Features
Fascinating Tanzania!
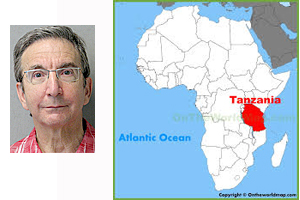
By MARTIN ZEILIG Our small motorized mangrove and mahogany canvas covered boat bounced along the choppy turquoise waters of the Indian Ocean as the captain and owner, Ahmed, manoeuvred the outboard engine towards Changuu Island, a small island about six kilometres northwest of Stone Town, Unguja Zanzibar.
As we sped along, a number of cargo ships and a Chinese fishing trawler were moored off shore, while long thin hulled dhows with billowing sails skimmed speedily on that sun searing day through the world’s third largest ocean.
I was at the tail end of my second trip to Tanzania in just over a year. The first trip was an eight day safari adventure in Northern Tanzania in June 2018. It was, as I wrote in a major two part article for the Lifestyles supplement of The Jewish Post & News afterwards, the fulfillment of a lifelong dream to go on safari in some of the big game parks, including the fabled Serengeti National Park, of East Africa.
This second trip in October 2019 was unplanned and unexpected. I was invited by a Canadian based representative of the Tanzanian government to attend the Swahili International Tourism Expo (S!TE), a three day event (October 18-20) held at the modern Julius Nyerere International Conference Center in Milimani City a region of Dar es Salaam, Tanzania. Dar es Salaam, which is situated on the Indian Ocean, is the largest city, former capital and commercial centre of Tanzania. The yearly event attracted 426 exhibitors, including safari tour operators from throughout Tanzania and other parts of Africa, and almost 1000 visitors over the three days. It also featured speakers, including representatives of the government of the United Republic of Tanzania.
I jumped at the opportunity. Why not? It also included a selection of four day side trips, or Familiarization Trips, afterwards to other parts of Tanzania. I chose to visit the historic town of Iringa and Ruaha National Park— the largest national park located in the middle of Tanzania and covering an area of about 13,000 square kilometres about 130 kilometres from Iringa. I also spent two days in Zanzibar upon returning from Ruaha.
Here are some other memorable moments:
The Expo centers around inbound and outbound travel business to and inside Africa. Tourism companies from 60 countries —Finland, Denmark, Lithuania, Ukraine, Malaysia, South Korea, Canada, India, among others — participated in the event.
“Protection and Sustainable tourism, and in addition tropical tourism and going inside East Africa, (is the goal of S!TE),” the Tanzanian Minister of Tourism, said during the opening address. “The tourism industry is here to help the economy of our country. Tanzania is a safari country in Africa. We are proud that Swahili was born in Tanzania. We encourage our foreign guests to see why we say, ‘Unforgettable Tanzania.’”
 (at left): Being entertained by the Dar es Salaam based, Tot Jazz Band, one of the biggest jazz bands in Tanzania, at the opening entertainment event at SITE. They perform a fusion of Swahili jazz and more recognized numbers.Strolling along the shore of the Indian Ocean by my hotel, located on the outskirts of Dar, in the evening with the twinkling lights of yachts and merchant ships moored in the distance was a peaceful way to unwind after being at the hectic SITE all day. The surf’s fresh and salty smell combined with the exotic locale was intoxicatingVisiting the National Museum & House of Culture: It takes you on a journey through Tanzania’s colorful past. The museum displays important fossils of some of the earliest human ancestors unearthed during the Leakey digs at Olduvai Gorge. You can also learn about Tanzania’s tribal heritage and the impact of the slave trade and colonial periods. Other highlights of the museum include ethnographic displays on traditional crafts, customs, ornaments, and musical instruments, as well as a small collection of vintage cars, including the Rolls Royce used by former president, Julius Nyerere.
