Features
Yvonne Singer, a Toronto artist who was saved by Wallenberg as an infant, is still on a voyage of self-discovery

By RON CSILLAG
As an artist herself, Yvonne Singer can well appreciate the esthetic merits of the open-air monument to Swedish Second World War hero Raoul Wallenberg that was unveiled over the summer at Churchill Park in Hamilton, Ont.
Though she had not, as of this writing, personally viewed the installation, dubbed “Be:longings,” Singer spoke admiringly of the 10 bronze-cast suitcases dispersed along a gravel path adjacent to the Hamilton aviary. She knows Simon Frank, one of the project’s three creators, and is aware that suitcases have been a potent symbol of the Holocaust.
“I like the fact that the suitcases are scattered,” Singer, a well-established visual artist and teacher in Toronto, said in an interview over lemon tea in her sun-drenched kitchen. “I think the imagery and symbolism are very effective in conveying the idea of displacement and emigration.” The old-timey valises evoke not just Wallenberg, Singer noted, but all victims and survivors of that terror-stricken era.
The outdoor project is also “minimal, which I like. I don’t like public sculptures that scream at you or are clichéd.”
Singer connects to the installation on a whole other level. The 78-year-old resident of Toronto’s Cabbagetown neighbourhood is Wallenberg’s goddaughter. She was born on his bed.
It’s a Hollywood-worthy tale that evolved over time, in a series of eye-popping twists, turns and coincidences—all amid Singer’s own personal voyage of self-discovery.
The backstory is its own blockbuster: The non-Jewish scion of a wealthy Swedish industrial and banking family, Wallenberg, then just 32, was recruited by the U.S. War Refugee Board and dispatched to Budapest to assist and rescue as many Jews in the Nazi-occupied Hungarian capital as possible. He arrived in July 1944, just as the Nazis had shipped some 440,000 Jews from the countryside to Auschwitz. They now set their sights on the Jews of Budapest.
Accorded diplomatic status, Wallenberg famously set off on a frenetic pace. He designed, printed and distributed thousands of the famous “Schutzpass”—an official-looking document that placed the holder under the protection of the neutral Swedish Crown. He also scoured the city for buildings to rent, finding 32, and crammed in as many souls as possible. The “safe houses” flew the yellow-and-blue Swedish flag and were declared protected by diplomatic immunity.
Known for his bluster and bravado, his greatest coup came when he persuaded Nazi commanders to call off the liquidation of Budapest’s Jewish ghetto, with its 70,000 inhabitants. The number of Jews Wallenberg is said to have rescued peaks at 100,000. In any event, he is credited with saving more Jewish lives during the war than any single government.
By January 1945, the Red Army was laying siege to Budapest, and Wallenberg was taken into custody, supposedly on suspicion of being a U.S. spy. He promptly vanished into the gulag. A Soviet report in 1956 stated he had died in July 1947 of a heart attack in Moscow’s notorious Lubyanka prison, but supposed eyewitness sightings and stories of contact with him from former inmates continued well into the 1970s.
In 2012, the diaries of a former head of the KGB, discovered in the walls of his Moscow home, stated there was “no doubt” that Wallenberg was “liquidated” in 1947.
But back to Singer.
On the night of Nov. 3, 1944, a desperate Tibor Vandor, who worked for Wallenberg as a courier and liaison to the underground, needed help for his wife, Agnes. She was in labour and had been turned away from Budapest’s hospitals, which barred Jews. Wallenberg allowed the couple to use his own room, while he slept in the corridor.
The next morning, he was called in to see a newborn girl. Asked by the grateful parents to name her, Wallenberg chose Nina Maria Ava (Nina was his half-sister’s name, Maria his mother’s). The couple changed the first name to Yvonne, and Wallenberg agreed to be the child’s godfather.
Singer knew nothing of this until she was 34 years old.
