the Skelly Oil Company in Tulsa, Oklahoma.
“I was working on special projects for the treasurer (of Skelly Oil). One of them was a computerized analysis of how to make oil drilling decisions, but it never got off the ground – even though the analysis was very sophisticated, because the exploration people would not accept it because they saw it as infringement on their turf.
“Still, I learned a lot from that particular project. It was my first serious analytical job that had some relationship to the work I was doing at Harvard (and, as Rodin explains later, proved to be of great value in his recent decision to create a website that emphasizes analytical tools.)
“As it turned out, the treasurer at Skelly wanted to hire me when I graduated, but at that time I couldn’t consider working in the States because I would have been drafted. The fact that I was a Canadian wouldn’t have made any difference.
“If I had been a student I wouldn’t get drafted. I also didn’t take any other opportunities that I had in the States. I limited myself to working in Canada.
“I ended up working for six months in Edmonton for a company called the Principal Group. While I worked there I had a lot of diverse responsibilities. I chose all their stocks for a new mutual fund they set up, and designed the text and written material for their first Annual Report. I also did all sorts of analysis for their mortgage operations.
“Then I got the news that the Central Grain plant had been hit by lightning and three-quarters of it had burned down.
“Central Grain was an animal feed processing plant. During the years that my dad was building it up we were basically selling pellet feed for export to the United Kingdom, to Japan, Taiwan. We would load railway cars with pellets, ship them to Thunder Bay, for destinations in the United Kingdom, or ship it to Vancouver for export.
“When this (the fire) happened in 1966, I had to come back to Winnipeg to help my dad settle all the insurance. There were a lot of issues and we rebuilt the plant, but all the key parts of the plant were burned down.
“I decided to settle down in Winnipeg. I took a job with Investors Group, which was similar to what I had in Edmonton. For the first year I was doing special projects, including a report on tax policy. We recommended how life insurance companies should be taxed. (This was before Investors bought Great West Life.) Most of our recommendations were adopted. We were competing with life insurance companies at that time and life insurance companies weren’t paying their fair share of taxes.
“After that year I did some product analyses. Then I started working for the securities department as an analyst. Over a period of time I became a portfolio manager. I ran the Investors international mutual fund. Then I ran the Investors pension accounts. We managed the Hudson’s Bay pension account.
“I was at Investors for 12 years (from 1968-80) and became a vice-president. I left to pursue some independent activities”, but joined Central Grain when it became clear that his dad needed Elliot’s help.
When he joined Central Grain full time in 1980, Rodin began focusing on broadening the markets for the company’s feed pellets. Markets in Western Canada and the United States were cultivated, but he says that he always made sure that the needs of his regular customers were attended to.
“I never took advantage of the fact that there might be a drought in Southern California, for instance, and short my customers in Saskatchewan because I depended on my regular customers for the long haul,” Rodin says.
“I would work long hours if necessary. If a truck came in late and had to be loaded, I would load the truck myself.
Although Central Grain had become a very successful business, Rodin says that the “maximum number of employees we had at one time was no more than 15. We had one truck, but for the most part we hired other trucking companies. We had a machine shop, but the stuff we couldn’t do – we hired other machine shops to do.
“We bought basically the ‘clean-outs’ from grain – all the leftover product. It was all categorized and separated out and properly blended to make different qualities of feed pellets. There was no plant in North America that shipped product as far as we did. We used to ship up to 2,000 miles. Most feed companies ship up to 200 miles.
“The business ran until about three and a half years ago. We were gradually losing customers for reasons that I can’t quite figure out. I needed additional volumes because the company had substantial overhead – for repairs and maintenance.
“So we started to do fuel pellets. We became the second largest manufacturer of fuel pellets in Manitoba – as a substitute for coal, using the same screenings – but the lower quality screenings. The top quality screenings were turned into top quality feed for cattle and bison.
“I was reasonably successful at doing this, but at the end of the day the plant was an old plant. Remember, it was rebuilt in 1966. What was new in 1966 was not new 50 years later. The costs of maintaining the plant to the standards we had to maintain were going up and up.
