Features
Palm oil is ubiquitous – yet the farming of palm oil trees is environmentally disastrous

By MARTIN ZEILIG Palm oil has been criticized by many, including scientists, activists and organizations such as Greenpeace and the Palm Oil Investigations, notes online information.
In a report published by the BBC, environmentalists argue that the farming of oil palm trees is having damaging effects on the environment.
“Palm oil production and deforestation go hand in hand,” says the report. “To build palm oil plantations, producers clear trees in tropical rainforests, destroying the biodiverse regions. Deforestation is a significant contributor to climate change; when the forests are lost, carbon is released into the atmosphere, causing global warming.”
In her book, author Jocelyn Zuckerman spent years travelling the world, “from Liberia to Indonesia, India to Brazil” covering the human and environmental impacts of “this poorly understood plant.”
Her book, “Planet Palm,” is a compelling blend of history, science, politics, and food as experienced by the people whose lives have been impacted by, as she states, “this hidden ingredient.”
Joceln C. Zuckerman is the former editor of Gourmet, articles editor of OnEarth, and executive editor of Modern Farmer. An alumna of Columbia University’s Graduate School of Journalism and a former fellow with the Washington DC-based Alicia Patterson Foundation, she has written for Fast Company, the American Prospect, Vogue, and many other publications. She lives in Brooklyn, with her husband and two children.
Ms. Zuckerman agreed to an email interview with The Jewish Post & News.
JP&N: Why did you decide to write this book? How long did it take to write?
JZ: It started with a trip I took a few years ago to Liberia, the West African country founded by freed American slaves. I’d gone there to write a magazine article about land grabs. This was the trend, in the aftermath of the food and fuel crises of 2008, of agribusiness and investment banks buying up huge swathes of fertile land in faraway places where governance is maybe not all that strong and traditional land rights are easy to exploit.
When I got down on the ground, I found a landscape that was completely barren. Two palm oil companies had cut down the rainforest in order to plant oil palm for miles and miles. In one village, a scattering of mud-block and thatch houses located inside an oil-palm concession owned by a Singapore-based company, a 50-year-old father of seven described how the outsiders had shown up and bulldozed the town in which he’d spent his entire life.
Other villagers talked of how the company had destroyed their crops and gravesites, polluted their streams, and run them out of their homes. I was so disturbed by the destruction I saw in Liberia that when I got home I dove into the topic, trying to learn everything I could about it. And I was fairly astonished by what I found. It turns out that palm oil has played an outsize role in shaping the world as we know it, from spurring the colonization of Nigeria and greasing the gears of the Second Industrial Revolution to transforming the societies of Southeast Asia and beyond.
“Following the plant’s journey over the decades,” I write in my book’s introduction, “served as a sort of master class in everything from colonialism and commodity fetishism to globalization and the industrialization of our modern food system.”
From the time I decided to write the book to the time I finished was about five years, but I was also doing other magazine work during that time.
JP&N: What has been the effect of palm plantations and the palm oil industry on the natural environment, and the economies of affected countries?
JZ: It’s had a profound effect on tropical forests and biodiversity. The landscapes of Indonesia and Malaysia in particular (the two countries account for 85 percent of global production) have been ravaged. In the last two decades alone, Malaysia has lost 20 million acres of tree cover.
The oil palm grows best at ten degrees to the north and south of the equator, which is a swathe of land that corresponds with the planet’s tropical rainforests. And tropical forests, though they cover less than ten percent of Earth’s land surface, support more than half of the world’s biodiversity.
The continued razing of the rainforest for oil-palm development means that creatures like the orangutan, the Sumatrian rhino and elephant, in addition to hundreds of bird species, are losing more and more of their natural habitat.
The palm oil industry is largely responsible for the fact that more than 100,000 orangutans have been wiped off the planet in the last 15 years. In 2019, hundreds of international experts issued a report finding that global biodiversity is declining faster than at any other time in human history, with one million species already facing extinction, many within decades, unless the world takes transformative action.