(at left): Being entertained by the Dar es Salaam based, Tot Jazz Band, one of the biggest jazz bands in Tanzania, at the opening entertainment event at SITE. They perform a fusion of Swahili jazz and more recognized numbers.Strolling along the shore of the Indian Ocean by my hotel, located on the outskirts of Dar, in the evening with the twinkling lights of yachts and merchant ships moored in the distance was a peaceful way to unwind after being at the hectic SITE all day. The surf’s fresh and salty smell combined with the exotic locale was intoxicatingVisiting the National Museum & House of Culture: It takes you on a journey through Tanzania’s colorful past. The museum displays important fossils of some of the earliest human ancestors unearthed during the Leakey digs at Olduvai Gorge. You can also learn about Tanzania’s tribal heritage and the impact of the slave trade and colonial periods. Other highlights of the museum include ethnographic displays on traditional crafts, customs, ornaments, and musical instruments, as well as a small collection of vintage cars, including the Rolls Royce used by former president, Julius Nyerere.
Iringa: Iringa is a city in Tanzania with a population of 1,211,900 (as of 2020), according to Wikipedia. The name is derived from the word lilinga, meaning .
Iringa is the administrative capital of Iringa Region. Iringa Municipal Council is the administrative designation of the Municipality of Iringa. “Iringa has been one of the coldest regions in Tanzania due to its geographical location but that has attracted a lot of tourists from colder regions abroad especially Western Europe,” notes online information. Iringa also hosts one of Africa’s largest national parks, the Ruaha National Park.
We also visited the Isimila Stone Age site, which lies about 20 km (12 mi) to the southwest. It contains archeological artifacts, particularly stone tools, from human habitation about 70,000 years ago. Homo Erectus lived here 300,000 years ago.
Excavation work was done by paleontologists from the University of Chicago, 1957-58; University of Illinois, 1968-70, and South Korea in 2003. Scrapers, slingshots, knives from stones, and different weapons were found and can still be seen in large open sided enclosures.
Iringa Region is home to the Hehe people.
“After their stunning defeat at Lugalo by the Hehe on August 17, 1871, led by Chief Mkwawa, the Germans built a military station at ‘Neu Iringa’ to avenge the death of their commander Emil Von Zelewski and to teach the Hehe respect for German authority,” says information in the Iringa Boma – Regional Museum and Cultural Centre. “The fortress and headquarters of Chief Mkwawa was in the nearby village of Kalenga, Alt Iringa.” It was only in July 1898, after being trapped, that Mkwawa shot himself. The Germans removed Mkwawa’s head and sent it to Germany.
Mkwawa still has “the status of a national hero in Tanzania,” even after over 120 years. A movie should be made about this man.
Ruaha NP: Ruaha is in a northern and southern transition zone.  Ruaha National Park is the largest national park in Tanzania. It covers an area of about 13,000 square kilometres.
Ruaha National Park is the largest national park in Tanzania. It covers an area of about 13,000 square kilometres.
It is located in the middle of Tanzania about 130 kilometres from Iringa. The park, which is located in the Great Rift Valley (East African Rift), is part of a more extensive ecosystem, which includes Rungwa Game Reserve, Usangu Game Reserve, and several other protected areas.
The name of the park is derived from the Great Ruaha River, which flows along its South-Eastern margin and is the focus for game-viewing.
The park can be reached by car via Iringa and there is an airstrip at Msembe, park headquarters.
I was part of a group that included three Dutch journalists. Our safari driver/expert guide, Serafino, was the owner of the Center for Research and Action, Limited (CRA)– a new company that started in 2019– in Irigina.
During our two days exploring Ruaha we encountered lions– including a male and female that mated several times as we clicked away on our cameras or cell phones– resting under a baobab tree and along a dry river bed; a beautiful male leopard nestled in the shade of an acacia tree a few hundred metres away from the lions; elephants, Cape buffalo, zebra, giraffes, elands and more. Ruaha is believed to have the highest concentration of elephants of any National Park in East Africa.
And it’s home to over 10 percent of Africa’s entire lion population, which is estimated to be only about 20,000 animals whereas about a century ago there were more than 200,000 lions in Africa, according to the World Atlas online. The International Union Conservation of Nature, though, has estimated that there might be as many 30,000 wild lions left on the continent. “From 1993 to 2014, the planet lost 43 percent of its population of African lions, conservationists estimate,” says National Geographic magazine (October 2019).