It was October 1979 when she read an article, reprinted from a U.S. newspaper, in the Toronto Star about Wallenberg’s plight. The story included a reference to Singer’s unusual birth taken from a Hungarian book on the Swedish hero written after the war. The baby with the Toronto connection, the parents, the godfather—were all there, mentioned by name.
When she read the piece, “I burst out crying,” she told the Star after contacting the paper. Her story spilled forth a week later in a large Saturday Star article headlined “Swedish hero saved my life: Metro woman.”
Singer is still struck by “the incredible coincidence of it all. Here I am in Toronto in 1979, reading the paper… it boggles the mind. I could have easily gone through life not knowing the story. Suddenly, I had a connection to this man, who sounds like he was fascinating.”
Her parents had not told her the story. And there was another missing piece of the puzzle: their Jewishness.
At war’s end, the Vandors went to Switzerland and Holland before settling in Montreal in 1949, where the parents shed their Jewish identities, doubtless seeking to forget. Tibor Vandor even became an elder in the United Church.
“I always pressed them for more information, and they always refused,” even following the revelations in the Toronto Star, Singer recalled. “They told me very, very little.” Her parents never revealed being Jews. Their silence encompassed “anything to do with the war. They were just not forthcoming.”
Singer graduated from McGill University and went on to teach English and French at local high schools. She converted to Judaism to marry her husband, Ron Singer, a theatre director and educator, in 1966. A few years later, a cousin in England recalled being a flower-girl at Yvonne’s parents’ wedding, which she said took place in a synagogue. The parents denied it but their daughter believed it.
Singer’s feelings of alienation as an immigrant child would evaporate on discovering that she had been born Jewish, whether the knowledge came from a cousin or the Toronto Star. “I felt like I’d come home, part of a history that goes back thousands of years. I no longer felt rootless.”
The Singers moved to Toronto in 1971, where Yvonne later began a prolific art career in various media and teaching visual arts at York University. Raising three daughters and a busy life meant there was little time to get involved in the Wallenberg file (though she was pleased when he became Canada’s first Honorary Citizen in 1985 and when Canada Post issued a stamp commemorating Wallenberg a decade ago).
It’s little surprise that Singer’s art has explored themes of identity, history and memory. The outsider status she felt in her early life “is what made me think about ways of expressing that, either through language or visual imagery. So you go to what you know when you’re an artist.”
In 2016, the Swedish government declared Wallenberg officially dead, but to Singer, that offered no finality. “From what I learned, the Swedish government is not exempt from blame for trying to get Wallenberg out. I cannot reconcile the fact that [Wallenberg’s family] could not exert any kind of leverage over the Russians to find out what happened to him.”
In Judaism, being a godparent carries little or no religious obligation. Singer considers the godfather connection to Wallenberg an honour, “but I’m also very sad that I never met him. I think he would have been a fascinating person to talk to. The story is just very, very tragic.”
The grandmother of nine sighed. Over the decades, the story for her was obviously very personal, “and I was still processing it. Maybe I’m still processing it, for a long, long time.”
A version of this article originally appeared in the Hamilton Jewish News. It is reprinted with the author’s permission.
Features
Why casinos reject card payments: common reasons
Online casino withdrawals seem simple, yet many players experience unanticipated decreases. Canada has more credit and debit card payout refusals than expected. Delays or rejections are rarely random. Casino rules and technical processes are rigorous. Identity verification, banking regulations, bonus terms, and technological issues might cause issues.
Card payment difficulties can result from insufficient identification verification. Canadian casinos must verify players’ identities before accepting card withdrawals. If documentation are missing, obsolete, or confusing, the request may be stopped or denied until verified.
Banks and card issuers’ gaming policies are another aspect. Some Canadian banks limit or treat online casino payments differently from card refunds. In such circumstances, the casino may recommend a more reliable withdrawal method.