Most of the folks where I reported from in Southeast Asia, Central America, and Africa used to work as farmers supporting themselves and their families by growing food. But as more and more of the land has been planted with oil palm—and often the water polluted by agrichemicals—they have no food and no means of supporting themselves and their families.
There’s also a connection to pandemics. Something like 75 percent of today’s emerging infectious diseases originate in animals, and 60 per cent of those can spread directly from animals. Over the past few decades, the number of such animal-to-human transmissions has skyrocketed.
A third of these new diseases can be linked directly to deforestation and agricultural intensification, most of it involving tropical rainforests. So, cutting down these forests doesn’t just deprive orangutans and rhinos of their homes, it also sends virus-carrying wildlife like bats in search of new habitat, forcing them into closer contact with humans.
There is also well-documented evidence of forced and child labor on plantations in Indonesia and Malaysia. Malaysia, in particular, relies on hundreds of thousands of migrant workers from countries like Indonesia, India, and Bangladesh to harvest its oil-palm fruits. The workers often are brought in by recruiters who lie to them about good jobs in hotels and restaurants and then confiscate their passports and traffic them to remote plantations.
Last year, the United States announced that it would block shipments of palm oil from two major Malaysian producers over allegations of forced labor, including concerns over child workers and physical and sexual abuse on plantations. And women on three continents told me that they’d been made sick from the pesticides they were forced to handle. Many have suffered from collapsed uteruses as a result of carrying the heavy sacks of fruit.
Some made the equivalent of $2 a day, after working for decades. Workers in the Democratic Republic of Congo, like those on other continents, complained of skin irritation, blisters, and eye damage resulting from the chemicals they handle. Of 43 male employees interviewed by Human Rights Watch in 2019, 27 said that they had become impotent since starting the job. A review published in the International Journal of Occupational and Environmental Medicine in 2019 found that male oil-palm workers in Malaysia were suffering from widespread abnormal sperm.
In 2015, an extended episode of haze linked to fires on oil-palm plantations led to an estimated 100,000 premature deaths in Southeast Asia. (A few weeks into the crisis, government officials ordered the evacuation of all babies under the age of six months.)
As yet untallied is the long-term health damage caused by the fires. The fires proved so difficult to extinguish in part because of the unique composition of the terrain on which so many of them burned. Indonesia is home to Earth’s largest composition of tropical peatlands—soils formed over thousands of years through the accumulation of organic matter—and when farmers and palm oil companies drain and burn that land as a precursor to planting, massive quantities of carbon dioxide escape into the atmosphere. The annual carbon emissions from Indonesia’s peatlands rival those of the entire state of California.
JP&N: What else would you like our readers to know?
JZ: Trade liberalization and economic growth in middle-income countries over the last two decades has led to a surge of oil flowing across international borders, where it’s enabled the production of ever-greater amounts of deep-fried snacks and ultra-processed foods, benefiting multinational companies like Unilever, PepsiCo, Grupo Bimbo, Nestle, Cargill, and others. Rates of obesity, diabetes, and heart disease are soaring in India and in the poorer countries where the multinational corporations that peddle such junk are focused on growing their markets.
Though most of us tend to blame sugar for the world’s weight woes, refined vegetable oils have added far more calories to the global diet in the last half-century than any other food group. A few months ago, a new study headed by researchers at the Institute for Research in Biomedicine found that palmitic acid, a fatty acid found in palm oil, alters the cancer genome increasing the likelihood that cancer will spread.
The industry is also impacting health and nutrition at its source. Studies have shown that diets among indigenous peoples in Indonesia are healthier than those of people working and living on the fringes of plantations, rather than in the forests as they’ve traditionally done.
In my book, I trace the political forces and dark money at work behind the scenes of the $65 billion business—from permits issued from inside jail cells and owners hidden behind offshore shell companies to long-dead villagers signing away their rights and elders hoodwinked by sweet-talking executives.