The park is home to the Ruaha Carnivore Project, which was established in 2009 by Dr. Amy Dickman, as a Kaplan Senior Research Fellow under Oxford University’s Wildlife Conservation Research Unit, says the RCP website.
“Ruaha’s Carnivore Project’s work in protecting lions and livestock, and helping local tribes, is clearly a win-win situation,” Sue Wats, an award-winning writer who specializes in African travel and conservation, wrote in an online article, How the Ruaha Carnivore Project is saving Tanzania’s Lions (SafariBookings).
It is also a place where magnificent mammals like Kudu, Sable and Roan antelopes can easily be spotted in Miombo woodland. The park is also a habitat for endangered wild dogs, although we didn’t see any. Other animals in the park include cheetah, giraffes, zebras, impala, bat eared foxes and Jackals.
The park also harbours a number of reptiles and amphibians such as crocodiles, poisonous and non-poisonous snakes, monitor lizards, agama lizards and frogs. We also spotted hippos relaxing in the Great Ruaha River. Ruaha is famous for being “Tanzania’s bird paradise” because more than 570 species of birds have been identified inside its boundaries, and some of them are known to be migrants from within and outside Africa, says information in a the park’s headquarters.
At one point on our bouncy dusty ride in the Land Rover, Serafino stopped at the side of the narrow dirt road. He got out of the vehicle and grabbed a handful of still steaming elephant dung, and told us all about its different uses by villagers. He then broke it open to reveal insects that were using the manure as a food source and to lay their eggs.
“When I stop for animals and trees and dung, it’s best for guests to listen carefully,” Serafino said afterwards. “It’s better to share with my guests.”
“It was gross, but interesting,” said fellow traveller Noel Vanbemmel, editor of the Travel section in the Dutch newspaper De Volkakrant, the biggest serious newspaper in Holland. “I’ve been on many safaris in sixteen different African countries, but this was the first time I’ve seen this demonstrated. He was doing his best.”
I booked my two day tour to Zanzibar at the SITE with Hassan Luzuba Majid, the owner of Hazaim Holiday and Safaris. His company is based in Zanzibar City (or Zanzibar Town or Stone Town, often simply referred to as Zanzibar)–the capital and largest city of Zanzibar, in Tanzania. It is located on the west coast of Unguja, the main island of the Zanzibar Archipelago, roughly due north of Dar es Salaam across the Zanzibar Channel.
My boat trip was onboard a super fast twin turbine powered ferry boat operated by Azam Marine Boats in Dar. The trip took a little over two hours.
I stayed at the not too pricey exotically named Golden Tulip Boutique Hotel. The rooms are spacious and the service is first rate.
Its open rooftop restaurant has a stunning view of the harbour.
Among the places I visited were the Jozani Forest, the largest area of indigenous forest on Zanzibar Island. Situated south of Chwaka Bay on low-lying land, the area is prone to flooding, which nurtures a lush swamp like environment of moisture-loving trees and ferns. Josanzi is the home of rare Red Colobus Monkey, which is only endemic to Zanzibar. We also spotted some grey and black monkeys.
The nearby Jambo Spice Plantation, about 12 acres in size, is owned by three families. This is a demonstration farm where you can see all different varieties of spices grown in Zanzibar. This farm is only for demonstration system.
Changuu Island saw use as a prison for rebellious slaves in the 1860s and also functioned as a coral mine, say the historical markers.
The British First Minister of Zanzibar, Lloyd Mathews, purchased the island in 1893 and constructed a prison complex there. But, it never held prisoners. Instead it became a quarantine station for yellow fever cases. The station was only occupied for around half of the year and the rest of the time it was a popular holiday destination. Visitors are able to explore the old prison and even stop for refreshments at an outdoor restaurant.