For Canadian players looking to compare bonus terms and payout conditions, check https://casinosanalyzer.ca/free-spins-no-deposit/free-chips. This article explores the main reasons Canadian casinos reject card payouts, from KYC hurdles to bank-specific restrictions, so you know exactly what to watch for.
Verification Issues: Why Identity Checks Matter
KYC rules must be activated by licensed casinos. Players need to submit proof of their identity, address and age. If any documentation is missing, expired or unclear, the withdrawal will be denied. In Canada, for instance, authorities like the AGCO or iGaming Ontario have been cracking down on KYCs by demanding that submitted documents – whether photo ID, utility bills or bank statements – be consistent with all account details.
Common errors are submitting screenshots, cropped photos or documents with names, dates or addresses that aren’t entirely visible. Just the slightest differences in spelling or abbreviations or formatting can get these blocks triggered.
Another possibility is that the account was red flagged if previous withdrawals were already made without partial verification. Keeping precise, readable documents helps facilitate approvals and cuts through delays and frustrating red tape, as Canadian gamblers access their winnings both safely and quickly.
Timing Matters
Verification isn’t always instant. Documents being submitted during the busiest times, or on weekends or holidays can only prolong that approval process, and the withdrawal sitting pre-approved – or refused for that matter – until the casino reviews the paperwork. A lot of players feel disappointment not due to mistakes, but only for that a verification team still hasn’t checked their documents! This can be especially frustrating when winnings come from free chips or bonus play and players are eager to cash out.
Keep personal information current and only submit clear legible files to reduce the processing time. Ensure that any scans or photos are sharp, fully visible and there is no detail missing. Preventing Gaffes With submission guidelines to read over ahead of time and directions for following them exactly, verification issues can often be significantly minimized, avoiding delay in accessing winnings and making the lie down withdrawal process that much smoother at Canadian online casinos.
Banking Restrictions and Card Policies
Not all credit or debit cards are eligible for casino withdrawals. Many Canadian banks restrict transactions related to gambling. For example, prepaid cards, virtual cards, or certain credit cards may allow deposits but block withdrawals. Even if deposits work, a payout can fail if the bank refuses incoming gambling credits.
Cards issued outside Canada can also be declined due to international processing rules. Currency conversion restrictions may prevent a CAD payout to a USD card, depending on the bank’s policies.
Banks keep an eye on abnormal or frequent transactions. Online casinos can flag large or multiple withdrawals as suspicious and in such cases may impose temporary blocks on withdrawals or outright decline the withdrawal until the issuing bank confirms them with its account holder. Contacting your bank in advance will avoid any surprises and make withdrawals go more smoothly. What to consider when using your card in Canada:
- Check if your card type supports gambling withdrawals (prepaid, virtual, and some credit cards may not).
- Confirm whether your bank allows international online casino payouts.
- Be aware of currency conversion restrictions.
- Monitor withdrawal frequency to avoid triggering fraud alerts.
- Contact your bank ahead of time to authorize or clarify online gambling transactions.
- Keep alternative withdrawal methods ready, such as e-wallets or bank transfers.
Being aware of these constraints prevents Canadian players from having declined payouts, delays and waste of time when it comes to handling the casino money properly.
Wagering Requirements and Bonus Conditions
Many Canadians chase casino bonuses, including deals built around free chips, but these offers always come with conditions, Wagering requirements usually require players to bet a multiple of the bonus before withdrawing. Attempting a payout before meeting these conditions will be automatically declined. Not all games contribute equally: slots often count 100%, table games 10–20%, and certain features nothing at all.
Misinterpretation of this, can make it appear as though a withdraw should be valid, while the casino believes there are unmet bonus requirements. Some casinos also impose a minimum withdrawal amount and will cap card payouts. And if you have more than the minimum in your account, a limit set off by your bonus could limit withdrawal. By testing these issues early on, you can save yourself a lot of aggravation. How to manage bonus conditions effectively:
- Have a close look at the terms of the bonus – check out wagering requirements, game contribution and time limits.