In 2019, the World Health Organization compared the tactics used by the palm oil industry to those employed by the tobacco and alcohol lobbies. It recently emerged that a Malaysian campaign accusing industry critics of being “neo-colonialists” was in fact the (very-highly-compensated) work of a Washington, DC–based lobbying firm, one whose previous clients include Exxon and the former Burmese military junta.
PepsiCo, the parent company of Frito-Lay, uses a lot of palm oil in its snacks. Activists have traced that oil to environmental destruction and labor abuses—what they call “conflict palm oil”. There have also been campaigns targeting Nestle, Kellogg’s, and Cargill for environmental and/or labor abuses linked to their supply chains.
They’ve definitely gotten some traction, and there have been reforms in the industry, though there is still a ways to go. Across the globe, those who have dared to speak out against the industry, whether environmental activists, laborers, peasant farmers, or investigative journalists, have often been met with violence.
Read labels. Reach out to the companies that use a lot of palm oil (PepsiCo, Dunkin Donuts, Unilever, Grupo Bimbo, etc) and ask them where they source it and how they can be sure that there wasn’t deforestation or land-grabbing or other labor or human rights abuses involved. Go to the websites of the Rainforest Action Network, Mighty Earth, Global Witness, Friends of the Earth, and Greenpeace, and get involved in their palm oil campaigns.
“Planet Palm: How Palm Oil Ended Up In Everything—And Endangered The World”
By Jocelyn C. Zuckerman
(The New Press 335 pg.$27.99 U.S.)
Features
Japanese Straightening/Hair Rebonding at SETS on Corydon

Japanese Straightening is a hair straightening process invented in Japan that has swept America.

Features
History of the Winnipeg Beach Synagogue: 1950-2025

By BERNIE BELLAN The history of the Winnipeg Beach Synagogue is a fascinating one. We have had several articles over the years about the synagogue in The Jewish Post & News.
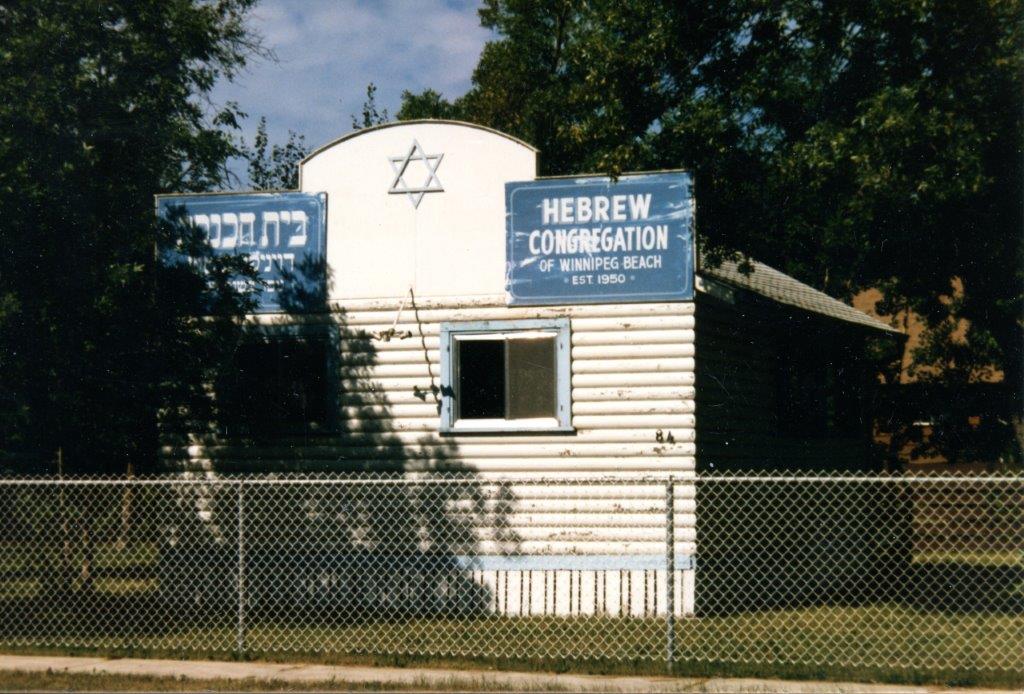


In June 2010 I wrote an article for The Jewish Post & News upon the 60th anniversary of the synagogue’s opening. Here are the opening paragraphs from that article:
“Sixty years ago a group of Winnipeg Beach vacationers decided that what their vacation area lacked was a synagogue. As it happened, a log cabin one-room schoolhouse in the Beausejour area happened to be available.