“Finally, I made the decision that I’m going to have to close it down. I thought: ‘If I can’t make a living at this, then nobody can.’ I decided I’d have to tear the whole place down – and that’s what I did.
“I realized I was getting older and if I didn’t do it I didn’t want to have my children to have the burden of doing it. So, everything that I had built up over 50 years was torn down. I sold whatever equipment that I could, but the rest all went for scrap.
To return to the initial reason for doing this article, Rodin explains his motivation in wanting to create HelpYouRetire.ca. As we already noted, the catalyst was reading about that U.S. report about social security and “that 90% of people in the United States take their pensions at the wrong time.”
He adds though, that “an additional underlying factor in my motivation is that I missed the daily rewards (not the aggravation) that I got from my job running Central Grain. I loved selling and enjoyed my interactions with customers. At the end of the day when I had loaded four big trucks I came home with a feeling of accomplishment. So, I was primed for another challenge where I could get these feelings back. With this website, I am now focusing on marketing where I have to sell myself and the site.”
I asked Rodin whether there was anything in particular in his background that lent itself to the kind of analytical exercise upon which he was to embark.
He answers that “a course that I took at Harvard Business School and the work that I did at Skelly Oil were very relevant to this process.”
I said though “that it sounds like you would need the same background as an actuary” in order to undertake the project into which Rodin has entered.
Rodin agreed, saying “you’re hitting upon a very key point when you say that, but there are a lot actuaries around. Nobody thought of doing what I’m doing.
“I guess part of the answer is most actuaries are fully employed. There aren’t a lot sitting around thinking about what they can do to help Canadians.
“You have to remember that I spent 13 years as a securities analyst and a portfolio manager, so my mind works in a certain way. Nothing that I did at Central Grain though related to this project.”
I asked what were the first steps that Rodin took in developing his website.
He says: “The first steps were that I needed to see whether I could develop the necessary mathematical models to do what I had in mind. Once I had the mathematical models I began working on the structure of a website that would put these mathematical models into practice.
“I was told by various people that setting up a website is not all that difficult.” (Boy, were they ever wrong when it came to this website!)
After an initial contact with someone who was working on their PhD and thought they might be able to produce the kind of website Rodin was looking to create didn’t pan out, a company in Ottawa that had built a similar kind of website agreed to take on the project.
“The idea was that it was going to take a few months” to create the website, Rodin explains.
“But from the time we started up toward the end of February (just before the pandemic hit Canada in full force) it took until the end of August” to finalize the site.
“Every aspect along the way had to be just right – from the mathematics to the functionality. It had to be there so that even people who don’t know much about computers or websites would be able to use this website. Finally, we reached the point where I’m extremely happy with the site.”
 So, having read this far, you might ask yourself: “Why should I go to HelpYouRetire.ca?”
So, having read this far, you might ask yourself: “Why should I go to HelpYouRetire.ca?”
It’s quite an easy site to navigate. As has already been explained, simply enter some basic information and the site will provide you with some quick results about how postponing your decision to begin taking either CPP/QPP or OAS by one year will benefit you – or might have benefitted you if you’re already taking your pension.
Then, as Rodin explained, if you’re wanting to know more about how much more your pension would be affected if you decide to wait even longer to begin taking your pension, for a fee you can obtain access to even more comprehensive analytical tools that will show that. The results might surprise you – and it may end up being one of the most important decisions you might ever make with regard to retirement planning.
Features
The Tech That Never Sleeps: Inside the Always-On Engines of No Limit Casinos

In communities across Canada, including Winnipeg’s dynamic Jewish community, technology has become an integral part of daily life, whether through synagogue livestreams, local cultural programming, or real-time coverage of global events affecting Israel and the diaspora. Modern digital infrastructure, while often unseen to the public, runs continuously behind the scenes, enabling information networks that never stop. The same notion of ongoing connectivity drives the 24-hour digital entertainment platforms.
One example of this infrastructure is seen in online gaming settings, where real-time data systems enable experiences that are meant to run without interruption. The global online gambling industry is expected to increase from around $97.9 billion in 2026, with internet penetration and mobile connectivity continuing to climb globally. As a result, readers interested in how these platforms work often consult a comprehensive list of No Limit casino platforms to gain a better understanding of the ecosystem.