- Track your progress – note how much of the bonus has been wagered and which games contribute most.
- Plan your gameplay – prioritize slots or eligible games to efficiently meet wagering.
- Check withdrawal limits – ensure your balance meets minimums and bonus-specific caps.
- Avoid early withdrawals – never attempt a cash-out before meeting all conditions.
- Use trusted sources – platforms like CA CasinosAnalyzer can clarify real requirements and prevent surprises.
Following these steps helps players meet bonus conditions without stress and makes bankroll management smoother.
Features
What is the return on investment of US military spending on Israel?

By GREGORY MASON A recurring theme of Israel’s critics is that were it not for US spending on its war machine, it would be unable to wage genocide. I will leave the genocide issue (sic, I mean non-issue) aside as it has been well covered here and here.
Of course, right now (March 11), the war is going well for Israel and the US. In fact, the Israeli and American air forces are showing a level of coordination enabled by decades of close cooperation between the two militaries. I recall a conversation with an IDF colonel, the commander of a base near Eilat, in 2010, during a mission that gave participants access to high-level military briefings. Tensions between Israel and the US had soured, as they periodically do, and I asked whether this ebb and flow in political posturing affected military operations. The colonel said political leaders come and go, but the cooperation between the Israeli and American militaries is very tight. To quote him, “they need us as much as we need them. We are their eyes and ears in this part of the world.”
Many on both the right and left call for the US to disengage from Israel, especially with respect to defence spending. First, let us look at facts.
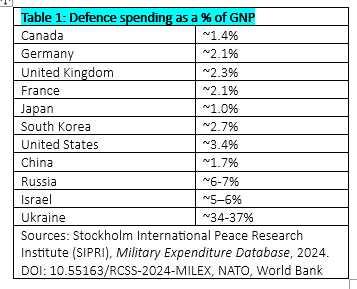
Table 1 readily shows the impact of the war in Ukraine, with Russia’s spending also reflecting wartime demands. Israel’s total commitment of 5-6% of GDP amounts to $45 billion in defence spending, reflecting its perpetual need to defend itself and maintain a permanent reserve force. Table 2 elaborates on defence spending as a share of public spending. Unlike other countries that have been free riding under the US military umbrella (and Canada is the most egregious of the lot), Israel has made very substantial commitments to its own defence. The $3.8 billion spent on hardware for US equipment is a fraction of Israel’s total defence budget of about $43 Billion. All U.S. financial aid to any country for military hardware must be spent on U.S.-manufactured equipment by law.
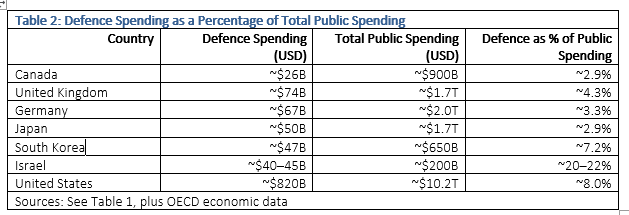
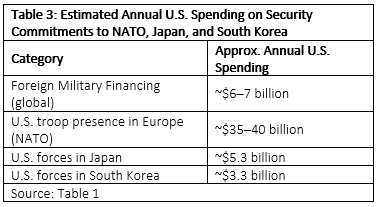
Critics of US defence funding for Israel miss two key points. First, as Table 3 shows, financing sent to Israel does not involve troop deployment. Israel does not want the US to station troops within its borders. The costs of maintaining troop deployments and all the associated support costs for NATO, Japan, and South Korea are orders of magnitude higher than the financing for the hardware it provides to Israel.
Second, and the current joint US/Israeli operations in Iran bear this out, Israel has dramatically improved the equipment platforms it purchased. Examples include:
- The F-15 has benefited from Israeli wartime use, resulting in major improvements, including a redesigned cockpit layout, increased range through fuel redesign, improved avionics, new weaponry, helmet-mounted targeting, and structural strengthening.