“In due course, the log cabin was relocated to the corner of Hazel and Grove in Winnipeg Beach, where it stayed for 48 years.”

In December 1994 my late brother, Matt, wrote a story about the spraying of antisemitic grafitti on the synagogue which, at that time, was still situated at its original location on the corner of Hazel and Grove in the town of Winnipeg Beach:
“Two 16-year-olds spraypainted slogans like ‘Die Jews,’ ‘I’ll kill you Jews,’ and other grafitti in big letters on the beach synagogue.
“Jim Mosher, a news reporter for the Interlake Spectator in Gimli, said last Halloween’s vandalism against the synagogue wasn’t the first. In the late 1980s, he claimed, it was spraypainted with swastikas.
“Jack Markson, a longtime member of the Winnipeg Beach Synagogue, last week also said he could remember finding anti-Semitic grafitti spraypainted on the synagogue ‘a few years ago,’ and at least twice in the 1970s, when the cottage season was over.”

My 2010 article continued: “In 1998 the Town of Winnipeg Beach informed the members of the synagogue that the building would have to be hooked up to the town’s sewer and water system. Rather than incur the cost of $3-4,000, which was thought to be ‘prohibitive,’ according to longtime beach synagogue attendee Laurie Mainster, synagogue goers looked elsewhere for a solution.
“As a result, the board of Camp Massad was approached and asked whether the synagogue might be relocated there, with the understanding that the synagogue would be made available to the camp at any time other than what were then Friday evening and Saturday morning services.
“Over the years the ‘beach synagogue’ had come to be a very popular meeting place for summertime residents of Winnipeg Beach and Gimli. In fact, for years minyans were held twice daily, in addition to regular Saturday morning services. Of course, in those years Winnipeg Beach was also home to a kosher butcher shop.
“While the little synagogue, which measured only 18 x 24 feet, has gone through several transformations, including the move to Camp Massad, and the opening up to egalitarian services in 2007 (The move to egalitarian services was as much a practical necessity as it was a nod to the equality of women – the only Kohen present at the time was a woman!), it has always remained cramped at the best of times.

“In recent years the synagogue has seen the addition of a window airconditioner (although to benefit from it, you really have to be sitting just a few feet away), as well as a fridge that allows synagogue attendees to enjoy a regular Saturday morning Kiddush meal following the service.
“According to Laurie Mainster, the Saturday morning service has continued to be popular, even though many of the attendees now drive in from Winnipeg, as they have sold the cottages they once maintained.
“On the other hand, one of the side benefits to being located on Camp Massad’s grounds has been an infusion of young blood from among the camp counsellors.
“Since there is no longer a rabbi available to conduct services (Rabbi Weizman did lead services for years while he had a cottage at the beach), those in attendance now take turns leading the services themselves.
“Anyone may attend services and, while there are no dues collected, donations are welcome. (Donations should be made to the Jewish Foundation of Manitoba, with donors asked to specify that their donations are to be directed to the beach synagogue.)