While conversations about casinos sometimes center on the games themselves, what’s underneath the narrative is technical. Behind every digital table or interactive game is a network of servers, verification tools, live data processors, and uptime monitoring systems that must run continually. Unlike traditional venues that close at night, online platforms rely on always-on design, which means that their software infrastructure must run 24 hours a day, seven days a week, independent of player time zones.
Infrastructure That Never Closes
Although Winnipeg readers may be more familiar with the servers that power newsrooms, streaming services, and community websites, the technology center of global platforms shares similar concepts. Modern digital systems rely significantly on distributed cloud computing, which means that data is handled simultaneously over several geographical locations rather than in a single location.
This layout increases credibility while also allowing platforms to run consistently even when millions of people are actively accessing the system. Similarly, big cloud providers operate worldwide networks of data centers capable of providing near-constant uptime. According to reliability measures released by major cloud providers, such as Google Cloud infrastructure reliability overview, modern corporate systems typically aim for uptime levels greater than 99.9 percent.
That figure may sound abstract, yet it corresponds to only a few minutes of disturbance every month. In fact, ensuring such regularity needs sophisticated monitoring systems that identify faults immediately, quickly divert traffic, and maintain redundant backups across different continents. Unlike early internet platforms, which relied on a single server room, today’s large-scale systems function as interconnected worldwide networks.
Real-Time Data: The Pulse of Modern Platforms
While infrastructure keeps systems operating, real-time data engines guarantee that information is constantly sent between users and servers. These systems handle massive amounts of data per second, including player activities, system status updates, and verification checks. Although the public rarely observes these operations, they are the digital pulse of today’s internet platforms.
Real-time computing has also revolutionized industries known to Canadian readers. Financial markets, for example, use comparable high-speed data processing to quickly update stock values across trading platforms. The same logic applies to global logistical networks, airline scheduling systems, and even newsrooms that monitor breaking news as it occurs.
This is essentially one of the distinguishing features of modern digital infrastructure: information no longer moves in batches, but rather continuously over high-capacity data pipelines. Regardless of how complicated these systems are, they must stay reliable and safe, which is why developers invest much in automated monitoring and predictive maintenance.
Security and Verification in the Always-On Era
Technology that never sleeps must also be self-verifying. Modern digital platforms use multilayer security systems to identify suspicious conduct, validate user identities, and safeguard critical data. Many of these procedures remain in the background, but they are extremely important for preserving confidence in online services.
Unlike older internet platforms, which depended heavily on passwords, newer systems often include behavioral analytics, device identification, and automatic danger detection. These technologies work silently, yet they examine patterns in real time, detecting unacceptable behavior before it spreads throughout a network.
The larger IT sector has made significant investments in these measures. Organizations such as the National Institute of Standards and Technology cybersecurity framework overview give guidelines for software developers throughout the world in designing resilient digital systems. Similarly, academic research from universities continues to investigate how internet infrastructure can stay safe while yet allowing for large-scale connectivity.
Lessons for the Wider Digital World
Although talks regarding entertainment platforms often focus on user experiences, the underlying technology symbolizes a larger revolution in the digital economy. Today’s online systems must run constantly, expand fast, and stay safe even under high demand. While normal user may only observe the automatic interface on their screen, the real story is the engineering it takes to maintain that experience.
While technology develops very quickly, one thing remains constant: systems meant to function indefinitely need both intelligent engineering and meticulous management. Despite their complexity, these digital engines have become the silent basis for modern life, powering everything from local news websites to global platforms that never sleep.
Features
ClarityCheck: Securing Communication for Authors and Digital Publishers
In the world of digital publishing, communication is the lifeblood of creation. Authors connect with editors, contributors, and collaborators via email and phone calls. Publishers manage submissions, coordinate with freelance teams, and negotiate contracts online.
However, the same digital channels that enable efficient publishing also carry risk. Unknown contacts, fraudulent inquiries, and impersonation attempts can disrupt projects, delay timelines, or compromise sensitive intellectual property.