 Spending time, along with other tourists, amongst the 200 giant Aldabra tortoises on Changuu Island was a wondrous experience. In 1919 the British governor of Seychelles sent a gift of four Aldabra giant tortoises to Changuu from the island of Aldabra, say information signs. These tortoises bred quickly and by 1955 they numbered around 200 animals. The Zanzibar government, with assistance from the World Society for the Protection of Animals- Now known as World Animal Protection– built a large compound for the protection of the animals and by 2000 numbers had recovered to 17 adults, 50 juveniles and 90 hatchlings.
Spending time, along with other tourists, amongst the 200 giant Aldabra tortoises on Changuu Island was a wondrous experience. In 1919 the British governor of Seychelles sent a gift of four Aldabra giant tortoises to Changuu from the island of Aldabra, say information signs. These tortoises bred quickly and by 1955 they numbered around 200 animals. The Zanzibar government, with assistance from the World Society for the Protection of Animals- Now known as World Animal Protection– built a large compound for the protection of the animals and by 2000 numbers had recovered to 17 adults, 50 juveniles and 90 hatchlings.
Their ages are painted in blue on their shells.
“The oldest right now is 195 years old,” said my outstanding guide in Zanzibar, Nemes Raphael. “The youngest brother is 161 years old, but bigger in size.”
 Old Stone Town is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. It’s narrow, meandering streets mean that pedestrians vie with motorized vehicles for the right of way.
Old Stone Town is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. It’s narrow, meandering streets mean that pedestrians vie with motorized vehicles for the right of way.
I also took a tour of the former slave market site. On June 6, 1873 the slave trade was officially abolished in East Africa. The slave trade continued underground, though, until 1909. It’s a sobering and claustrophobic experience to spend even a short time in the dank dungeons from the 16thcentury where slaves were squashed together under inhumane conditions before being taken to market for sale. The slaves from West Africa were sent to America. Those from East Africa were sent to Arab countries.
In 1869, Bishop Edward Steere from England settled in Zanzibar. Along with some British missionaries, Bishop Steere purchased the site of the slave market and began building the Anglican Christ Church there.
“He didn’t like the selling of slaves,” my guide at the site, Freddy, said. “He decided to go to the slave market. After purchasing slaves, he would teach them the bible and convert them to Christianity and then set them free. This is history. It’s very terrible. Sometimes I feel pain. My ancestors were among those who were set free from slavery by Bishop Steere.”
Having just seen the movie Bohemian Rhapsody, I visited Freddie Mercury House, which is now the Tembo House Hotel, on Kenyatta Road in Old Stone Town. Mercury, the former lead singer of Queen, was born in Zanzibar in 1946 where his name was Farrokh Bulsara. His father worked for the British colonial service and the family lived in various locations in Stone Town before immigrating to England.
Meanwhile, Forodhan Park is a busy seafood night market with n open sea front garden where people wait for friends or colleagues who are either arriving or leaving on the ferry.
I crammed so much into my two day visit to Zanzibar.
Tanzania is unforgettable.
Features
The Tech That Never Sleeps: Inside the Always-On Engines of No Limit Casinos

In communities across Canada, including Winnipeg’s dynamic Jewish community, technology has become an integral part of daily life, whether through synagogue livestreams, local cultural programming, or real-time coverage of global events affecting Israel and the diaspora. Modern digital infrastructure, while often unseen to the public, runs continuously behind the scenes, enabling information networks that never stop. The same notion of ongoing connectivity drives the 24-hour digital entertainment platforms.
One example of this infrastructure is seen in online gaming settings, where real-time data systems enable experiences that are meant to run without interruption. The global online gambling industry is expected to increase from around $97.9 billion in 2026, with internet penetration and mobile connectivity continuing to climb globally. As a result, readers interested in how these platforms work often consult a comprehensive list of No Limit casino platforms to gain a better understanding of the ecosystem.
While conversations about casinos sometimes center on the games themselves, what’s underneath the narrative is technical. Behind every digital table or interactive game is a network of servers, verification tools, live data processors, and uptime monitoring systems that must run continually. Unlike traditional venues that close at night, online platforms rely on always-on design, which means that their software infrastructure must run 24 hours a day, seven days a week, independent of player time zones.