“Mainster also says that the beach synagogue is now undergoing an expansion, which will be its first in 60 years. An entirely new space measuring 16 x 18 feet is being added – one that will allow for a real Kiddush area. (Until now, a table has been set up in the back of the synagogue and synagogue goers would help themselves to the buffet that is set up each Saturday during the summer. While pleasant enough, it will certainly be more comfortable to have an actual area set aside for the Saturday afternoon after service lunch.)
“As for dress, longtime attendee Abe Borzykowski (in an article written by Sharon Chisvin for the Free Press in 2007) remarked that ‘I don’t think there are many synagogues where people can attend in shorts, T-shirts and sandals and not feel out of place.’ “
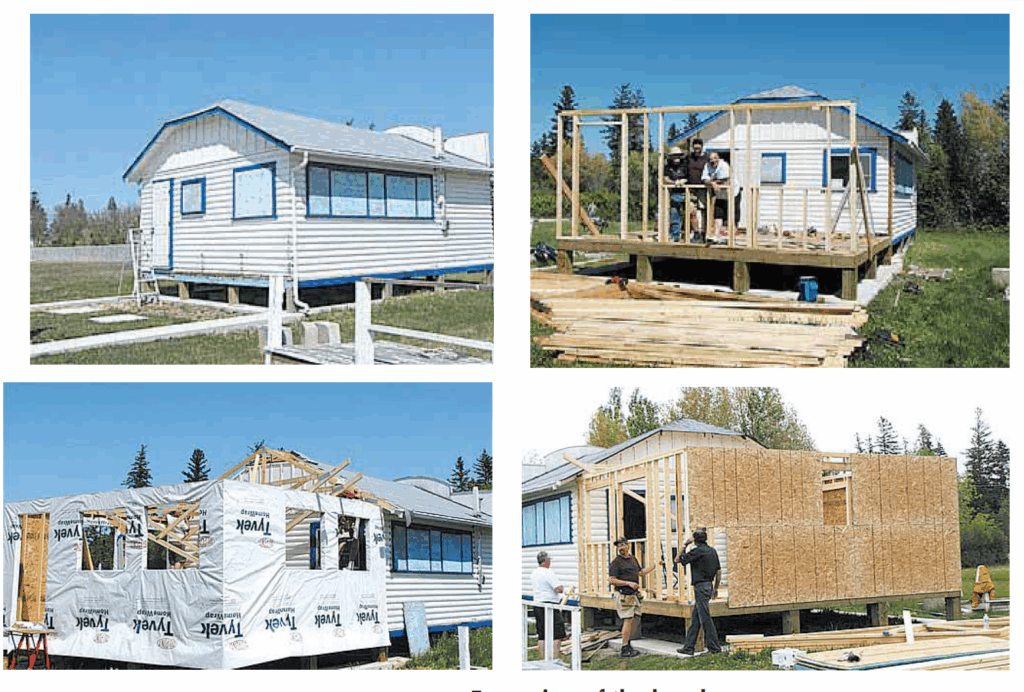
As mentioned in that 2010 article, the beach synagogue at that time was about to undergo an extensive remodelling. Here is an article from a January 2011 issue that describes that remodelling process. The article was written by Bernie Sucharov, who has been a longtime member of the beach synagogue:
“The Hebrew Congregation of Winnipeg Beach made a major change to the synagogue this past summer. With the help of many volunteers, Joel Margolese being the project manager, the synagogue was expanded and an addition was built to handle the overflow crowds, as well as to add more space for the kiddush following services.
“The volunteers spent many Sundays during the summer months building the addition. Bad weather caused many delays, but finally the addition was completed one week before the official summer opening.
“The volunteers were: Joel Margolese, Gordon Steindel, Sheldon Koslovsky, Viktor Lewin, Harvey Zabenskie, Nestor Wowryk, Kevin Wowryk, Victor Spigelman, Jerry Pritchard, and David Bloomfield.