This is where ClarityCheck becomes a vital tool for authors and digital publishers. By allowing users to verify phone numbers and email addresses, ClarityCheck enhances trust, supports safer collaboration, and minimizes operational risks.
Why Verification Matters in Digital Publishing
Digital publishing involves multiple types of external communication:
- Manuscript submissions
- Editing and proofreading coordination
- Author-publisher negotiations
- Marketing and promotional campaigns
- Collaboration with illustrators and designers
In these workflows, unverified contacts can lead to:
- Scams or fraudulent project offers
- Intellectual property theft
- Miscommunication causing delays
- Financial loss due to fraudulent payments
- Unauthorized sharing of sensitive drafts
Platforms like Reddit feature discussions from authors and freelancers about using verification tools to safeguard their work. This highlights the growing awareness of digital safety in creative industries.
What Is ClarityCheck?
ClarityCheck is an online service that enables users to search for publicly available information associated with phone numbers and email addresses. Its primary goal is to provide additional context about a contact before initiating or continuing communication.
Rather than relying purely on intuition, authors and publishers can access structured information to assess credibility. This proactive approach supports safer project management and protects intellectual property.
You can explore community feedback and discussions about the service here: ClarityCheck
Key Benefits for Authors and Digital Publishers
1. Protecting Manuscript Submissions
Authors often submit manuscripts to multiple editors or publishers. Before sharing full drafts:
- Verify the contact’s legitimacy
- Ensure the communication aligns with known publishing entities
- Reduce risk of unauthorized distribution
A quick lookup can prevent time-consuming disputes and protect original content.
2. Safeguarding Collaborative Projects
Digital publishing frequently involves external contributors such as:
- Illustrators
- Designers
- Editors
- Ghostwriters
Verification ensures all collaborators are trustworthy, minimizing the chance of intellectual property theft or miscommunication.
3. Enhancing Marketing and PR Outreach
Promoting a book or digital publication often involves connecting with:
- Bloggers
- Reviewers
- Book influencers
- Digital media outlets
Before sharing press kits or marketing materials, verifying email addresses or phone contacts adds confidence and prevents potential misuse.
How ClarityCheck Works
While the internal system is proprietary, the user workflow is straightforward and efficient:
| Step | Action | Outcome |
| 1 | Enter phone number or email | Search initiated |
| 2 | Aggregation of publicly available data | Digital footprint analyzed |
| 3 | Report generated | Structured overview presented |
| 4 | Review by user | Informed decision before engagement |
The platform’s simplicity makes it suitable for authors and publishing teams, even those with limited technical expertise.
Integrating ClarityCheck Into Publishing Workflows
Manuscript Submission Process
- Receive submission request
- Verify contact via ClarityCheck
- Confirm identity of editor or publisher
- Share draft or proceed with collaboration
Collaboration with Freelancers
- Initiate project with external contributors
- Run ClarityCheck to verify email or phone number
- Establish project agreement
- Begin content creation safely
Marketing Outreach
- Contact media or reviewers
- Verify digital identity
- Share promotional materials with confidence
Ethical and Privacy Considerations
While ClarityCheck provides useful context, it operates exclusively using publicly accessible information. Authors and publishers should always:
- Respect privacy and data protection regulations
- Use results responsibly
- Combine verification with personal judgment
- Avoid sharing sensitive data with unverified contacts
Responsible use ensures the platform supports security without compromising ethical standards.
Real-World Use Cases in Digital Publishing
Scenario 1: Verifying a New Editor
An author is contacted by an editor claiming to represent a small publishing house. Running a ClarityCheck report confirms the email domain aligns with publicly available information about the company, reducing risk before signing an agreement.
Scenario 2: Screening Freelance Illustrators
A digital publisher seeks an illustrator for a children’s book. Before sharing project details or compensation terms, ClarityCheck verifies contact information, ensuring the artist is legitimate.
Scenario 3: Marketing Outreach Safety
A self-publishing author plans a social media and email campaign. Verifying influencer or reviewer contacts helps prevent marketing materials from reaching fraudulent accounts.