Infrastructure That Never Closes
Although Winnipeg readers may be more familiar with the servers that power newsrooms, streaming services, and community websites, the technology center of global platforms shares similar concepts. Modern digital systems rely significantly on distributed cloud computing, which means that data is handled simultaneously over several geographical locations rather than in a single location.
This layout increases credibility while also allowing platforms to run consistently even when millions of people are actively accessing the system. Similarly, big cloud providers operate worldwide networks of data centers capable of providing near-constant uptime. According to reliability measures released by major cloud providers, such as Google Cloud infrastructure reliability overview, modern corporate systems typically aim for uptime levels greater than 99.9 percent.
That figure may sound abstract, yet it corresponds to only a few minutes of disturbance every month. In fact, ensuring such regularity needs sophisticated monitoring systems that identify faults immediately, quickly divert traffic, and maintain redundant backups across different continents. Unlike early internet platforms, which relied on a single server room, today’s large-scale systems function as interconnected worldwide networks.
Real-Time Data: The Pulse of Modern Platforms
While infrastructure keeps systems operating, real-time data engines guarantee that information is constantly sent between users and servers. These systems handle massive amounts of data per second, including player activities, system status updates, and verification checks. Although the public rarely observes these operations, they are the digital pulse of today’s internet platforms.
Real-time computing has also revolutionized industries known to Canadian readers. Financial markets, for example, use comparable high-speed data processing to quickly update stock values across trading platforms. The same logic applies to global logistical networks, airline scheduling systems, and even newsrooms that monitor breaking news as it occurs.
This is essentially one of the distinguishing features of modern digital infrastructure: information no longer moves in batches, but rather continuously over high-capacity data pipelines. Regardless of how complicated these systems are, they must stay reliable and safe, which is why developers invest much in automated monitoring and predictive maintenance.
Security and Verification in the Always-On Era
Technology that never sleeps must also be self-verifying. Modern digital platforms use multilayer security systems to identify suspicious conduct, validate user identities, and safeguard critical data. Many of these procedures remain in the background, but they are extremely important for preserving confidence in online services.
Unlike older internet platforms, which depended heavily on passwords, newer systems often include behavioral analytics, device identification, and automatic danger detection. These technologies work silently, yet they examine patterns in real time, detecting unacceptable behavior before it spreads throughout a network.
The larger IT sector has made significant investments in these measures. Organizations such as the National Institute of Standards and Technology cybersecurity framework overview give guidelines for software developers throughout the world in designing resilient digital systems. Similarly, academic research from universities continues to investigate how internet infrastructure can stay safe while yet allowing for large-scale connectivity.
Lessons for the Wider Digital World
Although talks regarding entertainment platforms often focus on user experiences, the underlying technology symbolizes a larger revolution in the digital economy. Today’s online systems must run constantly, expand fast, and stay safe even under high demand. While normal user may only observe the automatic interface on their screen, the real story is the engineering it takes to maintain that experience.
While technology develops very quickly, one thing remains constant: systems meant to function indefinitely need both intelligent engineering and meticulous management. Despite their complexity, these digital engines have become the silent basis for modern life, powering everything from local news websites to global platforms that never sleep.
Features
ClarityCheck: Securing Communication for Authors and Digital Publishers
In the world of digital publishing, communication is the lifeblood of creation. Authors connect with editors, contributors, and collaborators via email and phone calls. Publishers manage submissions, coordinate with freelance teams, and negotiate contracts online.
However, the same digital channels that enable efficient publishing also carry risk. Unknown contacts, fraudulent inquiries, and impersonation attempts can disrupt projects, delay timelines, or compromise sensitive intellectual property.
This is where ClarityCheck becomes a vital tool for authors and digital publishers. By allowing users to verify phone numbers and email addresses, ClarityCheck enhances trust, supports safer collaboration, and minimizes operational risks.