“On Sunday, June 25, 2010 a special ceremony was held to affix a mezzuzah to the front entrance door. Gordon Steindel had the honour of affixing the mezzuzah, which was donated by Sid Bercovich and Clarice Silver.
“Refreshments and food for the day were prepared by Phyllis Spigelman, also known as our catering manager. Throughout the summer, Phyllis, Lenore Kagan and other friends prepared the food for our kiddush.
“A sound system was donated by Arch and Brenda Honigman in memory of their father, Sam Honigman z”l. “The system was installed by Joel Margolese and Stevan Sucharov. This will allow the overflow crowd to hear the service in the new addition.
“There were also generous donations of 50 chumashim and an air conditioner. The chumashim were donated by Gwen, Sheldon and Mark Koslovsky. The air conditioner in the new addition was donated by Joel and Linda Margolese.
“The official opening of the synagogue for the summer took place on July 3, 2010. We had an overflow crowd of 70+ people.”

Since that 2010 major addition to the synagogue, it has also added a wheelchair ramp (although I’ve been unable to ascertain exactly when the ramp was built). Also, the synagogue also has its own outdoor privy now. (Attendees used to have to use facilities in Camp Massad.)
And, as already noted in article previously posted to this site (and which you can read at Beach Synagogue about to celebrate 75th anniversary), in recognition of that occasion, on August 2nd members of the synagogue will be holding a 75th anniversary celebration.
As part of the celebration anyone who is a descendant or relative of any of the original members of the first executive committee is invited to attend the synagogue that morning.
If you are a relative please contact Abe Borzykowski at wpgbeachshule@shaw.ca or aborzykowski@shaw.ca to let Abe know you might be attending.
Features
Kinzey Posen: CBC Winnipeg’s former “go-to guy”

By GERRY POSNER If former Winnipegger Lawrence Wall was the CBC go-to guy in Ottawa, CBC Winnipeg had its own version of a go-to guy for many years with none other than the very well known Kinzey Posen. Of course, many readers will recognize that name from his career with Finjan, the Klezmer group so famous across Canada and beyond. It has been written about Posen and his wife Shayla Fink that they have been involved in music since they got out of diapers. And, as an aside, their love and ability in music has now been transmitted to the next generation as in their son, Ariel Posen (but that’s another story).
Kinzey Posen (not to be confused with Posner, or maybe we are to be confused, but who knows for sure?), was a graduate of Peretz School, having attended there from nursery right until Grade 7, graduating in1966. That was followed by Edmund Partridge and West Kildonan Collegiate. Musically, he was in large part self taught. However, he did have some teachers along the way. After moving to Vancouver – from 1974-78, he had the chance to study acoustic classical bass with a member of the Vancouver Symphony Orchestra. When Kinzey lived in Vancouver, he also worked as a jazz musician.
Upon returning to Winnipeg, Kinzey enrolled as a mature student at the University of Winnipeg, where he obtained a Bachelor of Urban Studies degree. Although the degree was in no way connected to the career that followed, his attending the University of Winnipeg was critical to his connecting with the CBC. Why? you ask. Kinzey had a position after graduation working for the Institute of Urban Studies. While there, he met someone who invited him to work for the Department of Continuing Education as one of their program directors. At the time the Department of Continuing Education was located at 491 Portage Avenue, which was also known as the TJ Rice Building. The CBC also leased some space in the same building. According to Kinzey, the CBC part of the building “included HR, different shows and other support offices. Continuing Education was located in the basement and main floor and that’s where I worked.”
KInzey had long had an interest in the CBC, which made the fact that the CBC had some offices in the same building where he was working serendipitous. That Kinzey might be interested in visiting the CBC was not an accident. As a young boy he had a nightly connection to CBC, as it was his ritual to listen to CBC Radio (as well as all sorts of other radio stations across the USA) on his transistor radio every night in bed. He became enamoured of one particular CBC host, Bill Guest, so that when going to sleep, he imagined that he was Guest doing interviews with imaginary guests. That dream of working for CBC became a reality when he had a chance to do a one week gig with Jack Farr’s network program.