Why Verification Strengthens Publishing Operations
In digital publishing, speed and creativity are essential, but they must be balanced with security:
- Protect intellectual property
- Maintain trust with collaborators
- Ensure financial transactions are secure
- Prevent delays due to miscommunication
Verification tools like ClarityCheck integrate seamlessly, allowing authors and publishing teams to focus on creation rather than risk management.
Final Thoughts
In a world where publishing is increasingly digital and collaborative, verifying contacts is not just prudent — it’s necessary.
ClarityCheck empowers authors, editors, and digital publishing professionals to confidently assess phone numbers and email addresses, protect their intellectual property, and streamline communication.
Whether managing manuscript submissions, coordinating external contributors, or launching marketing campaigns, integrating ClarityCheck into your workflow ensures clarity, safety, and professionalism.
In digital publishing, trust is as important as creativity — and ClarityCheck helps safeguard both.
Features
Israel’s Arab Population Finds Itself in Dire Straits
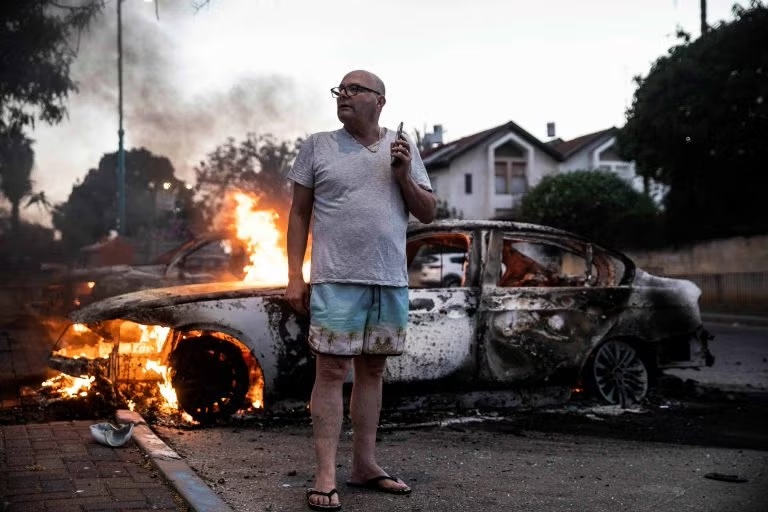

By HENRY SREBRNIK There has been an epidemic of criminal violence and state neglect in the Arab community of Israel. At least 56 Arab citizens have died since the beginning of this year. Many blame the government for neglecting its Arab population and the police for failing to curb the violence. Arabs make up about a fifth of Israel’s population of 10 million people. But criminal killings within the community have accounted for the vast majority of Israeli homicides in recent years.
Last year, in fact, stands as the deadliest on record for Israel’s Arab community. According to a year-end report by the Center for the Advancement of Security in Arab Society (Ayalef), 252 Arab citizens were murdered in 2025, an increase of roughly 10 percent over the 230 victims recorded in 2024. The report, “Another Year of Eroding Governance and Escalating Crime and Violence in Arab Society: Trends and Data for 2025,” published in December, noted that the toll on women is particularly severe, with 23 Arab women killed, the highest number recorded to date.
Violence has expanded beyond internal criminal disputes, increasingly affecting public spaces and targeting authorities, relatives of assassination targets, and uninvolved bystanders. In mixed Arab-Jewish cities such as Acre, Jaffa, Lod, and Ramla, violence has acquired a political dimension, further eroding the fragile social fabric Israel has worked to sustain.
In the Negev, crime families operate large-scale weapons-smuggling networks, using inexpensive drones to move increasingly advanced arms, including rifles, medium machine guns, and even grenades, from across the borders in Egypt and Jordan. These weapons fuel not only local criminal feuds but also end up with terrorists in the West Bank and even Jerusalem.
Getting weapons across the border used to be dangerous and complex but is now relatively easy. Drones originally used to smuggle drugs over the borders with Egypt and Jordan have evolved into a cheap and effective tool for trafficking weapons in large quantities. The region has been turning into a major infiltration route and has intensified over the past two years, as security attention shifted toward Gaza and the West Bank.