Why Verification Matters in Digital Publishing
Digital publishing involves multiple types of external communication:
- Manuscript submissions
- Editing and proofreading coordination
- Author-publisher negotiations
- Marketing and promotional campaigns
- Collaboration with illustrators and designers
In these workflows, unverified contacts can lead to:
- Scams or fraudulent project offers
- Intellectual property theft
- Miscommunication causing delays
- Financial loss due to fraudulent payments
- Unauthorized sharing of sensitive drafts
Platforms like Reddit feature discussions from authors and freelancers about using verification tools to safeguard their work. This highlights the growing awareness of digital safety in creative industries.
What Is ClarityCheck?
ClarityCheck is an online service that enables users to search for publicly available information associated with phone numbers and email addresses. Its primary goal is to provide additional context about a contact before initiating or continuing communication.
Rather than relying purely on intuition, authors and publishers can access structured information to assess credibility. This proactive approach supports safer project management and protects intellectual property.
You can explore community feedback and discussions about the service here: ClarityCheck
Key Benefits for Authors and Digital Publishers
1. Protecting Manuscript Submissions
Authors often submit manuscripts to multiple editors or publishers. Before sharing full drafts:
- Verify the contact’s legitimacy
- Ensure the communication aligns with known publishing entities
- Reduce risk of unauthorized distribution
A quick lookup can prevent time-consuming disputes and protect original content.
2. Safeguarding Collaborative Projects
Digital publishing frequently involves external contributors such as:
- Illustrators
- Designers
- Editors
- Ghostwriters
Verification ensures all collaborators are trustworthy, minimizing the chance of intellectual property theft or miscommunication.
3. Enhancing Marketing and PR Outreach
Promoting a book or digital publication often involves connecting with:
- Bloggers
- Reviewers
- Book influencers
- Digital media outlets
Before sharing press kits or marketing materials, verifying email addresses or phone contacts adds confidence and prevents potential misuse.
How ClarityCheck Works
While the internal system is proprietary, the user workflow is straightforward and efficient:
| Step | Action | Outcome |
| 1 | Enter phone number or email | Search initiated |
| 2 | Aggregation of publicly available data | Digital footprint analyzed |
| 3 | Report generated | Structured overview presented |
| 4 | Review by user | Informed decision before engagement |
The platform’s simplicity makes it suitable for authors and publishing teams, even those with limited technical expertise.
Integrating ClarityCheck Into Publishing Workflows
Manuscript Submission Process
- Receive submission request
- Verify contact via ClarityCheck
- Confirm identity of editor or publisher
- Share draft or proceed with collaboration
Collaboration with Freelancers
- Initiate project with external contributors
- Run ClarityCheck to verify email or phone number
- Establish project agreement
- Begin content creation safely
Marketing Outreach
- Contact media or reviewers
- Verify digital identity
- Share promotional materials with confidence
Ethical and Privacy Considerations
While ClarityCheck provides useful context, it operates exclusively using publicly accessible information. Authors and publishers should always:
- Respect privacy and data protection regulations
- Use results responsibly
- Combine verification with personal judgment
- Avoid sharing sensitive data with unverified contacts
Responsible use ensures the platform supports security without compromising ethical standards.
Real-World Use Cases in Digital Publishing
Scenario 1: Verifying a New Editor
An author is contacted by an editor claiming to represent a small publishing house. Running a ClarityCheck report confirms the email domain aligns with publicly available information about the company, reducing risk before signing an agreement.
Scenario 2: Screening Freelance Illustrators
A digital publisher seeks an illustrator for a children’s book. Before sharing project details or compensation terms, ClarityCheck verifies contact information, ensuring the artist is legitimate.
Scenario 3: Marketing Outreach Safety
A self-publishing author plans a social media and email campaign. Verifying influencer or reviewer contacts helps prevent marketing materials from reaching fraudulent accounts.