Kinzey took a week off from his Continuing Education job and spent five days at the CBC. That week was a training session for Posen, as he had to create ideas, research, pre-interview, write the script, and set up the studio for Farr’s interview. He was almost in his dream job – although not quite – since it was only for one week. His opportunity, however, came in 1988, when he was offered a one-year term as a production assistant – the lowest guy on the ladder, for a show called “ Simply Folk,” with the late Mitch Podolak as the host. Although he was indeed at the bottom as far as those working on the show were concerned, he took a chance and gave his notice to the U of W. The rest is history. In his new job, Kinzey learned how to become a producer. Lucky for him, at the end of the year, when the person he replaced was supposed to come back, she never returned (just like the song, “MTA,” by the Kingston Trio). At that point, Kinzey was hired full time at the CBC.
Kinzey was a fixture at the CBC for 27 years. During those years, Kinzey had the chance to work with Ross Porter, a respected former CBC host and producer, also with Karen Sanders – on the “Afternoon Edition.” One aspect of Kinzey’s job on the Afternoon Edition was to come up with ideas, mix sound effects, arrange interviews and music, to create a two-hour radio experience. In addition, he covered jazz and folk festivals and, as a result, was exposed to some of the best musicians in the world. With Ross Porter in the 1990s, he worked on a network jazz show called “ After Hours,” which was on from 8-10 PM five nights a week. Kinzey was involved with writing the scripts, picking the music, and recording the shows, as well as editing them and then presenting them to the network for playback.
Of course, over his career, Kinzey had many memorable moments. He told me about one of them. The story revolved around the National Jazz Awards one year in particular. The awards were to be broadcasted after the National News which, in those days, began much earlier in the evening, and were over by 8:00 pm. The legendary Oscar Peterson was lined up to play a half hour set at the awards, starting at 7:30. But, as Kinzey told me, Oscar Peterson had a “hate on” for the CBC ecause one of his recorded performances was wrongly edited and he refused to appear on CBC under any circumstances. As the time neared 8:05 PM, which was when the CBC was to begin its broadcast of the jazz awards, it became apparent that Oscar was not going to finish on time. As the producer of the awards show, Kinzey was tasked with telling Oscar Peterson to wrap it up and get off the stage. There was Kinzey Posen, a huge fan of Oscar Peterson, now faced with the prospect of telling Oscar – while he was still playing – with 500 people in the audience, to stop and get off the stage. Not often was or is Kinzey Posen frozen, but that was one such moment. There was one loud “Baruch Hashem” from Kinzey when Oscar completed his set literally just in time.
Clearly, Kinzey was part of a very successful run with After Hours as it was on the air for 14 years. It was easily one of the most popular shows on CBC Radio 2, and a winner of several broadcasting awards. Kinzey also played a major role in producing a two part documentary about legendary guitarist Lenny Breau.
When After Hours ended, Posen became one of the contributing producers to Canada Live and specialized in producing live radio specials for the network, such as the Junos, for CBC Radio One and Two. Needless to say, his career planted Posen in the world of some top notch musicians, including his time spent working with Robert Plant (Led Zeppelin), Dave Brubeck, Randy Bachman, Chantal Kreviazuk and a list of prominent names in the Canadian, American and European music spheres. Locally, the CBC came to refer to Kinzey as the Jewish expert. I would add music expert to that title.
After his 27 year run at the CBC – and before he fully retired, Kinzey went on to work for the Rady JCC as a program director for a year and a half. Of course, to say that Kinzey Posen is retired is a major contradiction in terms. You really can’t keep him down and he has his hand in a variety of programs and projects – most of which he remains silent about, as is his style.
When I realized the full depth and talent of Kinzey Posen, I quickly concluded that he must certainly be related to me. Even if he isn’t, I now tell people he is.