The Negev is not merely a local challenge; it serves as a gateway for crime and terrorism across Israel, including in cities. The weapons flow into mixed Jewish-Arab cities and from there penetrate the West Bank, fueling both organized crime and terrorist activity and blurring the line between them.
The smuggling of weapons into Israel is no longer a marginal criminal phenomenon but an ongoing strategic threat that traces a clear trail: from porous borders with Egypt and Jordan, through drones and increasingly sophisticated smuggling methods, into the heart of criminal networks inside Israel, and in a growing number of cases into lethal terrorist operations. A deal that begins as a profit-driven criminal transaction often ends in a terrorist attack. Israeli police warn that a population flooded with illegal weapons will act unlawfully, the only question being against whom.
The scale of the threat is vast. According to law enforcement estimates, up to 160,000 weapons are smuggled into Israel each year, about 14,000 a month. Some sources estimate that about 100,000 illegal weapons are circulating in the Negev alone.
Israeli cities are feeling this. Acre, with a population of about 50,000, more than 15,000 of them Arab, has seen a rise in violent incidents, including gunfire directed at schools, car bombings, and nationalist attacks. In August 2025, a 16-year-old boy was shot on his way to school, triggering violent protests against the police.
Home to roughly 35,000 Arab residents and 20,000 Jewish residents, Jaffa has seen rising tensions and repeated incidents of violence between Arabs and Jews. In the most recent case, on January 1, 2026, Rabbi Netanel Abitan was attacked while walking along a street, and beaten.
In Lod, a city of roughly 75,000 residents, about half of them Arab, twelve murders were recorded in 2025, a historic high. The city has become a focal point for feuds between crime families. In June 2025, a multi-victim shooting on a central street left two young men dead and five others wounded, including a 12-year-old passerby. Yet the killing of the head of a crime family in 2024 remains unsolved to this day; witnesses present at the scene refused to testify.
The violence also spilled over to Jewish residents: Jewish bystanders were struck by gunfire, state officials were targeted, and cars were bombed near synagogues. Hundreds of Jewish families have left the city amid what the mayor has described as an “atmosphere of war.”
Phenomena that were once largely confined to the Arab sector and Arab towns are spilling into mixed cities and even into predominantly Jewish cities. When violence in mixed cities threatens to undermine overall stability, it becomes a national problem. In Lod and Jaffa, extortion of Jewish-owned businesses by Arab crime families has increased by 25 per cent, according to police data.
Ramla recorded 15 murders in 2025, underscoring the persistence of lethal violence in the city. Many victims have been caught up in cycles of revenge between clans, often beginning with disputes over “honour” and ending in gunfire. Arab residents describe the city as “cursed,” while Jewish residents speak openly about being afraid to leave their homes
Reluctance to report crimes to the authorities is a central factor exacerbating the problem. Fear of retaliation by families or criminal organizations deters victims and their relatives from coming forward, contributing to a clearance rate of less than 15 per cent of all murders. The Ayalef report notes that approximately 70 per cent of witnesses refused to cooperate with police investigations, citing doubts about the state’s ability to provide protection.
Violence in Arab society is not just an Arab sector problem; it poses a direct and serious threat to Israel’s national security. The impact is twofold: on the one hand, a rise in crime that affects the entire population; on the other, the spillover of weapons and criminal activity into terrorism, threatening both internal and regional stability. This phenomenon reached a peak in 2025, with implications that could lead to a third intifada triggered by either a nationalist or criminal incident.
The report suggests that along the Egyptian and Jordanian borders, Israel should adopt a technological and security-focused response: reinforcing border fences with sensors and cameras, conducting aerial patrols to counter drones, and expanding enforcement activity.
This should be accompanied by a reassessment of the rules of engagement along the border area, enabling effective interdiction of smuggling and legal protocols that allow for the arrest and imprisonment of offenders. The report concludes by emphasizing that rising violence in cities, compounded by weapons smuggling in the Negev, is eroding Israel’s internal stability.
Henry Srebrnik is a professor of political science at the University of Prince Edward Island.