- Because Israel was an early partner in the fighter’s development and had access to its top-secret software suite, the Israeli version of the F-35 is a radically different plane than the model delivered. Improvements include increasing operational range, embedding advanced air defence detection, and integrating the fighter with Israel’s defence network, creating extensive system integration. This proved instrumental in the rapid establishment of air superiority in the 12-day war in 2025.
- The THAAD (Terminal High Altitude Area Defence) program has benefited from a joint research and development relationship between Israel and the U.S.
- Finally, Iron Dome has contributed to U.S. air defence development, particularly the Tamir interceptor technology, battle management, target discrimination, and the development of a layered air defence system.
No senior military or political official questions the return on investment American gains by funding Israel’s acquisition of U.S. military hardware.
Features
Why Returning Players Often Stick to a Few Favorite Games on Platforms Like Gransino Casino

Many online casino players develop clear preferences over time, and Gransino Casino highlights how familiar games often become the center of regular play sessions.
Online casinos typically offer large catalogs filled with hundreds of different slot titles. While this variety allows players to explore new experiences, many returning users gradually settle on a smaller group of games that they revisit regularly. This pattern appears across many digital gaming environments, where familiarity often becomes just as important as novelty.
Platforms such as Gransino Casino demonstrate how this behavior emerges in practice. Even though players have access to many different titles, returning visitors frequently gravitate toward games they already know and understand.
Familiar mechanics reduce learning time
One reason players return to the same games is that they already understand how those titles work. Each slot game has its own rules, bonus features, and payout structure. When a player first opens a new title, they often need a few minutes to understand the paytable, special symbols, and feature triggers.
Once that learning process has taken place, the game becomes easier to approach in future sessions. Players do not need to spend time reviewing instructions or exploring unfamiliar mechanics. Instead, they can begin playing immediately with a clear sense of how the game operates.
On platforms like Gransino Casino, this familiarity can make certain titles stand out as reliable choices. When players know what to expect from a game, the experience often feels smoother and more predictable during short play sessions.
Personal preferences shape long-term choices
Another factor influencing player behavior is personal preference. Some players enjoy specific visual themes such as mythology, adventure, or classic fruit machine designs. Others may prefer particular gameplay features, such as free spins, cascading reels, or bonus rounds.
Over time, players tend to identify the games that best match these preferences. Once they find titles that align with their interests, they are more likely to return to those games rather than start the search process again.
This pattern can be seen on Gransino Casino, where players browsing the lobby may explore different titles at first but eventually settle on a smaller group of favorites that suit their individual style.
Habit formation in digital gaming
Habit formation also plays a role in why players repeatedly choose the same games. In many digital environments, users develop routines that guide how they interact with a platform. This behavior is visible across streaming services, mobile games, and online casinos.
Once a player has established a routine, returning to familiar content often becomes part of that pattern. For example, a player might log in and immediately open the same slot they played during previous sessions. The familiarity of the interface, symbols, and features can make the experience feel more comfortable.
Platforms like Gransino Casino support this behavior by maintaining consistent game availability and allowing players to locate previously played titles easily within the lobby.
Exploration still remains part of the experience
Although many players develop favorite games, exploration remains an important part of the online casino experience. New titles continue to appear on casino platforms, introducing different mechanics, themes, and visual styles.
Players often alternate between their familiar choices and occasional experimentation with new games. A player might return to a favorite slot for most sessions while occasionally trying recently released titles to see if they offer something interesting.
The wide selection available on Gransino Casino allows this balance between familiarity and discovery. Players can continue returning to the games they enjoy while still having the option to explore new additions within the platform’s catalog.
Ultimately, the tendency to revisit favorite games reflects how players build their own routines within digital entertainment environments. Familiar titles offer a comfortable starting point, while new releases provide opportunities for occasional exploration, creating a mix of consistency and variety within each player’s experience.