Why Verification Strengthens Publishing Operations
In digital publishing, speed and creativity are essential, but they must be balanced with security:
- Protect intellectual property
- Maintain trust with collaborators
- Ensure financial transactions are secure
- Prevent delays due to miscommunication
Verification tools like ClarityCheck integrate seamlessly, allowing authors and publishing teams to focus on creation rather than risk management.
Final Thoughts
In a world where publishing is increasingly digital and collaborative, verifying contacts is not just prudent — it’s necessary.
ClarityCheck empowers authors, editors, and digital publishing professionals to confidently assess phone numbers and email addresses, protect their intellectual property, and streamline communication.
Whether managing manuscript submissions, coordinating external contributors, or launching marketing campaigns, integrating ClarityCheck into your workflow ensures clarity, safety, and professionalism.
In digital publishing, trust is as important as creativity — and ClarityCheck helps safeguard both.
Features
Israel’s Arab Population Finds Itself in Dire Straits
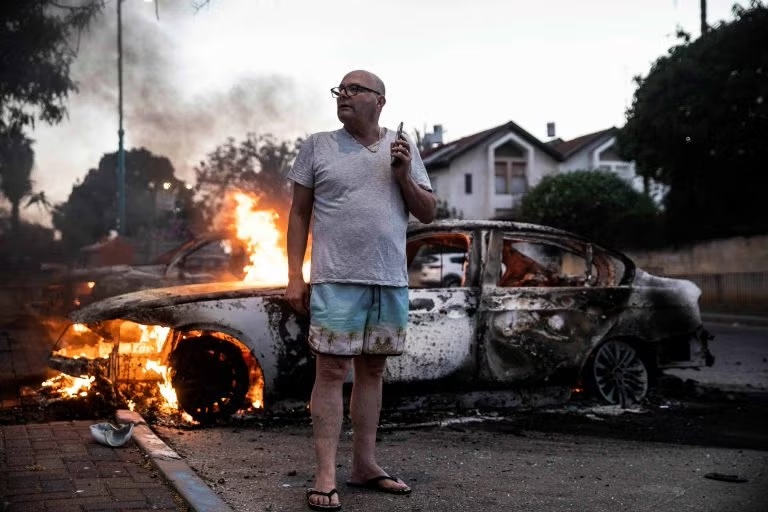

By HENRY SREBRNIK There has been an epidemic of criminal violence and state neglect in the Arab community of Israel. At least 56 Arab citizens have died since the beginning of this year. Many blame the government for neglecting its Arab population and the police for failing to curb the violence. Arabs make up about a fifth of Israel’s population of 10 million people. But criminal killings within the community have accounted for the vast majority of Israeli homicides in recent years.
Last year, in fact, stands as the deadliest on record for Israel’s Arab community. According to a year-end report by the Center for the Advancement of Security in Arab Society (Ayalef), 252 Arab citizens were murdered in 2025, an increase of roughly 10 percent over the 230 victims recorded in 2024. The report, “Another Year of Eroding Governance and Escalating Crime and Violence in Arab Society: Trends and Data for 2025,” published in December, noted that the toll on women is particularly severe, with 23 Arab women killed, the highest number recorded to date.
Violence has expanded beyond internal criminal disputes, increasingly affecting public spaces and targeting authorities, relatives of assassination targets, and uninvolved bystanders. In mixed Arab-Jewish cities such as Acre, Jaffa, Lod, and Ramla, violence has acquired a political dimension, further eroding the fragile social fabric Israel has worked to sustain.
In the Negev, crime families operate large-scale weapons-smuggling networks, using inexpensive drones to move increasingly advanced arms, including rifles, medium machine guns, and even grenades, from across the borders in Egypt and Jordan. These weapons fuel not only local criminal feuds but also end up with terrorists in the West Bank and even Jerusalem.
Getting weapons across the border used to be dangerous and complex but is now relatively easy. Drones originally used to smuggle drugs over the borders with Egypt and Jordan have evolved into a cheap and effective tool for trafficking weapons in large quantities. The region has been turning into a major infiltration route and has intensified over the past two years, as security attention shifted toward Gaza and the West Bank.
The Negev is not merely a local challenge; it serves as a gateway for crime and terrorism across Israel, including in cities. The weapons flow into mixed Jewish-Arab cities and from there penetrate the West Bank, fueling both organized crime and terrorist activity and blurring the line between them.
The smuggling of weapons into Israel is no longer a marginal criminal phenomenon but an ongoing strategic threat that traces a clear trail: from porous borders with Egypt and Jordan, through drones and increasingly sophisticated smuggling methods, into the heart of criminal networks inside Israel, and in a growing number of cases into lethal terrorist operations. A deal that begins as a profit-driven criminal transaction often ends in a terrorist attack. Israeli police warn that a population flooded with illegal weapons will act unlawfully, the only question being against whom.
The scale of the threat is vast. According to law enforcement estimates, up to 160,000 weapons are smuggled into Israel each year, about 14,000 a month. Some sources estimate that about 100,000 illegal weapons are circulating in the Negev alone.
Israeli cities are feeling this. Acre, with a population of about 50,000, more than 15,000 of them Arab, has seen a rise in violent incidents, including gunfire directed at schools, car bombings, and nationalist attacks. In August 2025, a 16-year-old boy was shot on his way to school, triggering violent protests against the police.
Home to roughly 35,000 Arab residents and 20,000 Jewish residents, Jaffa has seen rising tensions and repeated incidents of violence between Arabs and Jews. In the most recent case, on January 1, 2026, Rabbi Netanel Abitan was attacked while walking along a street, and beaten.
In Lod, a city of roughly 75,000 residents, about half of them Arab, twelve murders were recorded in 2025, a historic high. The city has become a focal point for feuds between crime families. In June 2025, a multi-victim shooting on a central street left two young men dead and five others wounded, including a 12-year-old passerby. Yet the killing of the head of a crime family in 2024 remains unsolved to this day; witnesses present at the scene refused to testify.
The violence also spilled over to Jewish residents: Jewish bystanders were struck by gunfire, state officials were targeted, and cars were bombed near synagogues. Hundreds of Jewish families have left the city amid what the mayor has described as an “atmosphere of war.”
Phenomena that were once largely confined to the Arab sector and Arab towns are spilling into mixed cities and even into predominantly Jewish cities. When violence in mixed cities threatens to undermine overall stability, it becomes a national problem. In Lod and Jaffa, extortion of Jewish-owned businesses by Arab crime families has increased by 25 per cent, according to police data.
Ramla recorded 15 murders in 2025, underscoring the persistence of lethal violence in the city. Many victims have been caught up in cycles of revenge between clans, often beginning with disputes over “honour” and ending in gunfire. Arab residents describe the city as “cursed,” while Jewish residents speak openly about being afraid to leave their homes
Reluctance to report crimes to the authorities is a central factor exacerbating the problem. Fear of retaliation by families or criminal organizations deters victims and their relatives from coming forward, contributing to a clearance rate of less than 15 per cent of all murders. The Ayalef report notes that approximately 70 per cent of witnesses refused to cooperate with police investigations, citing doubts about the state’s ability to provide protection.
Violence in Arab society is not just an Arab sector problem; it poses a direct and serious threat to Israel’s national security. The impact is twofold: on the one hand, a rise in crime that affects the entire population; on the other, the spillover of weapons and criminal activity into terrorism, threatening both internal and regional stability. This phenomenon reached a peak in 2025, with implications that could lead to a third intifada triggered by either a nationalist or criminal incident.
The report suggests that along the Egyptian and Jordanian borders, Israel should adopt a technological and security-focused response: reinforcing border fences with sensors and cameras, conducting aerial patrols to counter drones, and expanding enforcement activity.
This should be accompanied by a reassessment of the rules of engagement along the border area, enabling effective interdiction of smuggling and legal protocols that allow for the arrest and imprisonment of offenders. The report concludes by emphasizing that rising violence in cities, compounded by weapons smuggling in the Negev, is eroding Israel’s internal stability.
Henry Srebrnik is a professor of political science at the University of Prince Edward Island.


